Abstract
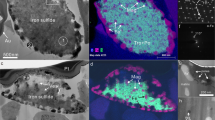
The results of TEM investigation indicate that magnetite and maghemite are the major ferromagnetic minerals in loess-paleosol sequences. Primary magnetite has the similar morphology and surface characteristics as eolian detrital particles. The magnetite can be classified into two categories, high-titanium and low-titanium, which may be the indicators of magmatic rocks and metamorphic rocks, respectively. TEM investigation at nanometer scale shows that primary detrital magnetite of micron scale had been partially weathered to maghemite of 5–20 nanometer during the pedogenic process, which maintain the pseudomorphism of the aeolian debris. Some chlorite particles were also weathered to nanometer scale magnetite or maghemite in the pedogenic process. So weathering of the two minerals leads to formation of superparamagnetism, which may be the important mechanism of magnetic-susceptibility increase in paleosols. The magnetite or maghemite resulting from the weathering of chlorite contains a small amount of P and S, which is the signal of microbe-mineral interaction, and indicates that microbes may play a certain role in chlorite weathering and formation of superparamagnetic particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heller, F., Liu, T. S., Magnetostratigraphical dating of loess deposits in China, Nature, 1982, 300: 431–433.
An, Z. S., Wang, J. D., Li, H. M., Study on paleogeomagnetism of Luochuan loess section, Geochimica, 1977 (4): 239–249.
Fine, P., Singer, M. J., Verosub, K. L., Use of magnetic-susceptibility measurements in assessing soil uniformity in chronosequence studies, Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1992, 56: 1195–1199.
Evans, M. E., Heller, F., Magnetic enhancement and paleoclimate: Study of a loess-paleosol couplet across the loess plateau of China, Geophysical Journal International, 1994, 117(1): 257–264.
Evans, M. E., Heller, F., Magnetism of loess-palaeosol sequences: recent developments, Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 54: 129–144.
Banerjee, S. K., Hunt, C. P., Liu, X. M., Separation of local signals from the regional paleomonsoon record of the Chinese loess plateau: A rock-magnetic approach, Geophysical Research Letters, 1993, 20: 843–846.
Lu, H. Y., Han, J. M., Wu, N. Q. et al., Susceptibility analysis and paleoclimate significance of Chinese modern soils, Science in China, Series D (in Chinese), 1994, 24(12): 1290–1297.
Liu, X. M., Rolph, T., Bloemendal, J. et al., Quantitative estimates of palaeoprecipitation at Xifeng area, in the Loess Plateau of China, Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Ppalaeoecology, 1995, 113: 243–248.
Maher, B. A., Thompson, R., Zhou, L. P., Spatial and temporal reconstructions of changes in the Asian palaeomonsoon: a new mineral magnetic approach, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 125: 461–471.
Maher, B. A., Thompson, R., Paleorainfall Reconstructions from Pedogenic Magnetic Susceptibility Variations in the Chinese Loess and Paleosols, Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(3): 383–391.
Heller, F., Liu, X. M., Liu, T. S. et al., Magnetic susceptibility of loess in China, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 103: 301–310.
Heller, F., Shen, C. D., Beer, J. et al., Quantitative estimates of pedogenic ferromagnetic mineral formation in Chinese loess and palaeomagnetic implications, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 114: 385–390.
Liu, X. M., Shaw, J., Liu, T. S. et al., Magnetic mineralogy of Chinese loess and its significance, Geophysical Journal International, 1992, 108: 301–308.
Zhou, L. P., Oldfield, F., Wintle, A. G. et al., Partly pedogenic origin of magnetic variations in Chinese loess, Nature, 1990, 346: 737–739.
Maher, B. A., Thompson, R., Mineral magnetic record of the Chinese loess and paleosols, Geology, 1991, 19(1): 3–6.
Zheng, H., Oldfield, F., Yu, L. et al., The magnetic properties of particle-sized samples from the Luo Chuan loess section: evidence for pedogenesis, Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interior, 1991, 68: 250–258.
Fine, P., Singer, M. J., Verosub, K. L. et al., New evidence for the origin of ferrimagnetic minerals in loess from China, Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1993, 57: 1537–1542.
Verosub, K. L., Fine, P., Singer, M. J. et al., Pedogenesis and paleoclimate: Interpretation of the magnetic susceptibility record of Chinese loess-paleosol sequences, Geology, 1993, 21: 1011–1014.
Eyre, J. K., Shaw, Magnetic enhancement of Chinese loess-the role of r-Fe2O3? Geophysical Journal of International, 1994, 117: 265–271.
Sun, W., Banerjee, S. K., Hunt, C. P., The role of maghemite in the enchancement of magnetic signal in the Chinese loess-paleosol sequence: An extensive rock magnetic study conbined with citrate-bicarbnon-dithionite treatment, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 133: 493–505.
Liu, X. M., Hesse, P., Rolph, T., Origin of maghaemite in Chinese loess deposits: aeolian or pedogenic? Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1999, 112(3–4): 191–201.
Heller, F., Liu, T. S., Magnetism of Chinese loess deposits. Geophysical Journal Royal Astronomical Society, 1984, 77: 125–141.
