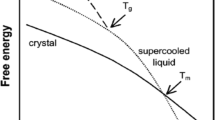
Abstract
The experimental techniques of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermally stimulated depolarization currents (TSDC) were used to study the thermal behavior of the pharmaceutical drug (±)-methocarbamol and its slow molecular mobility (in the 10−3–10−2 Hz range) in the amorphous solid state. The possibility of polymorphism was considered based on the DSC results. The glass forming ability and the glass stability were investigated by DSC, and the general kinetic features of the main relaxation, including the fragility or steepness index, were studied by both experimental techniques. The secondary relaxations detected by TSDC revealed fast and slow (Johari-Goldstein) modes. These secondary relaxations of different nature were assigned based on physical aging studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C. Hancock, G. Zografi, Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems, J. Pharm. Sci. 86, 1 (1997)
L. Yu, Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: preparation, characterization and stabilization, Adv. Drug. Delivery Rev. 48, 27 (2001)
A.M. Kaushal, P. Gupta, A.K. Bansal, Amorphous drug delivery systems: molecular aspects, design, and performance, Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug. Carrier Syst. 21, 133 (2004)
P. Karmwar, K. Graeser, K.C. Gordon, C.J. Strachan, T. Rades, Investigation of properties and recrystallisation behaviour of amorphous indomethacin samples prepared by different methods, Int. J. Pharm. 417, 94 (2011)
A.W. Lim, K. Löbmann, H. Grohganz, T. Rades, N. Chieng, Investigation of physical properties and stability of indomethacin-cimetidine and naproxen-cimetidine co-amorphous systems prepared by quench cooling, coprecipitation and ball milling, J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 68, 36 (2016)
S. Bhattacharya, R. Suryanarayanan, Local mobility in amorphous pharmaceuticals-characterization and implications on stability, J. Pharm. Sci. 98, 2935 (2009)
K. Kothari, V. Ragoonanan, R. Suryanarayanan, Influence of molecular mobility on the physical stability of amorphous pharmaceuticals in the supercooled and glassy states, Mol. Pharm. 11, 3048 (2014)
Y. Aso, S. Yoshioka, S. Kojima, Explanation of the crystallization rate of amorphous nifedipine and phenobarbital from their molecular mobility as measured by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time and the relaxation time obtained from the heating rate dependence of the glass transition temperature, J. Pharm. Sci. 90, 798 (2001)
S.P. Bhardwaj, K.K. Arora, E. Kwong, A. Templeton, S.D. Clas, R. Suryanarayanan, Correlation between molecular mobility and physical stability of amorphous itraconazole, Mol. Pharm. 10, 694 (2013)
M. Mehta, V. Ragoonanan, G.B. McKenna, R. Suryanarayanan, Correlation between Molecular Mobility and Physical Stability in Pharmaceutical Glasses, Mol. Pharm. 13, 1267 (2016)
M. Yoshioka, B.C. Hancock, G. Zografi, Crystallization of Indomethacin from the Amorphous State Below and Above Its Glass-Transition Temperature, J. Pharm. Sci. 83, 1700 (1994)
K. Grzybowska, M. Paluch, A. Grzybowski, Z. Wojnarowska, L. Hawelek, K. Kolodziejczyk, K.L. Ngai, Molecular Dynamics and Physical Stability of Amorphous Anti-Inflammatory Drug: Celecoxib, J. Phys. Chem. B. 114, 12792 (2010)
G. Van den Mooter, The use of amorphous solid dispersions: A formulation strategy to overcome poor solubility and dissolution rate, Drug. Discovery Today: Technologies 9, e79 (2012)
T. Vasconcelos, S. Marques, J. das Neves, B. Sarmento, Amorphous solid dispersions: Rational selection of a manufacturing process, Adv. Drug. Delivery Rev. 100, 85 (2016)
M.K. Riekes, A. Engelen, B. Appeltans, P. Rombaut, H.K. Stulzer, G. Van den Mooter, New Perspectives for Fixed Dose Combinations of Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds: a Case Study with Ezetimibe and Lovastatin, Pharm Res 33, 1259 (2016)
