Abstract
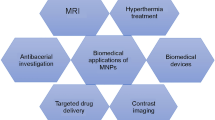
Nanosized ferrites and magnetic nanocrystals have attracted significant attention owing to their vast applications in various fields, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents, magnetic memory, efficient hyperthermia for cancer therapy, and catalysts. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been prepared by ferrite nanoparticles, MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn, Mg, Fe, for example). Because of their applications in medical diagnosis technology, sensor technology, information storage, cooling technology, and magnetic warming, MNPs have attracted considerable interest in the last few years. The magnetic properties of MNPs strongly depend on the size of the MNPs. Therefore, MNPs with a controlled size are crucial in controlling properties for different applications in the biomedical field. The efficacy of dopant ions in modifying the resultant MNPs’ size and shape could be directly related to variations in the rate of crystal growth and thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. In some situations, particle growth is due to the existence of some other physicochemical phenomenon like passivation of the nanoparticle surface, charging of the nanoparticles, and compartmentalization of nanoparticles in different zones. Various methods involved in the crystal growth of MNPs are also discussed in this chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grossman H, Myers W, Vreeland V, Bruehl R, Alper M, Bertozzi C, Clarke J (2004) Detection of bacteria in suspension by using a superconducting quantum interference device. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:129–134
Chung S, Hoffmann A, Bader S, Liu C, Kay B, Makowski L, Chen L (2004) Biological sensors based on Brownian relaxation of magnetic nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 85:2971–2973
Duan F, Guojun J (2005) Introduction to condensed matter physics. World Scientific, Singapore
Ehrenreich H, Spaepen F (2001) Solid state physics. Academic Press
Néel L (1949) Effects of thermal fluctuations on the magnetization of small particles. CR Acad Sci Paris 228:1953
Néel L (1949) Theory of magnetic viscosity of fine grained ferromagnetics with application to baked clays. Ann Geophys 5:41
Leslie-Pelecky DL, Rieke RD (1996) Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem Mater 8:1770–1783
Morrish AH (2001) In: Morrish AH (ed) The physical principles of magnetism. Wiley-VCH, p 696. isbn:ISBN 0-7803-6029-X
Akbarzadeh A, Samiei M, Davaran S (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:1
Rümenapp C, Gleich B, Haase A (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging and diagnostics. Pharm Res 29:1165–1179
Tang SC, Lo IM (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications. Water Res 47:2613–2632
Colombo M, Carregal-Romero S, Casula MF, Gutierrez L, Morales MP, Boehm IB, Heverhagen JT, Prosperi D, Parak WJ (2012) Biological applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 41:4306–4334
Sugimoto M (1999) The past, present, and future of ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc 82:269–280
Smit J, Wijn H (1954) Physical properties of ferrites. Adv Elect Electron Phys 6:69–136
Van Der Zaag P (1999) New views on the dissipation in soft magnetic ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 196:315–319
Polking MJ, Alivisatos AP, Ramesh R (2015) Synthesis, physics, and applications of ferroelectric nanomaterials. MRS Commun 5:27–44
Hausner HH (2015) Modern materials: advances in development and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Reddy DHK, Yun Y-S (2016) Spinel ferrite magnetic adsorbents: alternative future materials for water purification? Coord Chem Rev 315:90–111
Hill RJ, Craig JR, Gibbs G (1979) Systematics of the spinel structure type. Phys Chem Miner 4:317–339
Leem G, Sarangi S, Zhang S, Rusakova I, Brazdeikis A, Litvinov D, Lee TR (2009) Surfactant-controlled size and shape evolution of magnetic nanoparticles. Cryst Growth Des 9:32–34
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrences and uses. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ
