Abstract
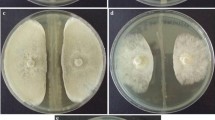
In the present study, a new strain of Bacillus stratosphericus LW-03 was isolated from the bulbs of Lilium wardii. The isolated endophytic strain LW-03 exhibited excellent antifungal activity against common plant pathogens, such as Fusarium oxysporum, Botryosphaeria dothidea, Botrytis cinerea, and Fusarium fujikuroi. The growth inhibition percentage of Botryosphaeria dothidea was 74.56 ± 2.35%, which was the highest, followed by Botrytis cinerea, Fusarium fujikuroi, and Fusarium oxysporum were 71.91 ± 2.87%, 69.54 ± 2.73%, and 65.13 ± 1.91%, respectively. The ethyl acetate fraction revealed a number of bioactive compounds and several of which were putatively identified as antimicrobial agents, such as 4-hydroxy-2-nonenylquinoline N-oxide, sphingosine ceramides like cer(d18:0/16:0(2OH)), cer(d18:0/16:0), and cer(d18:1/0:0), di-peptides, tri-peptide, cyclopeptides [cyclo(D-Trp-L-Pro)], [cyclo (Pro-Phe)], dehydroabietylamine, oxazepam, 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine like compound (PC(0:0/20:4), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE(18:1/0:0)), 3-Hydroxyoctadecanoic acid, 7.alpha.,27-Dihydroxycholesterol, N-Acetyl-d-mannosamine, p-Hydroxyphenyllactic acid, Phytomonic acid, and 2-undecenyl-quinoloin-4 (1H). The LW-03 strain exhibits multiple plant growth-promoting traits, including the production of organic acids, ACC deaminase, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), siderophores, and nitrogen fixation activity. The beneficial effects of the endophytic strain LW-03 on the growth of two lily varieties were further evaluated under greenhouse conditions. Our results revealed plant growth-promoting activity in inoculated plants relative to non-inoculated control plants. The broad-spectrum antifungal activity and multiple plant growth-promoting properties of Bacillus stratosphericus LW-03 make it an important player in the development of biological fertilizers and sustainable agricultural biological control strategies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles FB, Morgan PW, Saltveit ME Jr (1992) Ethylene in plant biology, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-03226-7
Akinrinlola RJ, Yuen GY, Drijber RA, Adesemoye AO (2018) Evaluation of bacillus strains for plant growth promotion and predictability of efficacy by in vitro physiological traits. Int J Microbiol 2018:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5686874
Asiri IAM, Badr JM, Youssef DTA (2015) Penicillivinacine, antimigratory diketopiperazine alkaloid from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium vinaceum. Phytochem Lett 13:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2015.05.014
Backer R, Rokem JS, Ilangumaran G, Lamont J, Praslickova D, Ricci E, Subramanian S, Smith DL (2018) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: context, mechanisms of action, and roadmap to commercialization of biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front Plant Sci 9:1473. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01473
Bashan Y, Holguin G, Lifshitz R (1993) Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Glick BR, Thompson JE (eds) Methods in plant molecular biology and biotechnology. CRC Press, BocaRaton, pp 331–345
Becam J, Walter T, Burgert A, Schlegel J, Sauer M, Seibel J, Schubert-Unkmeir A (2017) Antibacterial activity of ceramide and ceramide analogs against pathogenic Neisseria. Sci Rep 7:17627. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18071-w
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.033
Beneduzi A, Ambrosini A, Passaglia LMP (2012) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): their potential as antagonists and biocontrol agents. Genet Mol Biol 35:1044–1051
Borriss R (2011) "Use of plant-associated Bacillus strains as biofertilizers and biocontrol agents”,in Bacteria in Agrobiology. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Plant Growth Responses. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 41–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20332-9_3
Chambers MC, Maclean B, Burke R, Amodei D, Ruderman DL, Neumann S, Gatto L, Fischer B, Pratt B, Egertson J (2012) A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat Biotechnol 30:918. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2377
Chau CF, Wu SH (2006) The development of regulations of Chinese herbal medicines for both medicinal and food uses. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12.005
Chowdhury SP, Dietel K, Rändler M, Schmid M, Junge H, Borriss R et al (2013) Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 on lettuce growth and health under pathogen pressure and its impact on the rhizosphere bacterial community. PLoS ONE 8:e68818. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068818
