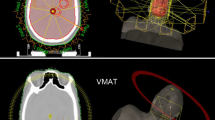
Abstract
Objective
To develop a feasible volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) treatment in whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) with a simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) and hippocampal (HP) sparing in 1–5 brain metastases (BMs).
Methods and materials
Ten patients with 20 BMs received a WBRT prescription of 20 Gy, SIB dose on BMs of 40 Gy/5 fractions. PTVWBRT was generated from brain minus BMs-PTVs (PTVSIB) and planning organ at risk volume to HP. All plans were evaluated in: homogeneity index (HI), target coverage (TC), maximum dose to prescription dose ratio (MDPD), prescription isodose to target volume ratio (PITV) and paddick conformity index (CI). We also evaluate D100 %, mean and maximum doses to HP. Planning objectives were for PTVWBRT, D2 % = 25 Gy with acceptable deviation of 26.7 Gy and D98 % ≥ 16.7 Gy; for PTVSIB D95 % ≥ 38 Gy; for HP, D100 % = 6 Gy with acceptable deviation of 6.7 Gy, Dmax = 10.7 Gy with acceptable deviation of 11.3 Gy, a mean dose of 8 Gy.
Results
Mean number of BMs was 2 (range 1–5). Mean values for BMs were volume of PTVSIB = 5.1 ± 4.9 cc, dose to 95 % of PTVSIB 39.3 ± 0.9 Gy, HI 0.083 ± 0.03, TC 0.96 ± 0.24, CI 0.78 ± 0.17. Mean MDPD was 1.06 ± 0.02 and PITV 0.96 ± 0.24. For WBRT, mean target volume was (13.46 ± 2)*102 cc, mean dose to 90 % of PTVWBRT 19.8 ± 0.2 Gy, mean HI 0.42 ± 0.12 and TC 0.78 ± 0.11. Mean and maximum HP doses were 7.7 ± 0.3 Gy and 10.5 ± 0.5 Gy. Mean dose to 100 % of HP volume (D100 %) was 6.7 ± 0.3 Gy.
Conclusions
WBRT plus SIB with HP avoidance with VMAT was feasible. All dosimetric parameters were satisfied for PTVWBRT and PTVSIB.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehta MP, Tsao MN, Whelan TJ, Morris DE, Hayman JA, Flickinger JC, Mills M, Rogers CL, Souhami L (2005) The American society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based review of the role of radiosurgery for brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:37–46
Kondziolka D, Patel A, Lunsford LD, Kassam A, Flickinger JC (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:427–434
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole-brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG-9508 randomized trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors in three radiation oncology group (RTOG) brain metastasis trials. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Rodrigues G, Yartsev S, Yaremko B et al (2011) Phase I trial of simultaneous in-field boost with helical tomotherapy for patients with one to three brain metastases. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys 80:1128–1133. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.03.047
Rodrigues G, Eppinga W, Lagerwaard F et al (2012) A pooled analysis of arc-based image-guided simultaneous integrated boost radiation therapy for oligometastatic brain metastases. Radiother Oncol 102:180–186. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2011.05.032
Lagerwaard FJ, van der Hoorn EA, Verbakel WF, Haasbeek CJ, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2009) Whole-brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost to multiple brain metastases using volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:253–259. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.03.029
Berk L (1995) An overview of radiotherapy trials for the treatment of brain metastases. Oncology 9(11):1205–1212
Laack NN, Brown PD (2004) Cognitive sequelae of brain radiation in adults. Semin Oncol 31:702–713
Shi L, Molina DP, Molina DP, Robbins ME, Wheeler KT, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2008) Hippocampal neuron number is unchanged 1-year after fractionated whole-brain irradiation at middle age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:526–532. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.02.015
Ghia A, Tomé WA, Thomas S, Cannon G, Khuntia D, Kuo JS, Mehta MP (2007) Distribution of brain metastases in relation to the hippocampus: implications for neurocognitive functional preservation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:971–977
Jack CR Jr (1994) MRI-based hippocampal volume measurements in epilepsy. Epilepsia 35(Suppl. 6):S21–S29
Gutiérrez AN, Westerly DC, Tomé WA et al (2007) Whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneously integrated brain metastases boost: a planning study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:589–597
Abayomi OK (1996) Pathogenesis of irradiation-induced cognitive dysfunction. Acta Oncol 35:659–663
Roman DDSP (1995) Neuropsychological effects of cranial radiation: current knowledge and future directions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:983–998
