Abstract
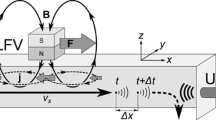
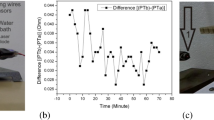
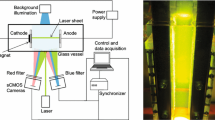
Magnetic fields are applied to electrically conducting fluids in order to influence electrochemical processes through the magnetohydrodynamic effect. Various phenomena, e.g. on electrodeposited metal layers, which can be attributed to forced convections were observed. To provide information about acting forces, the laser Doppler velocity profile sensor was applied to measure the transition layer of a Lorentz force influenced flow over a backward-facing step and the velocity boundary layer during copper deposition. With this sensor, the electrolyte convection within < 500 μm of the front of an electrode is measured with a spatial resolution down to 15 μm. The interaction of buoyancy, Lorentz and magnetic field gradient forces is studied by measuring the velocities down to 10 μm in front of the cathode. Inside the concentration boundary layer, complex electrolyte convection is induced, which varies not only in time but also in its structure, depending on the forces present and their influence over time. In inhomogeneous magnetic field configurations, the magnetic field gradient force dominates the velocity boundary layer at steady state and transports electrolyte toward regions of high magnetic gradients, where maximum deposit thicknesses are found. In this way, the measurements confirm the predicted influence of the magnetic field gradient force on the structuring of copper deposits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Albrecht, R. Grundmann, G. Mutschke, G. Gerbeth, Phys. Fluids 18, 4 (2006)
T. Weier, S. Wittwer, T. Albrecht, G. Gerbeth, in Proceedings of the 82nd annual GAMM meeting, Graz (2011)
G. Hinds, F.E. Spada, J.M.D. Coey, et al., J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 9487 (2001)
X. Yang, K. Eckert, S. Mühlenhoff, S. Odenbach, Electrochim. Acta 54, 7056 (2009)
X. Yang, K. Eckert, K. Seidel, M. Uhlemann, Electrochim. Acta 54, 352 (2008)
K. Tschulik, J.A. Koza, M. Uhlemann, A. Gebert, L. Schultz, Electrochem. Commun. 11, 2241 (2009)
K. Tschulik, C. Cierpka, G. Mutschke, A. Gebert, L. Schultz, M. Uhlemann, Anal. Chem. 84, 2328 (2012)
R. Sueptitz, K. Tschulik, M. Uhlemann, A. Gebert, L. Schultz, Electrochim. Acta 55, 5200 (2010)
J.A. Koza, S. Mühlenhoff, M. Uhlemann, K. Eckert, A. Gebert, L. Schultz, Electrochem. Commun. 11, 435 (2009)
K. Tschulik, R. Sueptitz, M. Uhlemann, L. Schultz, A. Gebert, Electrochim. Acta 56, 5174 (2011)
M.C. Weston, M.D. Gerner, I. Fritsch, Anal. Chem. 82, 3411 (2010)
N. Leventis, X. Gao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 1079 (2002)
T. Weier, K. Eckert, S. Mühlenhoff, C. Cierpka, A. Bund, M. Uhlemann, Electrochem. Commun. 9, 2479 (2007)
T. Weier, C. Cierpka, J. Hüller, G. Gerbeth, Magnetohydrodynamics 42, 379 (2006)
H. Li, M. Olsen, Heat Fluid Flow 27, 123 (2006)
J. Westerweel, Exp. Fluids 44, 831 (2008)
J. Czarske, L. Büttner, T. Razik, H. Müller, Meas. Sci. Technol. 13, 1979 (2002)
M. Neumann, L. Büttner, T. Weier, J. Czarske, PAMM 12, 663 (2011)
J. König, A. Voigt, L. Büttner, J. Czarske, Meas. Sci. Technol. 21, 074005 (2010)
J. König, L. Büttner, J. Czarske, S. Mühlenhoff, K. Eckert, Int. J. Microsc. Nanosc. Thermal Fluid Transp. Phenom. 3, 5 (2012)
B.F. Armaly, F. Durst, J.C.F. Peireira, B. Schönung, J. Fluid Mech. 127, 473 (1983)
J. Le, P. Moin, J. Kim, J. Fluid Mech. 330, 349 (1997)
J. Stiller, H. Metzkes, T. Albrecht, T. Weier, G. Gerbeth, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 220, 275 (2013)
K. Tschulik, C. Cierpka, A. Gebert, L. Schultz, C. Kähler, M. Uhlemann, Anal. Chem. 83, 3275 (2011)
T.Z. Fahidy, J. Appl. Electrochem. 13, 553 (1983)
R.A. Tacken, L.J.J. Janssen, J. Appl. Electrochem. 25, 1 (1995)
T.Z. Fahidy, Z. Thomas, Prog. Surf. Sci. 68, 155 (2001)
J. König, S. Mühlenhoff, K. Eckert, L. Büttner, S. Odenbach, J. Czarske, Electrochim. Acta 56, 6150 (2011)
N. Ibl, R. Müller, J. Electrochem. Soc. 105, 346 (1958)
P. Dunne, L. Mazza, J.M.D. Coey, Phys. Rev. Letters 107, 024501/1-4 (2011)
G. Mutschke, K. Tschulik, T. Weier, M. Uhlemann, A. Bund, J. Fröhlich, Electrochim. Acta 55, 9060 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
König, J., Neumann, M., Mühlenhoff, S. et al. Optical velocity measurements of electrolytic boundary layer flows influenced by magnetic fields. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 220, 79–89 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01798-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01798-x