Cunningham JE, Kuiack C (1992) Production of citric and oxalic acids and solubilization of calcium-phosphate by Penicillium bilaii. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1451–1458
de Werra P, Péchy-Tarr M, Keel C, Maurhofer M (2009) Role of Gluconic Acid Production in the Regulation of Biocontrol Traits of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Appl Environ Microbiol 4162–4174. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00295-09
Doebereiner J (1994) Isolation and identification of aerobic nitrogen fixing bacteria. Alef K, Nannipieri P(eds) Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic, Cambridge, pp 134–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02738.x
Durairaj K, Velmurugan P, Park JH et al (2018) Characterization and assessment of two biocontrol bacteria against Pseudomonas syringae wilt in Solanum lycopersicum and its genetic responses. Microbiol Res 206:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.09.003
Durairaj K, Velmurugan P, Park JH, Chang WS, Park YJ, Senthilkumar P, Choi KM, Lee JH, Oh BT (2017) Potential for plant biocontrol activity of isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus stratosphericus strains against bacterial pathogens acting through both induced plant resistance and direct antagonism. FEMS Microbiol Lett 364(23):fnx225. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnx225
Fan B, Wang C, Song X, Ding X, Wu L, Wu H, Gao X, Borriss R (2018) Bacillus velezensis FZB42 in 2018: the gram-positive model strain for plant growth promotion and biocontrol. Front Microbiol 9:2491. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02491
Ferreira CMH, Vilas-Boas A, Sousa CA, Soares HMVM, Soares EV (2019) Comparison of five bacterial strains producing siderophores with ability to chelate iron under alkaline conditions. AMB Express 9:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0796-3
Gill SS, Gill R, Trivedi DK et al (2016) Piriformospora indica: potential and significance in plant stress tolerance. Front Microbiol 7:332
Glick BR, Cheng Z, Czarny J, Duan J (2007) Promotion of plant growth by ACC deaminase-producing soil bacteria. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9162-4
Glick BR (2014) Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol Res 169:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.09.009
Gordon SA, Weber RP (1951) Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiol 26:192–195. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.26.1.192
Hashem A, Tabassum B, Abd Allah EF (2019) Bacillus subtilis: a plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:1291–1297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.05.004
Horst RK (2013) Field manual of diseases on fruits and vegetables. Springer Science+Business Media, Dordrecht
Idris EE, Iglesias DJ, Talon M, Borriss R (2007) Tryptophan-dependent production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) affects level of plant growth promotion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-6-0619
Junior AFC, Oliveira AGD, Oliveira LAD, Santos GRD, Costa JDL (2015) Production of indole-3-acetic acid by bacillus isolated from different soils. Bulg J Agric Sci 21:282–287
Kesaulya H, Hasinu JV, Tuhumury GNC (2018) Potential of Bacillus spp produces siderophores in suppressing the wilt disease of banana plants. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 102(1):012016. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/102/1/012016
Khamna S, Yokota A, Lumyong S (2009) Actinomycetes isolated from medicinal plant rhizospheric soils: diversity and screening of antifungal compounds, indole-3-acetic acid and siderophore production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:649–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9933-x
Kim YC, Leveau J, Mcspadden Gardener BB, Pierson EA, Pierson LS, Ryu CM (2011) The multifactorial basis for plant health promotion by plant-associated bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1548–1555. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01867-10
Kloepper JW, Leong J, Teintze M, Schroth MN (1980) Enhancing plant growth by siderophores produced by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Nature 286:885–886
Kumar VS, Menon S, Agarwal H, Gopalakrishnan D (2017) Characterization and optimization of bacterium isolated from soil samples for the production of siderophores. Resource Efficient Technol 3:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.04.004
Kumar S, Malik A, Dahiya DS, Kaur M (2018) Appraisal of Asiatic hybrid Lilium cultivars under polyhouse growing condition in semi0arid Haryana, India. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7:3389–3394. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.398
Lee S, Oh DG, Lee S, Kim G, Lee J, Son Y, Bae CH, Yeo J, Lee C (2015) Chemotaxonomic metabolite profiling of 62 indigenous plant species and its correlation with bioactivities. Molecules 20:19719–19734. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201119652
