Abstract
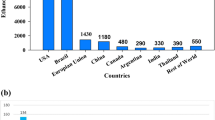
Cotton based textile industries are one of the major source of revenue to the Indian economy. India contributes around 30 % of world’s total cotton cultivation every year. Cotton accounts for more than 70 % of total textile production in the country. Cotton is subjected to various processes to produce cotton based textile apparels. During the processing of cotton, more amount of cotton-based wastes are generated and they are landfilled or incinerated, in general. Cotton textile industries are facing critical problems on solid-waste management, which results in environmental pollution and health hazards. These wastes comprise lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose, which can be utilized as sustainable feedstock for the production of bioethanol. Cotton based lignocellulosic biomass requires specific pretreatment strategy to efficiently remove lignin and to solubilize hemicellulose, which increases the accessibility of hydrolytic enzymes during saccharification. Till date, various pretreatment technologies such as physical, physico-chemical, acid/alkali-, ionic liquids (ILs) and biological treatment methods are widely evaluated for lignin removal, hemicellulose solubilization and cellulose crystallinity reduction in cotton wastes to enhance the enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation process. This paper reviews about different pretreatment methods implemented and its significance for the conversion of cotton wastes to bioethanol.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ethanol India-Information and useful links. http://www.ethanolindia.net/ (2015). Accessed 23 April 2015
Kumar, D., Murthy, G.S.: Impact of pretreatment and downstream processing technologies on economics and energy in cellulosic ethanol production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 4, 27 (2011)
Chavan, R.B.: Indian textile industry-Environmental issues. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 26, 11–21 (2001)
Babu, B.R., Parande, A.K., Raghu, S., Kumar, T.P.: Textile technology cotton textile processing: waste generation and effluent treatment. J. Cotton Sci. 11, 141–153 (2007)
Goswami, B.C., Martindale, J.G., Scardino, F.L.: Textile Yarns Technology, Structure, and Applications. Wiley Interscience Publication, New York (1995)
Placido, J., Imam, T., Capareda, S.: Evaluation of ligninolytic enzymes, ultrasonication and liquid hot water as pretreatments for bioethanol production from cotton gin trash. Bioresour. Technol. 139, 203–208 (2013)
Menon, V., Rao, M.: Trends in bioconversion of lignocellulose: biofuels, platform chemicals & biorefinery concept. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 38, 522–550 (2012)
Mosier, N., Wyman, C., Dale, B., Elander, R., Lee, Y.Y., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M.: Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 673–686 (2005)
Shi, J., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R., Chinn, M.S.: Microbial pretreatment of cotton stalks by submerged cultivation of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 4388–4395 (2009)
Agblevor, F.A., Batz, S., Trumbo, J.: Composition and ethanol production potential of cotton gin residues. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 105, 219–230 (2003)
Jeihanipour, A., Taherzadeh, M.J.: Ethanol production from cotton-based waste textiles. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 1007–1010 (2009)
Sharma-Shivappa, R.R., Chen, Y.: Conversion of cotton wastes to bioenergy and value-added products. Trans. ASABE 51, 2239–2246 (2008)
Reddy, N., Yang, Y.: Properties and potential applications of natural cellulose fibers from the bark of cotton stalks. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 3563–3569 (2009)
Shen, J., Agblevor, F.A.: Ethanol production of semi-continuous saccharification and fermentation from mixture of cotton gin waste and recycled paper sludge. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 34, 33–43 (2011)
Chen, J., Guo, J.: Improving the conversion efficiency of waste cotton to bioethanol by microwave hydrolysis technology. Sustain. Environ. Res. 23, 333–339 (2013)
