Abstract
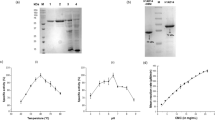
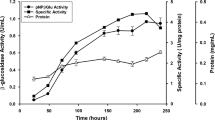
We recently discovered a novel glycoside hydrolase family 6 (GH6) cellobiohydrolase from Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus B-6 (PcCel6A), which is rarely found in bacteria. This enzyme is a true exo-type cellobiohydrolase which exhibits high substrate specificity on amorphous cellulose and low substrate specificity on crystalline cellulose, while this showed no activity on substitution substrates, carboxymethyl cellulose and xylan, distinct from all other known GH6 cellobiohydrolases. Product profiles, HPLC analysis of the hydrolysis products and a schematic drawing of the substrate-binding subsites catalysing cellooligosaccharides can explain the new mode of action of this enzyme which prefers to hydrolyse cellopentaose. PcCel6A was not inhibited by glucose or cellobiose at concentrations up to 300 and 100 mM, respectively. A good synergistic effect for glucose production was found when PcCel6A acted together with processive endoglucanase Cel9R from Clostridium thermocellum and β-glucosidase CglT from Thermoanaerobacter brockii. These properties of PcCel6A make it a suitable candidate for industrial application in the cellulose degradation process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai A, Zhao X, Jin Y, Yang G, Feng Y (2013) A novel thermophilic β-glucosidase from Caldicellulosiruptor bescii: characterization and its synergistic catalysis with other cellulases. J Mol Catal B Enzym 85–86:248–256. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2012.09.016
Baramee S, Phitsuwan P, Waeonukul R, Pason P, Tachaapaikoon C, Kosugi A, Ratanakhanokchai K (2015) Alkaline xylanolytic–cellulolytic multienzyme complex from the novel anaerobic alkalithermophilic bacterium Cellulosibacter alkalithermophilus and its hydrolysis of insoluble polysaccharides under neutral and alkaline conditions. Process Biochem 50:643–650. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2015.01.019
Barham D, Trinder P (1972) An improved colour reagent for the determination of blood glucose by the oxidase system. Analyst 97:142–145
Bauer S, Vasu P, Persson S, Mort AJ, Somerville CR (2006) Development and application of a suite of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes for analyzing plant cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11417–11422. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604632103
Breves R, Bronnenmeier K, Wild N, Lottspeich F, Staudenbauer WL, Hofemeister J (1997) Genes encoding two different β-glucosidases of Thermoanaerobacter brockii are clustered in a common operon. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3902–3910
Chen Y, Stipanovic A, Winter W, Wilson D, Kim Y-J (2007) Effect of digestion by pure cellulases on crystallinity and average chain length for bacterial and microcrystalline celluloses. Cellulose 14:283–293. doi:10.1007/s10570-007-9115-2
Chiriac AI, Cadena EM, Vidal T, Torres AL, Diaz P, Pastor FIJ (2010) Engineering a family 9 processive endoglucanase from Paenibacillus barcinonensis displaying a novel architecture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1125–1134. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2350-8
Chow C-M, Yagüe E, Raguz S, Wood DA, Thurston CF (1994) The cel3 gene of Agaricus bisporus codes for a modular cellulase and is transcriptionally regulated by the carbon source. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2779–2785
Das DB, Mitra MK, Wareham JF (1954) Structure of cotton alpha-cellulose. Nature 174:1058–1059. doi:10.1038/1741058a0
Davies GJ, Brzozowski AM, Dauter M, Varrot A, Schülein M (2000) Structure and function of Humicola insolens family 6 cellulases: structure of the endoglucanase, Cel6B, at 1.6 Å resolution. Biochem J 348:201–207. doi:10.1042/bj3480201
Harjunpää V, Teleman A, Koivula A, Ruohonen L, Teeri TT, Teleman O, Drakenberg T (1996) Cello-oligosaccharide hydrolysis by cellobiohydrolase II from Trichoderma reesei. Association and rate constants derived from an analysis of progress curves. Eur J Biochem 240:584–591. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0584h.x
Horn SJ, Sørlie M, Vårum KM, Väljamäe P, Eijsink VGH (2012) Measuring processivity. Methods Enzymol 510:69–95. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-415931-0.00005-7
Inoue H, Decker SR, Il LET, Yano S, Sawayama S (2014) Identification and characterization of core cellulolytic enzymes from Talaromyces cellulolyticus (formerly Acremonium cellulolyticus) critical for hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:151–163. doi:10.1186/s13068-014-0151-5
Irwin DC, Spezio M, Walker LP, Wilson DB (1993) Activity studies of eight purified cellulases: specificity, synergism, and binding domain effects. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:1002–1013. doi:10.1002/bit.260420811