Lopes R, Tsui S, Gonçalves PJRO, de Queiroz MV (2018) A look into a multifunctional toolbox: endophytic Bacillus species provide broad and underexploited benefits for plants. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2479-7
Martínez-Luis S, Ballesteros J, Gutiérrez M (2011) Antibacterial constituents from the octocoral-associated bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. Revista Latinoamericana Química 39:75–83
Mbarki S, Cerda A, Brestic M et al (2016) Vineyard compost supplemented with Trichoderma harzianum t78 improve saline soil quality. Land Degrad Develp. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2554
Mehta S, Nautiyal CS (2001) An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Curr Microbiol 43:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010259
Meng Q, Jiang H, Hao JJ (2016) Effects of Bacillus velezensis strain BAC03 in promoting plant growth. Biol Cont 98:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.03.010
Nishanth Kumar S, Mohandas C, Siji J, Rajasekharan K, Nambisan B (2012) Identification of antimicrobial compound, diketopiperazines, from a Bacillus sp. N strain associated with a rhabditid entomopathogenic nematode against major plant pathogenic fungi. J Appl Microbiol 113:914–924. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05385.x
Ongena M, Jacques P (2008) Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol 16:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2007.12.009
Perez-Garcia A, Romero D, de Vicente A (2011) Plant protection and growth stimulation by microorganisms: biotechnological applications of Bacilli in agriculture. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2010
Porwal S, Lal S, Cheema S, Kalia VC (2009) Phylogeny in aid of the present and novel microbial lineages: diversity in Bacillus. 2009. PLoS ONE 4(2):e4438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004438
Rathod DP, Brestic M, Shao HB (2011) Chlorophyll a fluorescence determines the drought resistance capabilities in two varieties of mycorrhized and non-mycorrhized Glycine max Linn. Afr J Microbiol Res 5:4197–4206
Revilla-Nuin B, Reglero A, Martínez-Blanco H, Bravo IG, Ferrero MA, Rodríguez-Aparicio LB (2002) Transport of N-acetyl-d-mannosamine and N-acetyl- d -glucosamine in Escherichia coli K1: effect on capsular polysialic acid production. FEBS Lett 30:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03318-x
Romero D, Perez-Garcia A, Rivera ME, Cazorla FM, de Vicente A (2004) Isolation and evaluation of antagonistic bacteria towards the cucurbit powdery mildew fungus Podosphaera fusca. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:263–269
Rong LP, Lei JJ, Wang C (2011) Collection and evaluation of the genus Lilium resources in Northeast China. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-010-9584-2
Salehi P, Ayyari M, Bararjanian M, Ebrahimi SN, Aliahmadi A (2014) Synthesis, antibacterial and antioxidant activity of novel 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one derivatives of dehydroabietylamine diterpene. J Iran Chem Soc 11:607–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-013-0330-5
Sana S, Datta S, Biswas D, Sengupta D (2018) Assessment of synergistic antibacterial activity of combined biosurfactants revealed by bacterial cell envelop damage. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1860:579–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem
Schulz B, Boyle C, Draeger S, Rommert AK, Krohn K (2002) Endophytic fungi: a source of novel biologically active secondary metabolites. Mycol Res 106:996–1004. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756202006342
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Shafi J, Tian H, Ji M (2017) Bacillus species as versatile weapons for plant pathogens: a review. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 31:446–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2017.1286950
Sharma R, Kumar R, Dahiya DS (2018) Studies on the performance of lilium varieties under polyhouse. J Pharma Phytochem 7:2711–2713
Shen FT, Yen JH, Liao CS, Chen WC, Chao YT (2019) Screening of rice endophytic biofertilizers with fungicide tolerance and plant growth-promoting characteristics. Sustainability 11:1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041133
Sjögren J, Magnusson J, Broberg A, Schnürer J, Kenne L (2003) Antifungal 3-Hydroxy Fatty Acids from Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 14. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7554–7557. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.12.7554-7557.2003
Smirnova TA, Zubasheva MV, Shevlyagina NV, Nikolaenko MA, Azizbekyan RR (2013) Electron microscopy of the surfaces of Bacillus spores. Microbiol 82:701–708
Song J (2017) The relationship of root system with the growth and development of bulbs and shoots in lilies. Hort Sci 52:245–250