S.J. Dengale, H. Grohganz, T. Rades, K. Löbmann, Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations, Adv. Drug. Delivery Rev. 100, 116 (2016)
S. Alessi-Severini, F. Jamali, R.T. Coutts, F.M. Pasutto, Methocarbamol (Academic Press, San Diego, 1994), pp. 371–399
A.A. Bredikhin, Z.A. Bredikhina, D.V. Zakharychev, A.V. Pashagin, Chiral drugs related to guaifenesin: synthesis and phase properties of methocarbamol and mephenoxalone, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 18, 1239 (2007)
J.J. Moura Ramos, R. Taveira-Marques, H.P. Diogo, Estimation of the fragility index of indomethacin by DSC using the heating and cooling rate dependency of the glass transition, J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 1503 (2004)
H.P. Diogo, M.T. Viciosa, J.J. Moura Ramos, Thermally Stimulated Currents: principles, methods for data processing and significance of the information provided, Supplementary Data to Thermochimica Acta 623, 29 (2016)
G. Teyssedre, C. Lacabanne, Some considerations about the analysis of thermostimulated depolarization peaks, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 28, 1478 (1995)
J. van Turnhout, Thermally Stimulated Discharge of Polymer Electrets (Elsevier Sci. Pub. Co., Amsterdam, 1975)
R. Chen, Y. Kirsh, Analysis of Thermally Stimulated Processes (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1981)
J. van Turnhout, Thermally stimulated discharge of electrets, in G.M. Sessler, editor. Electrets (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1987), pp. 81–lpg215
V.M. Gun’ko, V.I. Zarko, E.V. Goncharuk, L.S. Andriyko, V.V. Turov, Y.M. Nychiporuk, R. Leboda, Skubiszewska-J. Zieba, A.L. Gabchak, V.D. Osovskii, Y.G. Ptushinskii, G.R. Yurchenko, O.A. Mishchuk, P.P. Gorbik, P. Pissis, J.P. Blitz, TSDC spectroscopy of relaxational and interfacial phenomena, Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 131, 1 (2007)
B.B. Sauer, Thermally Stimulated Currents: recent developments in characterisation and analysis of polymers, in Applications to Polymers and Plastics, edited by S.Z.D. Cheng (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2002), pp. 653–711
A. Vassilikou-Dova, I.M. Kalogeras, Dielectric analysis (DEA), in Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals and Applications, edited by J.D. Menczel, R.B. Prime, 1st edn (John Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2009), pp. 497–613
N. Boutonnet-Fagegaltier, A. Lamure, J. Menegotto, C. Lacabanne, A. Caron, H. Duplaa, M. Bauer, The use of thermally stimulated current spectroscopy in the pharmaceutical sciences, in Thermal Analysis of Pharmaceuticals, edited by D.Q.M. Craig, M. Reading (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2007), pp. 359–382
S. Baker, M.D. Antonijevic, Thermal analysis - dielectric techniques, in Solid State Characterization of Pharmaceutics, edited by R.A. Storey, I. Ymén (Wiley, Chichester, UK, 2011), pp. 187–206
M.K. Saini, S.S.N. Murthy, Study of glass transition phenomena in the supercooled liquid phase of methocarbamol, acetaminophen and mephenesin, Thermochim Acta 575, 195 (2014)
K.C. Mercado, G.A. Rodríguez, D.R. Delgado, F. Martínez, A. Romdhani, Solution thermodynamics of methocarbamol in some ethanol + water mixtures, Quím. Nova 35, 1967 (2012)
A.A. Bredikhin, A.T. Gubaidullin, Z.A. Bredikhina, D.B. Krivolapov, A.V. Pashagin, I.A. Litvinov, Absolute configuration and crystal packing for three chiral drugs prone to spontaneous resolution: Guaifenesin, methocarbamol and mephenesin, J. Molec. Struct. 920, 377 (2009)
J.J. Moura Ramos, H.P. Diogo, M.H. Godinho, C. Cruz, K. Merkel, Anomalous thermal behavior of salicylsalicylic acid and evidence for a monotropic transition to a nematic phase, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 7955 (2004)
R. Svoboda, J. Málek Description of enthalpy relaxation dynamics in terms of TNM model, J. Non-Cryst Solids 378, 186 (2013)
R. Svoboda, How to determine activation energy of glass transition, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 118, 1721 (2014)