Jäger G, Wu Z, Garschhammer K, Engel P, Klement T, Rinaldi R, Spiess A, Büchs J (2010) Practical screening of purified cellobiohydrolases and endoglucanases with α-cellulose and specification of hydrodynamics. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:1–12. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-3-18
Kataeva IA, Seidel RD 3rd, Shah A, West LT, Li XL, Ljungdahl LG (2002) The fibronectin type 3-like repeat from the Clostridium thermocellum cellobiohydrolase CbhA promotes hydrolysis of cellulose by modifying its surface. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4292–4300. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.9.4292-4300.2002
Kim IJ, Lee HJ, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2014) Synergistic proteins for the enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose by cellulase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8469–8480. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-6001-3
Koivula A, Kinnari T, Harjunpaa V, Ruohonen L, Teleman A, Drakenberg T, Rouvinen J, Jones TA, Teeri TT (1998) Tryptophan 272: an essential determinant of crystalline cellulose degradation by Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase Cel6A. FEBS Lett 429:341–346
Kostylev M, Wilson D (2014) A distinct model of synergism between a processive endocellulase (TfCel9A) and an exocellulase (TfCel48A) from Thermobifida fusca. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:339–344. doi:10.1128/AEM.02706-13
Kurašin M, Väljamäe P (2011) Processivity of cellobiohydrolases is limited by the substrate. J Biol Chem 286:169–177. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.161059
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. doi:10.1038/227680a0
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2015) SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res 43:257–260. doi:10.1093/nar/gku949
Liu Y, Igarashi K, Kaneko S, Tonozuka T, Samejima M, Fukuda K, Yoshida M (2009) Characterization of glycoside hydrolase family 6 enzymes from Coprinopsis cinerea. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1432–1434. doi:10.1271/bbb.80888
Lombard V, Ramulu HG, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2014) The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 42:490–495. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1178
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mansfield SD, Meder R (2003) Cellulose hydrolysis—the role of monocomponent cellulases in crystalline cellulose degradation. Cellulose 10:159–169. doi:10.1023/a:1024022710366
Meinke A, Gilkes NR, Kwan E, Kilburn DG, Warren RAJ, Miller RC Jr (1994) Cellobiohydrolase A (CbhA) from the cellulolytic bacterium Cellulomonas fimi is a β-1,4-exocellobiohydrolase analogous to Trichoderma reesei CBH II. Mol Microbiol 12:413–422. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01030.x
Mertz B, Hill AD, Mulakala C, Reilly PJ (2007) Automated docking to explore subsite binding by glycoside hydrolase family 6 cellobiohydrolases and endoglucanases. Biopolymers 87:249–260. doi:10.1002/bip.20831
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Park C-S, Kawaguchi T, Sumitani J-I, Takada G, Izumori K, Arai M (2005) Cloning and sequencing of an exoglucanase gene from Streptomyces sp. M 23, and its expression in Streptomyces lividans TK-24. J Biosci Bioeng 99:434–436. doi:10.1263/jbb.99.434
Pason P, Kyu KL, Ratanakhanokchai K (2006) Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus strain B-6 xylanolytic-cellulolytic enzyme system that degrades insoluble polysaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2483–2490. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.4.2483-2490.2006
Poidevin L, Feliu J, Doan A, Berrin J-G, Bey M, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B, Record E, Heiss-Blanquet S (2013) Insights into exo- and endoglucanase activities of family 6 glycoside hydrolases from Podospora anserina. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4220–4229. doi:10.1128/AEM.00327-13
Sakka M, Higashi Y, Kimura T, Ratanakhanokchai K, Sakka K (2011) Characterization of Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus B-6 Xyn10D, a xylanase that contains a family 3 carbohydrate-binding module. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4260–4263. doi:10.1128/AEM.00226-11
Sandgren M, Wu M, Karkehabadi S, Mitchinson C, Kelemen BR, Larenas EA, Ståhlberg J, Hansson H (2013) The structure of a bacterial cellobiohydrolase: the catalytic core of the Thermobifida fusca family GH6 cellobiohydrolase Cel6B. J Mol Biol 425:622–635. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.039
Song J, Liu B, Liu Z, Yang Q (2010) Cloning of two cellobiohydrolase genes from Trichoderma viride and heterogeneous expression in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Rep 37:2135–2140. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9683-3