Gossuin Y, Gillis P, Hocq A, Vuong QL, Roch A (2009) Magnetic resonance relaxation properties of superparamagnetic particles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 1:299–310
Rohrer GS (2001) Structure and bonding in crystalline materials. Cambridge University Press, Delhi
Stadelmann P (1987) EMS-a software package for electron diffraction analysis and HREM image simulation in materials science. Ultramicroscopy 21:131–145
Jang JT, Nah H, Lee JH, Moon SH, Kim MG, Cheon J (2009) Critical enhancements of MRI contrast and hyperthermic effects by dopant-controlled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew Chem 121:1260–1264
Kang E, Park J, Hwang Y, Kang M, Park J-G, Hyeon T (2004) Direct synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse manganese ferrite nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 108:13932–13935
Song Q, Zhang ZJ (2004) Shape control and associated magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 126:6164–6168
Tromsdorf UI, Bigall NC, Kaul MG, Bruns OT, Nikolic MS, Mollwitz B, Sperling RA, Reimer R, Hohenberg H, Parak WJ (2007) Size and surface effects on the MRI relaxivity of manganese ferrite nanoparticle contrast agents. Nano Lett 7:2422–2427
Dronskowski R (2001) The little maghemite story: a classic functional material. Adv Funct Mater 11:27–29
Lévy M, Wilhelm C, Siaugue J-M, Horner O, Bacri J-C, Gazeau F (2008) Magnetically induced hyperthermia: size-dependent heating power of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J Phys Condens Matter 20:204133
Waychunas GA (1991) Crystal chemistry of oxides and oxyhydroxides. Rev Mineral Geochem 25:11–68
Chen T, Xu H, Ji J, Chen J, Chen Y (2003) Formation mechanism of ferromagnetic minerals in loess of China: TEM investigation. Chin Sci Bull 48:2260–2267
Matijevic E, Good RJ (2012) Surface and colloid science. Springer, Berlin
Klahr BM, Martinson AB, Hamann TW (2010) Photoelectrochemical investigation of ultrathin film iron oxide solar cells prepared by atomic layer deposition. Langmuir 27:461–468
Saremi-Yarahmadi S, Wijayantha KGU, Tahir AA, Vaidhyanathan B (2009) Nanostructured α-Fe2O3 electrodes for solar driven water splitting: effect of doping agents on preparation and performance. J Phys Chem C 113:4768–4778
Wu C, Yin P, Zhu X, Ouyang C, Xie Y (2006) Synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanorods: diameter-size and shape effects on their applications in magnetism, lithium ion battery, and gas sensors. J Phys Chem B 110:17806–17812
Zeng S, Tang K, Li T, Liang Z, Wang D, Wang Y, Zhou W (2007) Hematite hollow spindles and microspheres: selective synthesis, growth mechanisms, and application in lithium ion battery and water treatment. J Phys Chem C 111:10217–10225
Zhang G, Gao Y, Zhang Y, Guo Y (2010) Fe2O3-pillared rectorite as an efficient and stable Fenton-like heterogeneous catalyst for photodegradation of organic contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 44:6384–6389
Cheng C-J, Lin C-C, Chiang R-K, Lin C-R, Lyubutin IS, Alkaev EA, Lai H-Y (2008) Synthesis of monodisperse magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles from submicrometer hematite powders. Crystal Growth Design 8:877–883
Morrish AH (1994) Canted antiferromagnetism: hematite. World Scientific, Singapore
Cameron AG (1973) Abundances of the elements in the solar system. Space Sci Rev 15:121–146
Suess HE, Urey HC (1956) Abundances of the elements. Rev Mod Phys 28:53
Fleischer RL, Price PB, Walker RM (1975) Nuclear tracks in solids: principles and applications. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA
Ngo A, Pileni M (2001) Assemblies of ferrite nanocrystals: partial orientation of the easy magnetic axes. J Phys Chem B 105:53–58
Raj K, Moskowitz B, Casciari R (1995) Advances in ferrofluid technology. J Magn Magn Mater 149:174–180
Singhal S, Singh J, Barthwal S, Chandra K (2005) Preparation and characterization of nanosize nickel-substituted cobalt ferrites (Co 1− xNixFe2O4). J Solid State Chem 178:3183–3189
Sousa MH, Tourinho FA, Depeyrot J, Da Silva GJ, Lara MCF (2001) New electric double-layered magnetic fluids based on copper, nickel, and zinc ferrite nanostructures. J Phys Chem B 105:1168–1175
Rooksby H, Willis B (1953) Crystal structure and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite at low temperatures.
