Abstract
Rationale
The therapeutic potential of berberine has been well documented in various neurological problems. However, the neurological mechanism of berberine remains untapped in the light of its P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated gut efflux properties responsible for reduced bioavailability. Verapamil, a well known L-type calcium channel blocker, has additional inhibitory activity against P-gp efflux pump. Thus, there is a strong scientific rationale to explore the interaction of berberine with verapamil as a possible neuroprotective strategy.
Objective
The present study was designed to evaluate the effect of berberine, verapamil, and their combination on behavioral alterations, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and histopathological modifications in intracerebroventricular streptozocin (ICV-STZ)-induced sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type in rats.
Methods
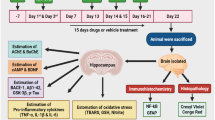
Single bilateral ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) administration was used as an experimental model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type.
Results
Berberine (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg, oral gavage) or verapamil (2.5 and 5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) were used as treatment drugs, and memantine (5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) was used as a standard. Berberine and verapamil significantly attenuated behavioral, biochemical, cellular, and histological alterations, suggesting their neuroprotective potential. Further, treatment of berberine (25 and 50 mg/kg) with verapamil (2.5 and 5.0 mg/kg) combinations respectively significantly potentiated their neuroprotective effect which was significant as compared to their effect per se in ICV-STZ-treated animals.
Conclusion
The augmentative outcome of verapamil on the neuroprotective effect of berberine can be speculated due to the inhibition of P-gp efflux mechanism and the prevention of calcium homeostasis alteration. Additionally, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of both berberine and verapamil could also contribute in their protective effect.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2009) A study of brain insulin receptors, AChE activity and oxidative stress in rat model of ICV STZ induced dementia. Neuropharmacology 56:779–787
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J et al (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
Berman SB, Hastings TG (1999) Dopamine oxidation alters mitochondrial respiration and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 73(3):1127–1137
Bhutada P, Mundhada Y, Bansod K, Tawari S, Patil S et al (2011) Protection of cholinergic and antioxidant system contributes to the effect of berberine ameliorating memory dysfunction in rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Behav Brain Res 220:30–41
Birdsall TC, Kelly GS (1997) Berberine therapeutic potential of an alkaloid found in several medicinal plants. Altern Med Rev 2:94–103
Bojarski L, Herms J, Kuznicki J (2008) Calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 52:621–633
Buchhave P, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Minthon L, Janciauskiene S, Hansson O (2010) Soluble TNF receptors are associated with Abeta metabolism and conversion to dementia in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 31:1877–1884
Butterfield DA (2014) The 2013 discovery award from the society for free radical biology and medicine: selected discoveries from the Butterfield Laboratory of Oxidative Stress and its sequelae in brain in cognitive disorders exemplified by Alzheimer disease and chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment. Free Radic Biol Med 74:157–174
Butterfield DA, Howard B, Yatin S, Koppal T, Drake J et al (1999) Elevated oxidative stress in models of normal brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci 65:1883–1892
Choi JS, Li X (2005) The effect of verapamil on the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel in rats. Eur J Pharm Sci 24:95–100
Correia SC, Santos RX, Carvalho C, Cardoso S, Candeias E et al (2012) Insulin signaling, glucose metabolism and mitochondria: major players in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes interrelation. Brain Res 1441:64–78
Eckert A, Schmitt K, Gotz J (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction—the beginning of the end in Alzheimer’s disease? Separate and synergistic modes of tau and amyloid-beta toxicity. Alzheimers Res Ther 3:15
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Essali A, Deirawan H, Soares-Weiser K, Adams CE (2011) Calcium channel blockers for neuroleptic-induced tardive dyskinesia. Cochrane Database of Systemic Reviews 11: CDO, 00206.