Safartalab, K., Dadashian, F., Vahabzadeh, F.: Fed batch enzymatic hydrolysis of cotton and viscose waste fibers to produce ethanol. Univers. J. Chem. 2, 11–15 (2014)
Agblevor, F.A., Ibrahim, M.M., El-Zawawy, W.K.: Coupled acid and enzyme mediated production of microcrystalline cellulose from corn cob and cotton gin waste. Cellulose 14, 247–256 (2007)
Arthe, R., Rajesh, R., Rajesh, E.M., Rajendran, R., Jeyachandran, S.: Production of bio-ethanol from cellulosic cotton waste through microbial extracellular enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 7, 2984–2992 (2008)
Jeihanipour, A., Karimi, K., Taherzadeh, M.J.: Enhancement of ethanol and biogas production from high-crystalline cellulose by different modes of NMO pretreatment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 105, 469–476 (2010)
Mahalakshmi, M., Angayarkanni, J., Rajendran, R., Rajesh, R.: Bioconversion of cotton waste from textile mills to bioethanol by microbial saccharification and fermentation. Ann. Biol. Res. 2, 380–388 (2011)
Wu, M., Zhao, D., Pang, J., Zhang, X., Li, M., Xu, F., Sun, R.: Separation and characterization of lignin obtained by catalytic hydrothermal pretreatment of cotton stalk. Ind. Crops Prod. 66, 123–130 (2015)
Hu, X., Hsieh, Y.: Crystalline structure of developing cotton fibers. J. Polym. Sci., Part B Polym. Phys. 34, 1451–1459 (1996)
Chornet, E., Overend, R.P.: Phenomenological kinetics and reaction engineering aspects of steam/aqueous treatments. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Steam Explosion Techniques: Fundamentals and Industrial Applications, Philadelphia, pp. 21–58 (1991)
Brodeur, G., Yau, E., Badal, K., Collier, J., Ramachandran, K.B., Ramakrishnan, S.: Chemical and physicochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Enzyme Res. 2011, 1–17 (2011)
Joeh, T., Agblevor, F.A.: Characterization and fermentation of steam exploded cotton gin waste. Biomass Bioenergy 21, 109–120 (2001)
Joeh, T.: Steam Explosion Pretreatment of Cotton Gin Waste for Fuel Ethanol Production. MSc Thesis Blacksburg, Virginia (1998)
Agblevor, F.A., Cundiff, J.S., Mingle, C., Li, W.: Storage and characterization of cotton gin waste for ethanol production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 46, 198–216 (2006)
Vani, S., Binod, P., Kuttiraja, M., Sindhu, R., Sandhya, S.V., Preeti, V.E., Sukumaran, R.K., Pandey, A.: Energy requirement for alkali assisted microwave and high pressure reactor pretreatments of cotton plant residue and hydrolysis for fermentable sugar production for biofuel application. Bioresour. Technol. 112, 300–307 (2012)
Binod, P., Satyanagalakshmi, K., Sindhu, R., Janu, K.U., Sukumaran, R.K., Pandey, A.: Short duration microwave assisted pretreatment enhances the enzymatic saccharification and fermentable sugar yield from sugarcane bagasse. Renew. Energ. 37, 109–116 (2012)
Hermiati, E., Azuma, J., Tsubaki, S., Mangunwidjaja, D., Sunarti, T.C., Suparno, O., Prasetya, B.: Improvement of microwave-assisted hydrolysis of cassava pulp and tapioca flour by addition of activated carbon. Carbohyd. Polym. 87, 939–942 (2012)
Ooshima, H., Aso, K., Harano, Y.: Microwave treatment of cellulosic materials for their enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Lett. 6, 289–294 (1984)
Chen, W., Ye, S., Sheen, H.: Hydrolysis characteristics of sugarcane bagasse pretreated by dilute acid solution in a microwave irradiation environment. Appl. Energy 93, 237–244 (2012)
Du, S., Zhu, X., Wang, H., Zhou, D., Yang, W., Xu, H.: High pressure assist-alkali pretreatment of cotton stalk and physiochemical characterization of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 148, 494–500 (2013)
Nitsos, C.K., Matis, K.A., Triantafyllidis, K.S.: Optimization of hydrothermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass in the bioethanol production process. Chem. Sus. Chem. 6, 110–122 (2013)
Lu, F.C., Ralph, J.: Solution-state NMR of lignocellulosic biomass. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 5, 169–180 (2011)
Wyman, C.E., Dale, B.E., Elander, R.T., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M.R., Lee, Y.Y.: Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 1959–1966 (2005)
Dogaris, I., Karapati, S., Mamma, D., Kalogeris, E., Kekos, D.: Hydrothermal processing and enzymatic hydrolysis of sorghum bagasse for fermentable carbohydrates production. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 6543–6549 (2009)