Thanh NT, Maclean N, Mahiddine S (2014) Mechanisms of nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in solution. Chem Rev 114:7610–7630
Fanun M (2016) Colloids in drug delivery. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Liveri VT (2006) Nucleation, growth, and arrested growth in confined space. In: Controlled synthesis of nanoparticles in microheterogeneous systems. Springer, New York, pp 75–90
Marchal P, David R, Klein J, Villermaux J (1988) Crystallization and precipitation engineering—I. An efficient method for solving population balance in crystallization with agglomeration. Chem Eng Sci 43:59–67
Mersmann A (1999) Crystallization and precipitation. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 38:345–353
Dirksen J, Ring T (1991) Fundamentals of crystallization: kinetic effects on particle size distributions and morphology. Chem Eng Sci 46:2389–2427
Franke J, Mersmann A (1995) The influence of the operational conditions on the precipitation process. Chem Eng Sci 50:1737–1753
Costa CBB, Maciel MRW, Maciel Filho R (2007) Considerations on the crystallization modeling: population balance solution. Comput Chem Eng 31:206–218
Banfield JF, Zhang H (2001) Nanoparticles in the environment. Rev Mineral Geochem 44:1–58
Pascal C, Pascal J, Favier F, Elidrissi Moubtassim M, Payen C (1999) Electrochemical synthesis for the control of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticle size. Morphology, microstructure, and magnetic behavior. Chem Mater 11:141–147
Cote LJ, Teja AS, Wilkinson AP, Zhang ZJ (2002) Continuous hydrothermal synthesis and crystallization of magnetic oxide nanoparticles. J Mater Res 17:2410–2416
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Vander Elst L, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110
Hua CC, Zakaria S, Farahiyan R, Khong LT (2008) Size-controlled synthesis and characterization of Fe. Sains Malaysiana 37:389–394
Mehnert W, Mäder K (2001) Solid lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47:165–196
Sun L, Huang C, Gong T, Zhou S (2010) A biocompatible approach to surface modification: biodegradable polymer functionalized super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 30:583–589
Marciano V, Minore A, Liveri VT (2000) A simple method to prepare solid nanoparticles of water-soluble salts using water-in-oil microemulsions. Colloid Polym Sci 278:250–252
Chen D, Tang X, Wu J, Zhang W, Liu Q, Jiang Y (2011) Effect of grain size on the magnetic properties of superparamagnetic Ni 0.5 Zn 0.5 Fe2O4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation process. J Magn Magn Mater 323:1717–1721
Wilson K, Harris L, Goff J, Riffle J, Dailey J (2002) A generalized method for magnetite nanoparticle steric stabilization utilizing block copolymers containing carboxylic acids. Eur Cell Mater 3:206–209
Levy L, Hochepied J, Pileni M (1996) Control of the size and composition of three dimensionally diluted magnetic semiconductor clusters. J Phys Chem 100:18322–18326
Wang W, Efrima S, Regev O (1999) Directing silver nanoparticles into colloid-surfactant lyotropic lamellar systems. J Phys Chem B 103:5613–5621
Qi L, Gao Y, Ma J (1999) Synthesis of ribbons of silver nanoparticles in lamellar liquid crystals. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 157:285–294
Andersson M, Alfredsson V, Kjellin P, Palmqvist AE (2002) Macroscopic alignment of silver nanoparticles in reverse hexagonal liquid crystalline templates. Nano Lett 2:1403–1407
Liveri VT (2006) Controlled synthesis of nanoparticles in microheterogeneous systems. Springer, Berlin
Wu S-H, Chen D-H (2004) Synthesis of high-concentration Cu nanoparticles in aqueous CTAB solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 273:165–169
Rabatic BM, Pralle MU, Tew GN, Stupp SI (2003) Nanostructured semiconductors templated by cholesteryl-oligo (ethylene oxide) amphiphiles. Chem Mater 15:1249–1255
Yang H, Guo R, Wang H (2001) Lubrication of the mixed system of Triton X-100/n-C 10 H 21 OH/H2O lamellar liquid crystal and ZnS nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 180:243–251