Hsu F, Carolan H, Nichol A et al (2010) Whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneous integrated boost for 1-3 brain metastases: a feasibility study using Volumetric Modulated Arch Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:1480–1485. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.03.032
Timmerman RD (2008) An overview of hypofractionation and introduction to the issue of seminars in radiation oncology. Semin Radiat Oncol 18:215–222. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2008.04.001
International commission on radiation units and measurements, ICRU report 62 (1999) Prescribing, recording, and reporting photon beam therapy (supplement to ICRU report 50) Bethesda: ICRU
Shaw E, Kline R, Gillin M, Souhami L, Hirschfeld A, Dinapoli R, Martin L (1993) Radiation therapy oncology group: radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 27:1231–1239
van’t Riet A, Mak AC, Moerland MA, Elders LH, van der Zee W (1997) A conformation number to quantify the degree of conformity in brachytherapy and external beam irradiation: application to the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:731–736
Paddick I (2000) A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 93(Suppl 3):219–222
Low DA, Harms WB, Mutic S, Purdy JA (1998) A technique for the quantitative evaluation of dose distributions. Med Phys 25:656–661
Alongi F, Fiorentino A, Navarria P, Bello L, Scorsetti M (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. Lancet Oncol 15:e246–e247. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70151-2
D’Agostino GR, Autorino R, Pompucci A et al (2011) Whole-brain radiotherapy combined with surgery or stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with brain oligometastases: long-term analysis. Strahlenther Onkol 187:421–425
Levegrün S, Pöttgen C, Wittig A, Lübcke W, Abu Jawad J, Stuschke M (2013) Helical tomotherapy for whole-brain irradiation with integrated boost to multiple brain metastases: evaluation of dose distribution characteristics and comparison with alternative techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:734–742. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.03.031
Gupta T, Basu A, Master Z, Jalali R, Munshi A, Sarin R (2009) Planning and delivery of whole brain radiation therapy with simultaneous integrated boost to brain metastases and synchronous limited-filed thoracic radiotherapy using helical tomotherapy: a preliminary experience. Technol Cancer Res Treat 8:15–22
Sterzing F, Welzel T, Srok-Perez G, Schubert K, Debus J, Herfarth KK (2009) Reirradiation of multiple brain metastases with helical tomotherapy. A multifocal simultaneous integrated boost for eight or more lesions. Strahlenther Onkol 185:89–93. doi:10.1007/s00066-009-1971-2
Laack NN, Brown PD (2004) Cognitive sequelae of brain radiation in adults. Semin Oncol 31:702–713
Shi L, Molina DP, Molina DP, Robbins ME, Wheeler KT, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2008) Hippocampal neuron number is unchanged 1-year after fractionated Whole-Brain Irradiation at Middle Age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:526–532. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.02.015
Prokic V, Wiedenmann N, Fels F, Schmucker M, Nieder C, Grosu AL (2013) Whole brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on multiple brain metastases: a planning study on treatment concepts. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:264–270. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.02.036
Kim KH, Cho BC, Lee CG, Kim HR, Suh YG, Kim JM, et al. (2015) Hippocampus-sparing Whole-Brain Radiotherapy and Simultaneous Integrated Boost for Multiple Brain Metastases From Lung Adenocarcinoma: Early Response and Dosimetric Evaluation. Technol Cancer Res Treat (Epub ahead of print)
Gondi V, Tolakanahalli R, Mehta M et al (2010) Hippocampal-sparing Whole-Brain radiotherapy: a “How-to” technique using helical tomotherapy and linear accelerator-based intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:1244–1252. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.01.039
Fiorentino A, Ricchetti F, Mazzola R, Fersino S, Giaj Levra N, Alongi F (2015) Regarding Ening et al. Charlson comorbidity index: an additional prognostic parameter for preoperative glioblastoma patient stratification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol (Epub ahead of print)
Fiorentino A, Caivano R, Chiumento C, Cozzolino M, Clemente S, Pedicini P, Fusco V (2012) Comorbidity assessment and adjuvant radiochemotherapy in elderly affected by glioblastoma. Med Oncol 29:3467–3471. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0246-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giaj Levra, N., Sicignano, G., Fiorentino, A. et al. Whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneous integrated boost for brain metastases: a dosimetric volumetric-modulated arc therapy study. Radiol med 121, 60–69 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-015-0563-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-015-0563-8