Yu, G., Yano, S., Inoue, H., Inoue, S., Endo, T., Sawayama, S.: Pretreatment of rice straw by a hot-compressed water process for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 160, 539–551 (2010)
Hansen, M.A., Kristensen, J.B., Felby, C., Jørgensen, H.: Pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw (Triticum aestivum L)—the impact of lignin relocation and plant tissues on enzymatic accessibility. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 2804–2811 (2011)
Kumar, S., Kothari, U., Kong, L.Z., Lee, Y.Y., Gupta, R.B.: Hydrothermal pretreatment of switchgrass and corn stover for production of ethanol and carbon microspheres. Biomass Bioenergy 35, 956–968 (2011)
Torget, R., Walter, P., Himmel, M., Grohmann, K.: Dilute acid pretreatment of corn residues and short-rotation woody crops. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 28–29, 75–86 (1991)
Karimi, K.: Lignocellulose-based bioproducts: Biofuel and Biorefinery Technologies. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland (2015)
Silverstein, R.A., Chen, Y., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R., Boyette, M.D., Osborne, J.: A comparison of chemical pretreatment methods for improving saccharification of cotton stalks. Biorsour. Technol. 98, 3000–3011 (2007)
Imamoglu, E., Sukan, F.V.: The effects of single and combined cellulosic agrowaste substrates on bioethanol production. Fuel 134, 477–484 (2014)
Akpinar, O., Levent, O., Bostanci, S., Bakir, U., Yilmaz, L.: The optimization of dilute acid hydrolysis of cotton stalk in xylose production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 163, 313–325 (2011)
Weil, J.R., Dien, B., Bothast, R., Hendrickson, R., Mosier, N.S., Ladisch, M.R.: Removal of fermentation inhibitors formed during pretreatment of biomass by polymeric adsorbents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 41, 6132–6138 (2002)
Sandhya, S.V., Kiran, K., Kuttiraja, M., Preeti, V.E., Sindhu, R., Vani, S., Kumar, S.R., Pandey, A., Binod, P.: Evaluation of polymeric adsorbent resins for efficient detoxification of liquor generated during acid pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 51, 1012–1017 (2013)
Tarkov, H., Feist, W.C.: A mechanism for improving the digestibility of lignocellulosic materials with dilute alkali and liquid ammonia. In: Gould, R.F. (ed.) Cellulases and their Applications, pp. 197–218. American Chemical Society, Washington (1969)
Fernandes, T.V., Bos, G.J.K., Zeeman, G., Sanders, J.P.M., Van-Lier, J.B.: Effects of thermo-chemical pre-treatment on anaerobic biodegradability and hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 2575–2579 (2009)
Kim, S., Holtzapple, M.T.: Lime pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 1994–2006 (2005)
Kaur, U., Oberoi, H.S., Bhargav, V.K., Sharma-Shivappa, R., Dhaliwal, S.S.: Ethanol production from alkali- and ozone-treated cotton stalks using thermotolerant Pichia kudriavzevii HOP-1. Ind. Crops Prod. 37, 219–226 (2012)
Liu, C., Wang, F., Stiles, A.R., Guo, C.: Ionic liquids for biofuel production: opportunities and challenges. Appl. Energy 92, 406–414 (2012)
Zhao, H., Jones, C.L., Baker, G.A., Xia, S., Olubajo, O., Person, V.N.: Regenerating cellulose from ionic liquids for an accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Biotechnol. 139, 47–54 (2009)
Haykir, N.I., Bahcegul, E., Bicak, N., Bakir, U.: Pretreatment of cotton stalk with ionic liquids including 2-hydroxy ethyl ammonium formate to enhance biomass digestibility. Ind. Crops Prod. 41, 430–436 (2013)
López-Abelairas, M., Lu-Chau, T.A., Lema, J.M.: Enhanced saccharification of biologically pretreated wheat straw for ethanol production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 169, 1147–1159 (2013)
Ravikumar, R., Ranganathan, B.V., Chathoth, K.N., Gobikrishnan, S.: Innovative and intensified technology for the biological pretreatment of agro waste for ethanol production. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30, 1051–1057 (2013)
Zhang, J., Ren, X., Chen, W., Bao, J.: Biological pretreatment of corn stover by solid state fermentation of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 6, 146–151 (2012)