Padhi A, Nanjundaswamy K, Masquelier C, Okada S, Goodenough J (1997) Effect of structure on the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple in iron phosphates. J Electrochem Soc 144:1609–1613
Lu AH, Salabas EEL, Schüth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1222–1244
Park BK, Jeong S, Kim D, Moon J, Lim S, Kim JS (2007) Synthesis and size control of monodisperse copper nanoparticles by polyol method. J Colloid Interface Sci 311:417–424
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Saleh A, Rezaee M, Ghambarian M, Hassani R (2010) A nanoparticle-based solid-phase extraction procedure followed by flow injection inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry to determine some heavy metal ions in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 659:172–177
Ramimoghadam D, Bagheri S, Hamid SBA (2014) Progress in electrochemical synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 368:207–229
Cabrera L, Gutierrez S, Menendez N, Morales M, Herrasti P (2008) Magnetite nanoparticles: electrochemical synthesis and characterization. Electrochim Acta 53:3436–3441
Teja AS, Koh P-Y (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 55:22–45
Suwalka O, Sharma RK, Sebastian V, Lakshmi N, Venugopalan K (2007) A study of nanosized Ni substituted Co–Zn ferrite prepared by coprecipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 313:198–203
Wu W, Wu Z, Yu T, Jiang C, Kim W-S (2016) Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater 16(2):023501
Massart R (1981) Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans Magn 17:1247–1248
Wei W, Quanguo H, Rong H, Jingke H, Hong C (2007) Preparation and characterization of magnetite Fe3O4 nanopowders. Rare Metal Mater Eng 36:238–243
Azcona P, Zysler R, Lassalle V (2016) Simple and novel strategies to achieve shape and size control of magnetite nanoparticles intended for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 504:320–330
Morales MDP, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Montero M, Serna C, Roig A, Casas L, Martinez B, Sandiumenge F (1999) Surface and internal spin canting in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem Mater 11:3058–3064
Sugimoto T (1987) Preparation of monodispersed colloidal particles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 28:65–108
Boistelle R, Astier J (1988) Crystallization mechanisms in solution. J Cryst Growth 90:14–30
Jolivet J, Henry M, Livage J (2000) Metal oxide chemistry and synthesis: from solution to oxide. Wiley, New York
Babes L, Denizot BT, Tanguy G, Le Jeune JJ, Jallet P (1999) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles used as MRI contrast agents: a parametric study. J Colloid Interface Sci 212:474–482
Jiang W, Yang H-C, Yang S-Y, Horng H-E, Hung J, Chen Y, Hong C-Y (2004) Preparation and properties of superparamagnetic nanoparticles with narrow size distribution and biocompatible. J Magn Magn Mater 283:210–214
Tartaj P, González-Carreño T, Serna CJ (2004) From hollow to dense spheres: control of dipolar interactions by tailoring the architecture in colloidal aggregates of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocrystals. Adv Mater 16:529–533
Wang X, Zhuang J, Peng Q, Li Y (2005) A general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis. Nature 437:121–124
Anderson SA, Rader RK, Westlin WF, Null C, Jackson D, Lanza GM, Wickline SA, Kotyk JJ (2000) Magnetic resonance contrast enhancement of neovasculature with αvβ3-targeted nanoparticles. Magn Reson Med 44:433–439
Khollam Y, Dhage S, Potdar H, Deshpande S, Bakare P, Kulkarni S, Date S (2002) Microwave hydrothermal preparation of submicron-sized spherical magnetite (Fe3O4) powders. Mater Lett 56:571–577
Kasapoğlu N, Baykal A, Toprak MS, Köseoğlu Y, Bayrakdar H (2007) Synthesis and characterization of NiFe2O4 nano-octahedrons by EDTA-assisted hydrothermal method. Turk J Chem 31:659–666
Wang G, Shen X, Horvat J, Wang B, Liu H, Wexler D, Yao J (2009) Hydrothermal synthesis and optical, magnetic, and supercapacitance properties of nanoporous cobalt oxide nanorods. J Phys Chem C 113:4357–4361
Kadier W, Sadeh B, Duamet B, Aman M (2014) Hydrothermal synthesis and properties of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles 31.
