Abstract
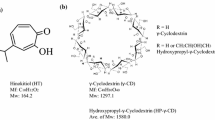
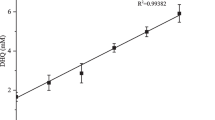
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of β-cyclodextrin on aqueous solubility of hesperidin. The inclusion complexes were prepared by different methods (kneading, co-evaporation and lyophilization) and were tested for their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Solubility diagrams were drawn at four temperatures (20, 25, 37 and 40 °C) and the corresponding stability constants were calculated. The solubility diagrams obtained were of AL type and the stoichiometric ratio was 1:1. Moreover, the thermodynamic parameters of the complexation reaction were calculated: Gibbs free energy change, free energy change, enthalpy change and entropy change. The results showed that the complexation reaction is more effective with the increase in temperature and in cyclodextrin concentration. The inclusion process is endothermic and spontaneous and the interactions between hesperidin and β-cyclodextrin are hydrophobic. UV–Vis, FTIR, 1HNMR, methods provided valuable information about complex formation. Antibacterial activity was investigated by the agar diffusion method, against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Candida albicans ATCC 10231. The results revealed that all the prepared compounds display a higher antibacterial activity compared to hesperidin. Also, the inclusion compounds presented an improved antioxidant activity, demonstrated by the determination of inhibition of lipoxygenase activity, DPPH radical scavenging activity and determination of reducing capacity. In vitro dissolution tests demonstrated that the inclusion compounds have an improved dissolution, compared to free hesperidin. The enhancement in the solubility, antibacterial and antioxidant activities depend on the method of preparation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tong, N., Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., Qiu, Y., Gong, Y., Yin, L., Qiu, Q., Wu, X.: Diosmin alleviates retinal edema by protecting the blood-retinal barrier and reducing retinal vascular permeability during ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLos One 8, 1–10 (2013)
Sezer, A., Usta, U., Kocak, Z., Yagci, M.A.: The effect of a flavonoid fractions diosmin + hesperidin on radiation-induced acute proctitis in a rat model. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 7, 152–156 (2011)
Lee, C.J., Wilson, L., Jordan, M.A., Nguyen, V., Tang, J., Smiyun, G.: Hesperidin suppressed proliferations of both human breast cancer and androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 24, 15–19 (2010)
Monforte, M.T., Trovato, A., Kirjavainen, S., Forestieri, A.M., Galati, E.M., Lo Curto, R.B.: Biological effects of hesperidin, a Citrus flavonoid. (note II): hypolipidemic activity on experimental hypercholesterolemia in rat. Farmaco 50, 595–599 (1995)
Chiba, H., Uehara, M., Wu, J., Wang, X., Masuyama, R., Suzuki, K., Kanazawa, K., Ishimi, Y.: Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits bone loss and decreases serum and hepatic lipids in ovariectomized mice. J. Nutr. 133, 1892–1897 (2003)
Loscalzo, L.M., Wasowski, C., Paladini, A.C., Marder, M.: Opioid receptors are involved in the sedative and antinociceptive effects of hesperidin as well as in its potentiation with benzodiazepines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 580, 306–313 (2008)
Brewster, M.E., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 645–666 (2007)
Arun, R., Ashok, K.C.K., Sravanthi, V.V.N.S.S.: Cyclodextrins as drug carrier molecule: a review. Sci. Pharm. 76, 567–598 (2008)
Davis, M.E., Brewster, M.E.: Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 1023–1035 (2004)
Loftsson, T., Brewster, M.E.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 62, 1607–1621 (2010)
Spulber, M., Pinteala, M., Fifere, A., Moldoveanu, C., Mangalagiu, I., Harabagiu, V., Simionescu, B.C.: Water soluble complexes of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin and sulconazole nitrate. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 62, 135–142 (2008)
Challa, R., Ahuja, A., Ali, J., Khar, R.K.: Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: an updated review. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 6, 329–357 (2005)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–122 (1965)