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Grammas P (2011) Neurovascular dysfunction, inflammation and endothelial activation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 8:26
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Griffin WS, Sheng JG, Roberts GW, Mrak RE (1995) Interleukin-1 expression in different plaque types in Alzheimer’s disease: significance in plaque evolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54:276–281
Grünblatt E, Salkovic‐Petrisic M, Osmanovic J, Riederer P, Hoyer S (2007) Brain insulin system dysfunction in streptozotocin intracerebroventricularly treated rats generates hyperphosphorylated tau protein. J Neurochem 101:757–770
Harris ME, Carney JM, Cole PS, Hensley K, Howard BJ et al (1995) [beta]-Amyloid peptide-derived, oxygen-dependent free radicals inhibit glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 6:1875–1879
He P, Zhong Z, Lindholm K, Berning L, Lee W et al (2007) Deletion of tumor necrosis factor death receptor inhibits amyloid beta generation and prevents learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s mice. J Cell Biol 178:829–841
Hoyer S, Lannert H (2008) Long-term effects of corticosterone on behavior, oxidative and energy metabolism of parietotemporal cerebral cortex and hippocampus of rats: comparison to intracerebroventricular streptozotocin. J Neural Transm 115:1241–1249
Hsu YY, Tseng YT, Lo YC (2013) Berberine, a natural antidiabetes drug, attenuates glucose neurotoxicity and promotes Nrf2-related neurite outgrowth. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272:787–796
Javed H, Khan M, Ahmad A, Vaibhav K, Ahmad M et al (2012) Rutin prevents cognitive impairments by ameliorating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuroscience 210:340–352
Ji HF, Shen L (2011) Berberine: a potential multipotent natural product to combat Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 16:6732–6740
Kajiyama K, Pauly DF, Hughes H, Yoon SB, Entman ML, McMillin-Wood JB (1987) Protection by verapamil of mitochondrial glutathione equilibrium and phospholipid changes during reperfusion of ischemic canine myocardium. Circ Res 61:301–310
Kalonia H, Kumar P, Kumar A (2011) Attenuation of proinflammatory cytokines and apoptotic process by verapamil and diltiazem against quinolinic acid induced Huntington like alterations in rats. Brain Res 1372:115–126
King T (1967) Preparation of succinate dehydrogenase and reconstitution of succinate oxidase. In: Estabrook R, Pullman M (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 322–331
King T, Howard R (1967) Preparations and properties of soluble NADH dehydrogenases from cardiac muscle. In: Estabrook R, Pullman M (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 275–294
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 186:189–195
Kovalskii I, Krasnyuk I, Krasnyuk I Jr, Nikulina O, Belyatskaya A et al (2014) Mechanisms of rutin pharmacological action (review). Pharm Chem J 48:73–76
Kuhlmann O, Carlile D, Noe J, Bentley D (2014) Interaction potential of Carmegliptin with P-glycoprotein (Pgp) transporter in healthy volunteers. J Drug Assessment 3:28–37
Kulkarni S, Dhir A (2010) Berberine: a plant alkaloid with therapeutic potential for central nervous system disorders. Phytother Res 24:317–324
Kumar A, Dogra S (2008) Neuropathology and therapeutic management of Alzheimer’s disease—an update. Drugs Future 33:433–446
Kumar A, Prakash A, Pahwa D, Mishra J (2012) Montelukast potentiates the protective effect of rofecoxib against kainic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behavior 103:43–52
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795
Liu Y, Lo YC, Qian L, Crews FT, Wilson B et al (2011) Verapamil protects dopaminergic neuron damage through a novel anti-inflammatory mechanism by inhibition of microglial activation. Neuropharmacology 60:373–380
Luck H (1965) Catalase. In: Hans UB (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic, New York, pp 885–894
Lupo E, Locher R, Weisser B, Vetter W (1994) In vitro antioxidant activity of calcium antagonists against LDL oxidation compared with α-tocopherol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 203:1803–1808
Maeng HJ, Yoo HJ, Kim IW, Song IS, Chung SJ, Shim CK (2002) P‐glycoprotein-mediated transport of berberine across Caco‐2 cell monolayers. J Pharm Sci 91:2614–2621
Mak I, Weglicki W (1990) Comparative antioxidant activities of propranolol, nifedipine, verapamil, and diltiazem against sarcolemmal membrane lipid peroxidation. Circ Res 66:1449–1452
Marier JF, Deschênes JL, Hage A, Seliniotakis E, Gritsas A et al (2005) Enhancing the uptake of dextromethorphan in the CNS of rats by concomitant administration of the P-gp inhibitor verapamil. Life Sci 77:2911–2926