Haw CY, Mohamed F, Chia CH, Radiman S, Zakaria S, Huang NM, Lim HN (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Ceram Int 36:1417–1422
Nejati K, Zabihi R (2012) Preparation and magnetic properties of nano size nickel ferrite particles using hydrothermal method. Chem Cent J 6:1
Tartaj P, Del Puerto MM, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, González-Carreño T, Serna CJ (2003) The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R182
Sugimoto T (2000) Fine particles: synthesis, characterization, and mechanisms of growth. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Cai W, Wan J (2007) Facile synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles in liquid polyols. J Colloid Interface Sci 305:366–370
Viau G, Ravel F, Acher O, Fiévet-Vincent F, Fiévet F (1994) Preparation and microwave characterization of spherical and monodisperse Co20Ni80 particles. J Appl Phys 76:6570–6572
Majidi S, Zeinali Sehrig F, Farkhani SM, Soleymani Goloujeh M, Akbarzadeh A (2016) Current methods for synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Artificial Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:722–734
Viau G, Fievet-Vincent F, Fievet F (1996) Monodisperse iron-based particles: precipitation in liquid polyols. J Mater Chem 6:1047–1053
Fievet F, Lagier J, Blin B, Beaudoin B, Figlarz M (1989) Homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleations in the polyol process for the preparation of micron and submicron size metal particles. Solid State Ionics 32:198–205
Tzitzios V, Petridis D, Zafiropoulou I, Hadjipanayis G, Niarchos D (2005) Synthesis and characterization of L1 0 FePt nanoparticles from Pt–Fe3O4 core-shell nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 294:e95–e98
Jezequel D, Guenot J, Jouini N, Fievet F (1995) Submicrometer zinc oxide particles: elaboration in polyol medium and morphological characteristics. J Mater Res 10:77–83
Liu J, Qiao SZ, Hu QH (2011) Magnetic nanocomposites with mesoporous structures: synthesis and applications. Small 7:425–443
Reetz MT, Helbig W, Quaiser SA (1996) Electrochemical methods in the synthesis of nanostructured transition metal clusters. Active Metals Prep Charact Appl:279–297
Khan H, Petrikowski K (2000) Anisotropic structural and magnetic properties of arrays of Fe 26 Ni 74 nanowires electrodeposited in the pores of anodic alumina. J Magn Magn Mater 215:526–528
Pankhurst Q, Thanh N, Jones S, Dobson J (2009) Progress in applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:224001
Salazar-Alvarez G, Muhammed M, Zagorodni AA (2006) Novel flow injection synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with narrow size distribution. Chem Eng Sci 61:4625–4633
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R167
Rodríguez-López A, Cruz-Rivera J, Elías-Alfaro C, Betancourt I, Ruiz-Silva H, Antaño-López R (2015) Fine tuning of magnetite nanoparticle size distribution using dissymmetric potential pulses in the presence of biocompatible surfactants and the electrochemical characterization of the nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 46:538–547
Chatterjee K, Sarkar S, Rao KJ, Paria S (2014) Core/shell nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 209:8–39
Herea D, Chiriac H, Lupu N, Grigoras M, Stoian G, Stoica B, Petreus T (2015) Study on iron oxide nanoparticles coated with glucose-derived polymers for biomedical applications. Appl Surf Sci 352:117–125