Pena, R., Lu-Chau, T.A., Lema, J.M.: Use of white-rot fungi for valorization of stillage from bioethanol production. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 3, 295–303 (2012)
Thakur, S., Shrivastava, B., Ingale, S., Kuhad, R.C., Gupte, A.: Degradation and selective ligninolysis of wheat straw and banana stem for an efficient bioethanol production using fungal and chemical pretreatment. 3 Biotech 3, 365–372 (2013)
Deswal, D., Gupta, R., Nandal, P., Kuhad, R.C.: Fungal pretreatment improves amenability of lignocellulosic material for its saccharification to sugars. Carbohyd. Polym. 99, 264–269 (2014)
Gnanambal, V.S., Jabastin, J., Swaminathan, K.: Biological pretreatment of six lignocellulosic wastes for bioethanol production. Int. J. Sci. Res. 3, 1860–1864 (2014)
Xu, C., Ma, F., Zhang, X., Chen, S.: Biological Pretreatment of Corn Stover by Irpex lacteus for Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 10893–10898 (2010)
Shi, J., Chinn, M.S., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R.: Microbial pretreatment of cotton stalks by solid state cultivation of Phanerachaete chrysosporium. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 6556–6564 (2008)
Tien, M., Kirk, T.K.: Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Methods Enzymol. 161, 238–249 (1988)
Klein-Marcuschamer, D., Simmons, B.A., Blanch, H.W.: Techno-economic analysis of a lignocellulosic ethanol biorefinery with ionic liquid pre-treatment. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 5, 562–569 (2011)
Eggeman, T., Elander, T.R.: Process and economic analysis of pretreatment technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 2019–2025 (2005)
Kazi, F.K., Fortman, J., Anex, R., Kothandaraman, G., Hsu, D., Aden, A., Dutta, A.: Techno-Economic analysis of biochemical scenarios for production of cellulosic ethanol Technical Report NREL/TP-6A2-46588 June, United States Department of Energy (2010)
Chandel, A.K., Chan, E.S., Rudravaram, R., Narasu, M.L., Rao, L.V., Ravindra, P.: Economics and environmental impact of bioethanol production technologies: an appraisal. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2, 12–32 (2007)
Oleskowicz-Popiel, P., Klein-Marcuschamer, D., Simmons, B.A., Blanch, H.W.: Lignocellulosic ethanol production without enzymes—Technoeconomic analysis of ionic liquid pretreatment followed by acidolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 158, 294–299 (2014)
Akpinar, O., Ak, O., Kavas, A., Bakir, U., Yilmaz, L.: Enzymatic production of xylooligosaccharides from cotton stalks. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55, 5544–5551 (2007)
Shen, J., Agblevor, F.A.: Optimization of enzyme loading and hydrolytic time in the hydrolysis of mixtures of cotton gin waste and recycled paper sludge for the maximum profit rate. Biochem. Eng. J. 41, 241–250 (2008)
Binod, P., Kuttiraja, M., Archana, M., Janu, K.U., Sindhu, R., Sukumaran, R.K., Pandey, A.: High temperature pretreatment and hydrolysis of cotton stalk for producing sugars for bioethanol production. Fuel 92, 340–345 (2012)
McIntosh, S., Vancov, T., Palmer, J., Morris, S.: Ethanol production from cotton gin trash using optimized dilute acid pretreatment and whole slurry fermentation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 173, 42–51 (2014)
Shi, J., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R., Chinn, M., Howell, N.: Effect of microbial pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of cotton stalks for ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 33, 88–96 (2009)
Placido, J., Capareda, S.: Analysis of alkali ultrasonication pretreatment in bioethanol production from cotton gin trash using FT-IR spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 1, 23 (2014)
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Tamil Nadu State Council for Science and Technology (TNSCST) for sanctioning fund (TNSCST/S&T-Projects/VR/ES/2013-14) to carry out the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjithkumar, M., Ravikumar, R., Sankar, M.K. et al. An Effective Conversion of Cotton Waste Biomass to Ethanol: A Critical Review on Pretreatment Processes. Waste Biomass Valor 8, 57–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9563-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9563-8