Mark RJ, Hensley K, Butterfield DA, Mattson MP (1995) Amyloid beta-peptide impairs ion-motive ATPase activities: evidence for a role in loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J Neurosci 15:6239–6249
Mason RP, Mak IT, Trumbore MW, Mason PE (1999) Antioxidant properties of calcium antagonists related to membrane biophysical interactions. Am J Cardiol 84:16–22
Mehla J, Pahuja M, Gupta P, Dethe S, Agarwal A, Gupta YK (2013) Clitoria ternatea ameliorated the intracerebroventricularly injected streptozotocin induced cognitive impairment in rats: behavioral and biochemical evidence. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 230:589–605
Misra S, Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Chopra K (2011) Modulation of nitrergic pathway by sesamol prevents cognitive deficits and associated biochemical alterations in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin administered rats. Eur J Pharmacol 659:177–186
Morales I, Guzmán-Martínez L, Cerda-Troncoso C, Farías GA, Maccioni RB (2014) Neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. A rational framework for the search of novel therapeutic approaches. Front Cell Neurosci 8:1–9
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Nicita F, Spalice A, Papetti L, Nikanorova M, Iannetti P, Parisi P (2014) Efficacy of verapamil as an adjunctive treatment in children with drug-resistant epilepsy: a pilot study. Seizure 23:36–40
Nimmrich V, Eckert A (2013) Calcium channel blockers and dementia. Br J Pharmacol 169:1203–1210
Pagani L, Eckert A (2011) Amyloid-Beta interaction with mitochondria. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:1–12
Paola D, Domenicotti C, Nitti M, Vitali A, Borghi R et al (2000) Oxidative stress induces increase in intracellular amyloid β-protein production and selective activation of βI and βII PKCs in NT2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 268:642–646
Pauli-Magnus C, von Richter O, Burk O, Ziegler A, Mettang T et al (2000) Characterization of the major metabolites of verapamil as substrates and inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:376–382
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Peng WH, Lo KL, Lee YH, Hung TH, Lin YC (2007) Berberine produces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test and in the tail suspension test in mice. Life Sci 81:933–938
Peng WH, Wu CR, Chen CS, Chen CF, Leu ZC, Hsieh MT (2004) Anxiolytic effect of berberine on exploratory activity of the mouse in two experimental anxiety models: interaction with drugs acting at 5-HT receptors. Life Sci 75:2451–2462
Pirker S, Baumgartner C (2011) Termination of refractory focal status epilepticus by the P‐glycoprotein inhibitor verapamil. Eur J Neurol 18:e151–e51
Plaschke K, Hoyer S (1993) Action of the diabetogenic drug streptozotocin on glycolytic and glycogenolytic metabolism in adult rat brain cortex and hippocampus. Int J Dev Neurosci 11:477–483
Popović M, Caballero-Bleda M, Popović N, Puelles L, van Groen T, Witter MP (2006) Verapamil prevents, in a dose-dependent way, the loss of ChAT-immunoreactive neurons in the cerebral cortex following lesions of the rat nucleus basalis magnocellularis. Exp Brain Res 170:368–3675
Rai S, Kamat PK, Nath C, Shukla R (2014) Glial activation and post-synaptic neurotoxicity: the key events in streptozotocin (ICV) induced memory impairment in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behavior 117:104–117
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Hoyer S (2007) Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: an experimental approach. J Neural Trans 72:217–233
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic-Barilar J, Knezovic A, Hoyer S, Mosetter K, Reutter W (2014) Long-term oral galactose treatment prevents cognitive deficits in male Wistar rats treated intracerebroventricularly with streptozotocin. Neuropharmacology 77:68–80
Salkovic‐Petrisic M, Tribl F, Schmidt M, Hoyer S, Riederer P (2006) Alzheimer‐like changes in protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase‐3 in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after damage to the insulin signalling pathway. J Neurochem 96:1005–1015
Salmon SE, Dalton WS, Grogan TM, Plezia P, Lehnert M et al (1991) Multidrug-resistant myeloma: laboratory and clinical effects of verapamil as a chemosensitizer. Blood 78:44–50
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Schorer-Apelbaum D, Weinstock M (2007) Ladostigil prevents gliosis, oxidative–nitrative stress and memory deficits induced by intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Neuropharmacology 52:836–843
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Weinstock M (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin causes neurotoxicity to myelin that contributes to spatial memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol 184:1043–1052