Khoee S, Shagholani H, Abedini N (2015) Synthesis of quasi-spherical and square shaped oligoamino-ester graft-from magnetite nanoparticles: effect of morphology and chemical structure on protein interactions. Polymer 56:207–217
Calatayud MP, Sanz B, Raffa V, Riggio C, Ibarra MR, Goya GF (2014) The effect of surface charge of functionalized Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles on protein adsorption and cell uptake. Biomaterials 35:6389–6399
Šutka A, Lagzdina S, Käämbre T, Pärna R, Kisand V, Kleperis J, Maiorov M, Kikas A, Kuusik I, Jakovlevs D (2015) Study of the structural phase transformation of iron oxide nanoparticles from an Fe2+ ion source by precipitation under various synthesis parameters and temperatures. Mater Chem Phys 149–150:473–479
Lassalle V, Avena M, Ferreira M (2009) A review of the methods of magnetic nanocomposites synthesis and their applications as drug delivery systems and immobilization supports for lipases. Current Trends Polymer Sci 13:37–67
Roth H-C, Schwaminger SP, Schindler M, Wagner FE, Berensmeier S (2015) Influencing factors in the c-precipitation process of superparamagnetic iron oxide nano particles: a model based study. J Magn Magn Mater 377:81–89
Fang M, Ström V, Olsson RT, Belova L, Rao KV (2012) Particle size and magnetic properties dependence on growth temperature for rapid mixed co-precipitated magnetite nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 23:145601
Mascolo MC, Pei Y, Ring TA (2013) Room temperature co-precipitation synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles in a large pH window with different bases. Materials 6:5549–5567
Adeli M, Yamini Y, Faraji M (2012) Removal of copper, nickel and zinc by sodium dodecyl sulphate coated magnetite nanoparticles from water and wastewater samples. Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.10.012
Reddy LH, Arias JL, Nicolas J, Couvreur P (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles: design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem Rev 112:5818–5878
Wang B, Chen K, Jiang S, Reincke F, Tong W, Wang D, Gao C (2006) Chitosan-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles on patterned poly (dimethylsiloxane) surfaces. Biomacromolecules 7:1203–1209
Naik RR, Stringer SJ, Agarwal G, Jones SE, Stone MO (2002) Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nat Mater 1:169–172
Reiss BD, Mao C, Solis DJ, Ryan KS, Thomson T, Belcher AM (2004) Biological routes to metal alloy ferromagnetic nanostructures. Nano Lett 4:1127–1132
Galloway JM, Bird SM, Bramble JP, Critchley K, Staniland SS (2013) Biotemplating magnetic nanoparticles on patterned surfaces for potential use in data storage. In: MRS Proceedings. Cambridge University Press, Delhi, pp 231–237
Arakaki A, Webb J, Matsunaga T (2003) A novel protein tightly bound to bacterial magnetic particles in Magnetospirillum magneticum strain AMB-1. J Biol Chem 278:8745–8750
Galloway JM, Arakaki A, Masuda F, Tanaka T, Matsunaga T, Staniland SS (2011) Magnetic bacterial protein Mms6 controls morphology, crystallinity and magnetism of cobalt-doped magnetite nanoparticles in vitro. J Mater Chem 21:15244–15254
Wang L, Prozorov T, Palo PE, Liu X, Vaknin D, Prozorov R, Mallapragada S, Nilsen-Hamilton M (2011) Self-assembly and biphasic iron-binding characteristics of Mms6, a bacterial protein that promotes the formation of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles of uniform size and shape. Biomacromolecules 13:98–105
Bird SM, El-Zubir O, Rawlings AE, Leggett GJ, Staniland SS (2016) A novel design strategy for nanoparticles on nanopatterns: interferometric lithographic patterning of Mms6 biotemplated magnetic nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 4:3948–3955