Domańska, U., Pelczarska, A., Pobudkowska, A.: Effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on solubility of sparingly soluble drug derivatives of anthranilic acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 2383–2394 (2011)
Lv, H.X., Zhang, Z.H., Jiang, H., Waddad, A.Y., Zhou, J.P.: Preparation, physicochemical characteristics and bioavailability studies of an atorvastatin hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex. Pharmazie 67, 46–53 (2012)
Hadžiabetdić, J., Elezović, A., Rahić, O., Mujezin, I.: Effect of cyclodextrin complexation on the aqueous solubility of diazepam and nitrazepam: phase-solubility analysis, thermodynamic properties. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 3, 811–819 (2012)
Batt, D.K., Garala, K.C.: Preparation and evaluation of inclusion complexes of diacerein with β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 77, 471–481 (2013)
George, S.J., Vasudevan, D.T.: Studies on preparation, characterization and solubility of 2-HP-beta-cyclodextrin-meclizine HCl inclusion complexes. Pharmaceutics 4, 220–227 (2012)
Salústio, P.J., Feio, G., Figueirinhas, J.L., Pinto, J.F., Cabral Marques, H.M.: The influence of the preparation methods on the inclusion of model drugs in a beta-cyclodextrin cavity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 71, 377–386 (2009)
Patel, R., Patel, M.: Solid-state characterization and in vitro dissolution behavior of lorazepam: hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Drug Discov. Ther. 4, 442–452 (2010)
Petralito, S., Zanardi, I., Memoli, A., Annesini, M.C., Travagli, V.: Solubility, spectroscopic properties and photostability of rhein/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Spectrochim. Acta. A. 74, 1254–1259 (2009)
Dani, R.M.A.M., Elbashir, A.A.: Host-guest inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin and cephalexin and its analytical application. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Res. 2, 1–13 (2013)
Marangoci, N., Mares, M., Silion, M., Fifere, A., Varganici, C., Nicolescu, A., Deleanu, C., Coroaba, A., Pinteala, M., Simionescu, B.C.: Inclusion complex of a new propiconazole derivative with beta-cyclodextrin: NMR, ESI-MS and preliminary pharmacological studies. Results Pharma. Sci. 1, 27–37 (2011)
Cui, L., Zhang, Z.H., Sun, E., Jia, X.B.: Effect of beta-cyclodextrin complexation on solubility and enzymatic conversion of naringin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 14251–14261 (2012)
Valnet, J., Duraffourd, C., Duraffourd, P., Lapraz, J.C.: L’aromatogramme: nouveaux resultats et essai d’interpretation sur 268 cas cliniques. Plant Médicin. Phytothér. 12, 43–52 (1978)
Danciu, C., Soica, C., Oltean, M., Avram, S., Borcan, F., Csanyi, E., Ambrus, R., Zupko, I., Muntean, D., Dehelean, C.A., Craina, M., Popovici, R.A.: Genistein in 1:1 inclusion complexes with ramified cyclodextrins: theoretical, physicochemical and biological evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 1962–1982 (2014)
Malterud, K.E., Rydland, K.M.: Inhibitors of 15-lipoxygenase from orange peel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 5576–5580 (2000)
Hatano, T., Kagawa, H., Yasuhara, T., Okuda, T.: Two new flavonoids and other constituents in licorice root: their relative astringency and radical scavenging effects. Chem. Pharm. Bull 36, 2090–2097 (1988)
Jullian, C., Moyano, L., Yañez, C., Olea-Azar, C.: Complexation of quercetin with three kinds of cyclodextrins: an antioxidant study. Spectrochim. Acta. A. 67, 230–234 (2007)
Oyazu, M.: Studies on products of browning reactions: antioxidative activities of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Jpn. J. Nutr. 44, 307–315 (1986)
Samal, H.B., Debata, J., Kumar, N.N., Sneha, S., Patra, P.K.: Solubility and dissolution improvement of aceclofenac using β-Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 4, 326–333 (2012)
Dua, K., Pabreja, K., Ramana, M.V., Lather, V.: Dissolution behavior of β-cyclodextrin molecular inclusion complexes of aceclofenac. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 3, 417–425 (2011)