Shonesy BC, Thiruchelvam K, Parameshwaran K, Rahman EA, Karuppagounder SS et al (2012) Central insulin resistance and synaptic dysfunction in intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin injected rodents. Neurobiol Aging 33(2):430, e5-18
Singh DP, Chopra K (2013) Verapamil augments the neuroprotectant action of berberine in rat model of transient global cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 720:98–106
Sonkusare S, Srinivasan K, Kaul C, Ramarao P (2005) Effect of donepezil and lercanidipine on memory impairment induced by intracerebroventricular streptozotocin in rats. Life Sci 77:1–14
Sottocasa GL, Kuylenstierna B, Ernster L, Bergstrand A (1967) An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol 32:415–438
Tan ZS, Beiser AS, Vasan RS, Roubenoff R, Dinarello CA (2007) Inflammatory markers and the risk of Alzheimer disease: the Framingham Study. Neurology 68:1902–1908
Tarkowski E, Andreasen N, Tarkowski A, Blennow K (2003) Intrathecal inflammation precedes development of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1200–1205
Tarrago T, Kichik N, Seguí J, Giralt E (2007) The natural product berberine is a human prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitor. ChemMedChem 2:354–359
Thies W, Bleiler L (2013) 2013 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 9:208–245
Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Bishnoi M, Chopra K (2009) Chronic treatment with tocotrienol, an isoform of vitamin E, prevents intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative–nitrosative stress in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behavior 93:183–189
Tobinick EL, Gross H (2008) Rapid cognitive improvement in Alzheimer’s disease following perispinal etanercept administration. J Neuroinflammation 5:2
Toescu EC, Verkhratsky A (2007) The importance of being subtle: small changes in calcium homeostasis control cognitive decline in normal aging. Aging Cell 6:267–273
Tuzcu M, Baydas G (2006) Effect of melatonin and vitamin E on diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 537:106–110
Vuddanda PR, Chakraborty S, Singh S (2010) Berberine: a potential phytochemical with multispectrum therapeutic activities. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19:1297–1307
Weinstock M, Shoham S (2004) Rat models of dementia based on reductions in regional glucose metabolism, cerebral blood flow and cytochrome oxidase activity. J Neural Trans 111:347–366
Widener LL, Mela-Riker LM (1983) Verapamil pretreatment preserves mitochondrial function and tissue magnesium in the ischemic kidney. Circ Shock 13:27–37
Wills E (1966) Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J 99:667–676
Wisner KL, Peindl KS, Perel JM, Hanusa BH, Piontek CM, Baab S (2002) Verapamil treatment for women with bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 51:745–752
Witte ME, Geurts JJ, De Vries HE, van der Valk P, van Horssen J (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction: a potential link between neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration? Mitochondrion 10:411–418
Xiang J, Yu C, Yang F, Yang L, Ding H (2009) Conformation-activity studies on the interaction of berberine with acetylcholinesterase: physical chemistry approach. Prog Nat Sci 19:1721–1725
Yamamoto M, Kiyota T, Horiba M, Buescher JL, Walsh SM et al (2007) Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulate amyloid-beta plaque deposition and beta-secretase expression in Swedish mutant APP transgenic mice. Am J Pathol 170:680–692
Yasojima K, Schwab C, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1999) Up-regulated production and activation of the complement system in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am J Pathol 154:927–936
Zhang Y, Cui YL, Gao LN, Jiang HL (2013) Effects of beta-cyclodextrin on the intestinal absorption of berberine hydrochloride, a P-glycoprotein substrate. Int J Bio Macromol 59:363–71
Zhu F, Qian C (2006) Berberine chloride can ameliorate the spatial memory impairment and increase the expression of interleukin-1beta and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurosci 7:78
Zhu X, Raina AK, Lee H-g, Casadesus G, Smith MA, Perry G (2004) Oxidative stress signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1000:32–39
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (09/135/705/2014-EMR-I) and University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India, for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Ekavali, Mishra, J. et al. Possible role of P-glycoprotein in the neuroprotective mechanism of berberine in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive dysfunction. Psychopharmacology 233, 137–152 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4095-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4095-7