Strobel GA, Sears J, Kramer R, Sidhu RS, Hess WM (1996) Taxol from Pestalotiopsis microspora an endophytic fungus of Taxus wallichiana. Microbiology 142:435–440. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-142-2-435
Syed-Ab-Rahman SF, Carvalhais LC, Chua E, Xiao Y, Wass TJ, Schenk PM (2018) Identification of soil bacterial isolates suppressing different Phytophthora spp. and promoting plant growth. Front Plant Sci 9:1502. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01502
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tan RX, Zou WX (2001) Endophytes: a rich source of functional metabolites. Nat Prod Rep 18:448–459. https://doi.org/10.1039/B100918O
Truyens S, Jambon I, Croes S, Janssen J, Weyens N, Mench M, Carleer R, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J (2014) The effect of long-term cd and ni exposure on seed endophytes of Agrostis capillaris and their potential application in phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils. Int J Phytorem 16:643–659. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2013.837027
Vial L, Lépine F, Milot S, Groleau MC, Dekimpe V, Woods DE et al (2008) Burkholderia pseudomallei, B. thailandensis, and B. ambifaria produce 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinoline analogues with a methyl group at the 3 position that is required for quorum-sensing regulation. J Bacteriol 190:5339–5352. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00400-08
Vincent JM, Humphrey B (1970) Taxonomically significant group antigens in Rhizobium. J Gen Microbiol 63:379–382. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-63-3-379
Wang XM, Bai YJ, Cai YJ, Zheng XH (2017) Biochemical characteristics of three feruloyl esterases with a broad substrate spectrum from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H47. Process Biochem 53:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.12.012
Wang J, Liu J, Chen H, Yao J (2007) Characterization of Fusarium graminearum inhibitory lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis IB. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:889–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1054-1
Wang M, Carver JJ, Phelan VV, Sanchez LM, Garg N, Peng Y, Nguyen DD, Watrous J, Kapono CA, Luzzatto-Knaan T (2016) Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with global natural products social molecular networking. Nat Biotechnol 34:828. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3597
Wu L, Wang J, Huang W et al (2015) Plant-microbe rhizosphere interactions mediated by Rehmannia glutinosa root exudates under consecutive monoculture. Sci Rep 5:15871. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15871
Xu M, Sheng J, Chen L, Men Y, Gan L, Guo S, Shen L (2014) Bacterial community compositions of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) seeds and plant growth promoting activity of ACC deaminase producing Bacillus subtilis (HYT-12–1) on tomato seedlings. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:835–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1486-y
You X, Xie C, Liu K, Gu Z (2010) Isolation of non-starch polysaccharides from bulb of tiger lily (Lilium lancifolium Thunb) with fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Carbohydr Polym 81:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.051
Zhang Y, Gao X, Wang S et al (2018) Application of Bacillus velezensis NJAU-Z9 enhanced plant growth associated with efficient rhizospheric colonization monitored by qPCR with primers designed from the whole genome sequence. Curr Microbiol 75:1574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1563-4
Zhao L, Xu Y, Sun R, Deng Z, Yang W, Wei G (2011) Identification and characterization of the endophytic plant growth prompter Bacillus Cereus strain mq23 isolated from Sophora alopecuroides root nodules. Braz J Microbiol 42:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838220110002000022
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China [2017YFD0501005]; Science and Technology Innovation Ability Construction of Beijing Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences (KJCX20170415).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MSK conducted the research, analyzed data, and prepared the manuscript. JG provided the pathogenic fungal strains. MZ and XC provided technical support in experimentation. TSM analyzed the LC/MS data. YD and FY assisted in greenhouse experiment. JX and XZ supervised the research and provided financial assistance. All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.S., Gao, J., Zhang, M. et al. Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria Bacillus stratosphericus LW-03 from Lilium wardii. 3 Biotech 10, 305 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02294-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02294-2