Calabro, M.L., Tommasini, S., Donato, P., Stancanelli, R., Raneri, D., Catania, S., Costa, C., Villari, V., Ficarra, P., Ficarra, R.: The rutin/β-cyclodextrin interactions in fully aqueous solution: spectroscopic studies and biological assays. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 36, 1019–1027 (2005)
Markham, K.R.: Techniques of flavonoid identification. Academic Press, New York (1982)
Connors, K.A.: Thermodynamics of pharmaceutical systems: an introduction for students of pharmacy. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken, New Jersey (2002)
Liu, B., Li, W., Nguyen, T.A., Zhao, J.: Empirical, thermodynamic and quantum-chemical investigations of inclusion complexation between flavanones and (2-hydroxypropyl)-cyclodextrins. Food Chem. 134, 926–932 (2012)
Bloch, D.W., Elegakey, M.A., Speiser, P.P.: Solid dispersion of chlorthalidone in urea phase diagram and dissolution characteristics. Pharm. Acta Helv. 57, 231–235 (1982)
Guo, X., Shuang, S., Wang, X., Dong, C., Pan, J., Aboul-Enein, H.Y.: Comparative study on the inclusion behaviour of cyclodextrin derivatives with venoruton and rutin by thin layer chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 18, 559–563 (2004)
Roik, N.V., Belyakova, L.A.: Thermodynamic, IR spectral and X-ray diffraction studies of the β-cyclodextrin-para-aminobenzoic acid inclusion complex. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 69, 315–319 (2011)
Lin, S.Y., Lin, H.L., Lin, C.C., Hsu, C.H., Wu T.K., Huang Y.T.: Thermodynamic study of grinding-induced loratadine inclusion complex formation using thermal analysis and curve-fitted FTIR determination. In: Moreno-Piraján, J.C. (ed.) Thermodynamics - Physical Chemistry of Aqueous Systems (2011). doi: 10.5772/21338
Şamli, M., Korel, F., Bayraktar, O.: Characterization of silk fibroin based films loaded with rutin–β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. (2014). doi:10.1007/s10847-014-0396-4
Miron, L., Mares, M., Nastasa, V., Spulber, M., Fifere, A., Pinteala, M., Harabagiu, V., Simionescu, B.C.: Water soluble sulconazole-β-cyclodextrin complex: physico-chemical characterization and preliminary pharmacological studies. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 63, 159–162 (2009)
Fatiha, M., Khatmi, D.E., Largate, L.: Theoretical approach in the study of the inclusion processes of sulconazole with β-cyclodextrin. J. Mol. Liq. 154, 1–5 (2010)
Piel, G., Dive, G., Ervard, B., Van Hees, T., Henry de Hassonville, S., Delattre, L.: Molecular modeling study of β- and γ-cyclodextrin complexes with miconazole. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13, 271–279 (2001)
Grandelli, H.E., Stickle, B., Whittington, A., Kiran, E.: Inclusion complex formation of β-cyclodextrin and naproxen: a study on exothermic complex formation by differential scanning calorimetry. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 77, 269–277 (2013)
Panda, S., Singh, D.L.: Study of antioxidant, antimicrobial and anthelmintic properties of 1-nicotinoyl-4-aryl-3-methyl 3a,4-dihydropyrazolo [3,4c] pyrazoles and their inclusion complexes with β-cyclodextrin. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 3, 1639–1654 (2014)
Stavniichuk, R., Drel, V.R., Shevalye, H., Vareniuk, I., Stevens, M.J., Nadler, J.L., Obrosova, I.G.: Role of 12/15-lipoxygenase in nitrosative stress and peripheral prediabetic and diabetic neuropathies. Free Radicals Biol. Med. 49, 1036–1045 (2010)
Wittwer, J., Hersberger, M.: The two faces of the 15-lipoxygenase in atherosclerosis. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 77, 67–77 (2007)
Yang, H., Zhuo, J.M., Chu, J., Chinnici, C., Praticò, D.: Amelioration of the Alzheimer’s disease phenotype by absence of 12/15-Lipoxygenase. Biol. Psychiatry 68, 922–929 (2010)
Acknowledgments
Scientific research funded by the University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Grigore T. Popa” Iasi, based on the contract no. 4872/18.03.2013 and the PN-II-ID-PCCE-2011-2-0028 Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corciova, A., Ciobanu, C., Poiata, A. et al. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of hesperidin:β-cyclodextrin complexes obtained by different techniques. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 81, 71–84 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-014-0434-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-014-0434-2