Sweeney MD, Xu F (2012) Biomass converting enzymes as industrial biocatalysts for fuels and chemicals: recent developments. Catalysts 2:244–263. doi:10.3390/catal2020244
Takahashi M, Takahashi H, Nakano Y, Konishi T, Terauchi R, Takeda T (2010) Characterization of a cellobiohydrolase (MoCel6A) produced by Magnaporthe oryzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6583–6590. doi:10.1128/AEM.00618-10
Teeri T, Penttilä M, Keränen S, Nevalainen H, Knowles JKC (1991) Structure, function, and genetics of cellulases. In: Ball C, Finkelstein D (eds) Biotechnology of filamentous fungi. Butterworth, London, United Kingdom, pp. 419–447
Teugjas H, Väljamäe P (2013) Product inhibition of cellulases studied with 14C-labeled cellulose substrates. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:104–117. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-6-104
Toda H, Nagahata N, Amano Y, Nozaki K, Kanda T, Okazaki M, Shimosaka M (2008) Gene cloning of cellobiohydrolase II from the white rot fungus Irpex lacteus MC-2 and its expression in Pichia pastoris. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:3142–3147. doi:10.1271/bbb.80316
Tsai CF, Qiu X, Liu JH (2003) A comparative analysis of two cDNA clones of the cellulase gene family from anaerobic fungus Piromyces rhizinflata. Anaerobe 9:131–140. doi:10.1016/S1075-9964(03)00087-8
Varrot A, Frandsen TP, von Ossowski I, Boyer V, Cottaz S, Driguez H, Schülein M, Davies GJ (2003) Structural basis for ligand binding and processivity in cellobiohydrolase Cel6A from Humicola insolens. Structure 11:855–864. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(03)00124-2
Vuong TV, Wilson DB (2009) Processivity, synergism, and substrate specificity of Thermobifida fusca Cel6B. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6655–6661. doi:10.1128/AEM.01260-09
Waeonukul R, Kosugi A, Tachaapaikoon C, Pason P, Ratanakhanokchai K, Prawitwong P, Deng L, Saito M, Mori Y (2012) Efficient saccharification of ammonia soaked rice straw by combination of Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome and Thermoanaerobacter brockii beta-glucosidase. Bioresour Technol 107:352–357. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.126
Walseth CS (1952) Occurrence of cellulases in enzyme preparations from microorganisms. Tappi 35:228–233
Wang H-C, Chen Y-C, Huang C-T, Hseu R-S (2013) Cloning and characterization of a thermostable and pH-stable cellobiohydrolase from Neocallimastix patriciarum J11. Protein Expr Purif 90:153–159. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2013.06.004
Warren RAJ (1996) Microbial hydrolysis of polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:183–212. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.183
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulase activities. Meth Enzymol 160:87–112
Wu M, Bu L, Vuong TV, Wilson DB, Crowley MF, Sandgren M, Ståhlberg J, Beckham GT, Hansson H (2013) Loop motions important to product expulsion in the Thermobifida fusca glycoside hydrolase family 6 cellobiohydrolase from structural and computational studies. J Biol Chem 288:33107–33117. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.502765
Zhang Y-HP, Lynd LR (2006) A functionally based model for hydrolysis of cellulose by fungal cellulase. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:888–898. doi:10.1002/bit.20906
Zhang S, Irwin DC, Wilson DB (2000) Site-directed mutation of noncatalytic residues of Thermobifida fusca exocellulase Cel6B. Eur J Biochem 267:3101–3115. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01315.x
Zverlov VV, Schantz N, Schwarz WH (2005) A major new component in the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum is a processive endo-β-1,4-glucanase producing cellotetraose. FEMS Microbiol Lett 249:353–358. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2005.06.037
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. program of the Thailand Research Fund, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, Thailand under the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission (2015–2016) and the Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The present work was funded by the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. program of the Thailand Research Fund (grant number PHD/0069/2556).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 112 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baramee, S., Teeravivattanakit, T., Phitsuwan, P. et al. A novel GH6 cellobiohydrolase from Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus B-6 and its synergistic action on cellulose degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 1175–1188 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7895-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7895-8