Kolosnjaj-Tabi J, Lartigue L, Javed Y, Luciani N, Pellegrino T, Wilhelm C, Alloyeau D, Gazeau F (2016) Biotransformations of magnetic nanoparticles in the body. Nano Today 11(3):280–284
Lartigue L, Alloyeau D, Kolosnjaj-Tabi J, Javed Y, Guardia P, Riedinger A, Péchoux C, Pellegrino T, Wilhelm C, Gazeau F (2013) Biodegradation of iron oxide nanocubes: high-resolution in situ monitoring. ACS Nano 7:3939–3952
Javed Y, Lartigue L, Hugounenq P, Vuong QL, Gossuin Y, Bazzi R, Wilhelm C, Ricolleau C, Gazeau F, Alloyeau D (2014) Biodegradation mechanisms of iron oxide monocrystalline nanoflowers and tunable shield effect of gold coating. Small 10:3325–3337
Mazuel F, Espinosa A, Luciani N, Reffay M, Le Borgne R, Motte L, Desboeufs K, Michel A, Pellegrino T, Lalatonne Y (2016) Massive intracellular biodegradation of iron oxide nanoparticles evidenced magnetically at single endosome and tissue levels. ACS Nano 10(8):7627–7638
Kolosnjaj-Tabi J, Javed Y, Lartigue L, Volatron J, Elgrabli D, Marangon I, Pugliese G, Caron B, Figuerola A, Luciani N (2015) The one year fate of iron oxide coated gold nanoparticles in mice. ACS Nano 9:7925–7939
Jun YW, Choi JS, Cheon J (2006) Shape control of semiconductor and metal oxide nanocrystals through nonhydrolytic colloidal routes. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3414–3439
Nunez NO, Tartaj P, Morales MP, Pozas R, Ocana M, Serna CJ (2003) Preparation, characterization, and magnetic properties of Fe-based alloy particles with elongated morphology. Chem Mater 15:3558–3563
Park S-J, Kim S, Lee S, Khim ZG, Char K, Hyeon T (2000) Synthesis and magnetic studies of uniform iron nanorods and nanospheres. J Am Chem Soc 122:8581–8582
Dumestre F, Chaudret B, Amiens C, Renaud P, Fejes P (2004) Superlattices of iron nanocubes synthesized from Fe [N (SiMe3) 2] 2. Science 303:821–823
Wang L, Luo J, Fan Q, Suzuki M, Suzuki IS, Engelhard MH, Lin Y, Kim N, Wang JQ (2005) Monodispersed core-shell Fe3O4@ Au nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 109:21593–21601
Caruntu D, Cushing BL, Caruntu G, O’connor CJ (2005) Attachment of gold nanograins onto colloidal magnetite nanocrystals. Chem Mater 17:3398–3402
Lyon JL, Fleming DA, Stone MB, Schiffer P, Williams ME (2004) Synthesis of Fe oxide core/Au shell nanoparticles by iterative hydroxylamine seeding. Nano Lett 4:719–723
Zambaux M, Bonneaux F, Gref R, Dellacherie E, Vigneron C (1999) Preparation and characterization of protein C-loaded PLA nanoparticles. J Control Release 60:179–188
Stolnik S, Illum L, Davis S (1995) Long circulating microparticulate drug carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 16:195–214
Savva M, Duda E, Huang L (1999) A genetically modified recombinant tumor necrosis factor-α conjugated to the distal terminals of liposomal surface grafted polyethyleneglycol chains. Int J Pharm 184:45–51
Peracchia MT, Vauthier C, Passirani C, Couvreur P, Labarre D (1997) Complement consumption by poly (ethylene glycol) in different conformations chemically coupled to poly (isobutyl 2-cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Life Sci 61:749–761
Sah H (1999) Stabilization of proteins against methylene chloride/water interface-induced denaturation and aggregation. J Control Release 58:143–151
Velge-Roussel F, Breton P, Guillon X, Lescure F, Bru N, Bout D, Hoebeke J (1996) Immunochemical characterization of antibody-coated nanoparticles. Experientia 52:803–806