C.T. Moynihan, A.J. Easteal, J. Wilder, J. Tucker, Dependence of the glass transition temperature on heating and cooling rate, J. Phys. Chem. 78, 2673 (1974)
C.A. Angell, Relaxation in liquids, polymers and plastic crystals – strong/fragile patterns and problems, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 131–133, 13 (1991)
R. Böhmer, C.A. Angell, Local and global relaxations in glass-forming materials, in Disorder Effects on Relaxational Processes, edited by R. Richert, A. Blumen (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1994), pp. 11–54
L.M. Wang, C.A. Angell, Response to Comment on Direct determination of the fragility indices of glassforming liquids by differential scanning calorimetry: Kinetic versus thermodynamic fragilities, J. Chem. Phys. 118, 10351 (2003)
L.M. Wang, C.A. Angell, R. Richert, Fragility and thermodynamics in nonpolymeric glass-forming liquids, J. Chem. Phys. 125, 074505 (2006)
X. Xia, P.G. Wolynes, Fragilities of liquids predicted from the random first order transition theory of glasses, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2990 (2000)
N.T. Correia, C. Alvarez, J.J. Moura Ramos, Fragility in side-chain liquid crystalline polymers: the TSDC contribution, Polymer 41, 8625 (2000)
N.T. Correia, C. Alvarez, J.J. Moura Ramos, M. Descamps, Molecular motions in molecular glasses as studied by thermally stimulated depolarisation currents (TSDC), Chem. Phys. 252, 151 (2000)
J.J. Moura Ramos, N.T. Correia, The Deborah number, relaxation phenomena and thermally stimulated currents, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3, 5575 (2001)
H.W. Starkweather, Simple and complex relaxations, Macromolecules 14, 1277 (1981)
H.W. Starkweather, Noncooperative relaxations, Macromolecules 21, 1798 (1988)
H.W. Starkweather, Aspects of simple, non-cooperative relaxations, Polymer 32, 2443 (1991)
N.T. Correia, J.J. Moura Ramos, On the cooperativity of the β-relaxation: A discussion based on dielectric relaxation and thermally stimulated depolarisation currents data, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 5712 (2000)
J.J. Moura Ramos, H.P. Diogo, S.S. Pinto Local motions in L-iditol glass: identifying different types of secondary relaxations, Thermochim. Acta 467, 107 (2008)
S.S. Pinto, J.J. Moura Ramos, H.P. Diogo, The slow molecular mobility in poly(vinyl acetate) revisited: new contributions from Thermally Stimulated Currents, Eur. Polym. J. 45, 2644 (2009)
E. Mora, H.P. Diogo, J.J. Moura Ramos, The slow molecular dynamics in amorphous probucol, Thermochim. Acta 595, 83 (2014)
H.P. Diogo, J.J. Moura Ramos, Contribution of the technique of thermostimulated currents for the elucidation of the nature of the Johari-Goldstein and other secondary relaxations in the vitreous state, IEEE Trans. Dielect. Elect. Insul. 21, 2301 (2014)
M. Paluch, C.M. Roland, S. Pawlus, J. Ziolo, K.L. Ngai, Does the Arrhenius temperature dependence of the Johari-Goldstein relaxation persist above T(g)? Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 115701 (2003)
K.L. Ngai, Relaxation and diffusion in complex systems (Springer, New York, 2011)
K.L. Ngai, An extended coupling model description of the evolution of dynamics with time in supercooled liquids and ionic conductors, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15, S1107 (2003)
S. Capaccioli, K.L. Ngai, Relation between the alpha-relaxation and Johari-Goldstein beta-relaxation of a component in binary miscible mixtures of glass-formers, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 9727 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moura Ramos, J.J., Diogo, H.P. Study of the molecular mobility of (±)-methocarbamol in the amorphous solid state. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 226, 889–904 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2016-60233-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2016-60233-y