Hunt, C. P., Singer, M. J., Kletetschka, G. et al., Effect of citrate-bicarbonate-dithionite treatment on fine-grained magnetite and maghemite, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 130: 87–94.
Deng, C., Zhu, R., Jackson, M. J. et al., Variability of the temperature-dependent susceptibility of the Holocene eolian deposits in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A pedogenesis indicator, Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy, 2001, 26(11–12): 873–878.
Kukla, G., An, Z. S., Loess stratigraphy in central China, Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, and Palaeoecology, 1989, 72: 203–225.
Rolph, T. C., Shaw, J., Derbyshire, E. et al., The magnetic mineralogy of a loess section near Lanzhou, China (ed. Pye, K.). The dynamics and environmental context of aeolian sedimentary systems, Geological Society Special Publication, 1993, 72: 311–323.
Kleteschka, G., Banerjee, S. K., Magnetic stratigraphy of Chinese loess as a record of natural fire, Geophysical Research Letters, 1995, 22: 1341–1343.
Meng, X. M., Derbyshire, E., Kemp, B. A., Origin of magnetic susceptibility signal in Chinese loess, Quaternary Science Review, 1997, 16: 833–839.
Jia, R. F., Yan, B. Z., Li, R. S., Features of Magnetotactic bacteria in Duanjiapo loess section Shanxi and environmental significance, Science in China, Series D (in Chinese), 1996, 26(5): 411–416.
Petersen, N., Dobeneck, T. V., Vali, H., Fossil bacterial magnetite in deep-sea sediments from the South Atlantic Ocean, Nature, 1986, 320(17): 611–614.
Maher, B. A., Talor, R. M., Formation of ultrafine-graine magnetite in soils, Nature, 1988, 336: 368–370.
Fassbinder, W. E., Stanjek, H., Vail, H., Occurrence of magnetic bacteria in soil, Nature, 1990, 343: 161–163.
Oldfield, F. The source of fine-grained magnetite in sediments, Holocene, 1992, 2: 180–182.
Snowball, I. F., Bacterial magnetite and the magnetic properties of sediments in a Swedish lake., Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 126: 129–142.
Banfield, J. F., Welch, S. A., Zhang, H. Z. et al., Aggregation-based crystal growth and microstructure development in natural iron oxyhydroxide biomineralization products, Science, 2000, 289: 751–753.
Josifovska, M. G., Mcclean, R. G., Schofield, M. A. et al., Discovery of nanocrystalline botanical magnetite, European Journal of Mineralogy, 2001, 13: 863–870.
Maher, B. A., Thompson, R., Paleoclimatic significance of the mineral magnetic record of the Chinese loess and paleosols, Quaternary Research, 1992, 37: 155–170.
Liu, D. S., Loess and the Environment (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1985, 1–358.
Hounslow, M. W., Maher, B. A., Laboratory procedures for quantitative extraction and analysis of magnetic minerals from sediments (eds. Waiden, J., Oldfield, F., Smith, J. P.), Environmental magnetism: a practical guide, Quaternary Research Association, Cambridge, UK, Extraction and Analysis of Magnetic Minerals from Sediments, 1999, 139–184.
Barrn, V., Torrent, J., Evidence for a simple pathway to maghemite in Earth and Mars soil, Geochimica et Comochimica Acta, 2002, 66(15): 2801–2806.
Maher, B. A., Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites, Geophysical Journal of International, 1988, 94: 83–96.
Proust, D., Eymery, J., Beaufort, D., Supergene vermiculitization of a magnesium chlorite: iron and magnesium removal processes, Clays and Clay Minerals, 1986, 34(5): 572–580.
Righi, D., Petit, S., Bouchet, A., Characterization of hydroxy-interlayered vermiculite and illite/smectite interstratified minerals from the weathering of chlorite in a Cryorthod, Clays and Clay minerals, 1993, 41(4): 484.
Carnicelli, S., Mirabella, A., Cecchini, G. et al., Weathering of chlorite to a low-charge expandable mineral in a Spodosol on the Apennine mountains, Italy, Clays and Clay Minerals, 1997, 45(1): 28–41.
Ji, J. F., Chen, J., Liu, L. W. et al., Chemical weathering of Chlorite and increase of susceptibility in Luochuan loess, Progress in Natural Science, 1999, 9(7): 619–623.
Blakemore, R. P., Magnetotactic bacteria, Science, 1975, 190: 377–379.
Lower, S. K., Hochella, Jr. M. F., Beveridge, T. J., Bacterial recognition of mineral surfaces: nanoscale interactions between shewanella and α-FeOOH, Science, 2001, 292: 1360–1363.
Glasauer, S., Langley, S., Beveridge, T. J., Intracellular iron minerals in a dissimilatory iron-reducing bacterium, Science, 2002, 295: 117–119.
Robert, M., Berthelin, J., Role of biological and biochemical factors in soil mineral weathering (eds. Huang, P. M., Schnitzer, M.), Interactions of Soil Minerals with Natural Organics and Microbes, SSSA Special Publication 17, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, 1986, 453–495.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Xu, H., Ji, J. et al. Formation mechanism of ferromagnetic minerals in loess of China: TEM investigation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 2260–2267 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182863
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182863