Piao Y, Kim J, Na HB, Kim D, Baek JS, Ko MK, Lee JH, Shokouhimehr M, Hyeon T (2008) Wrap–bake–peel process for nanostructural transformation from β-FeOOH nanorods to biocompatible iron oxide nanocapsules. Nat Mater 7:242–247
Liu C, Wu X, Klemmer T, Shukla N, Weller D, Roy AG, Tanase M, Laughlin D (2005) Reduction of sintering during annealing of FePt nanoparticles coated with iron oxide. Chem Mater 17:620–625
Mikhaylova M, Kim DK, Bobrysheva N, Osmolowsky M, Semenov V, Tsakalakos T, Muhammed M (2004) Superparamagnetism of magnetite nanoparticles: dependence on surface modification. Langmuir 20:2472–2477
Jeong U, Teng X, Wang Y, Yang H, Xia Y (2007) Superparamagnetic colloids: controlled synthesis and niche applications. Adv Mater 19:33–60
Hyeon T (2003) Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem Commun:927–934
Casula MF, Jun Y-W, Zaziski DJ, Chan EM, Corrias A, Alivisatos AP (2006) The concept of delayed nucleation in nanocrystal growth demonstrated for the case of iron oxide nanodisks. J Am Chem Soc 128:1675–1682
Kwon SG, Piao Y, Park J, Angappane S, Jo Y, Hwang N-M, Park J-G, Hyeon T (2007) Kinetics of monodisperse iron oxide nanocrystal formation by “heating-up” process. J Am Chem Soc 129:12571–12584
Dubertret B, Skourides P, Norris DJ, Noireaux V, Brivanlou AH, Libchaber A (2002) In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles. Science 298:1759–1762
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LW, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22:969–976
Pellegrino T, Manna L, Kudera S, Liedl T, Koktysh D, Rogach AL, Keller S, Rädler J, Natile G, Parak WJ (2004) Hydrophobic nanocrystals coated with an amphiphilic polymer shell: a general route to water soluble nanocrystals. Nano Lett 4:703–707
White MA, Johnson JA, Koberstein JT, Turro NJ (2006) Toward the syntheses of universal ligands for metal oxide surfaces: controlling surface functionality through click chemistry. J Am Chem Soc 128:11356–11357
Caruso F (2001) Nanoengineering of particle surfaces. Adv Mater 13:11–22
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Yi DK, Selvan ST, Lee SS, Papaefthymiou GC, Kundaliya D, Ying JY (2005) Silica-coated nanocomposites of magnetic nanoparticles and quantum dots. J Am Chem Soc 127:4990–4991
Yi DK, Lee SS, Papaefthymiou GC, Ying JY (2006) Nanoparticle architectures templated by SiO2/Fe2O3 nanocomposites. Chem Mater 18:614–619
Kim J, Lee JE, Lee J, Yu JH, Kim BC, An K, Hwang Y, Shin C-H, Park J-G, Kim J (2006) Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 128:688–689
Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Kim E, Kim JS, Kim BG, Yun SH, Sohn BH, Cho MH, Lee JK, Park SB (2006) Specific targeting, cell sorting, and bioimaging with smart magnetic silica core–shell nanomaterials. Small 2:209–215
Yoon T-J, Kim JS, Kim BG, Yu KN, Cho M-H, Lee J-K (2005) Multifunctional nanoparticles possessing a “magnetic motor effect” for drug or gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:1068–1071
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ali, K., Javed, Y., Jamil, Y. (2017). Size and Shape Control Synthesis of Iron Oxide–Based Nanoparticles: Current Status and Future Possibility. In: Sharma, S. (eds) Complex Magnetic Nanostructures. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52087-2_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52087-2_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-52086-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-52087-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)