Abstract
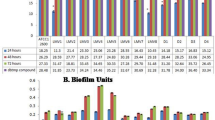
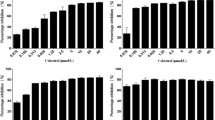
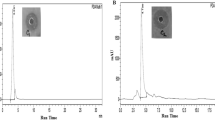
In the present study a novel Dibenzyl (benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl(hydroxy)methyl) phosphonate (3b) derived from α-Hydroxyphosphonate exhibited anti-Staphylococcus aureus and anti-biofilm properties against penicillin, ampicillin and methicillin-resistant strains of S. aureus. The compound 3b showed Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC90) at 160 ± 1 µg/ml and lethal dose (LD50) at 80 ± 1 µg/ml. S. aureus growing as planktonic culture shows a formation of aggregates which is the prerequisite for the formation of biofilms, the compound 3b disrupted aggregates and cleared all the preformed planktonic biofilms and prevented their recurrence. The SDS-PAGE analysis of compound 3b treated S. aureus showed gradual lysis of total proteins. The zymogram analysis indicated overexpression of proteases which is the principle reason for lysis of total proteins of S. aureus on incubation with compound 3b. Further, the dot blot analysis indicated complete lysis of Protein-A in the culture filtrate of all the drug-resistant strains of S. aureus a prominent virulence factor and biofilm forming protein. All these features exhibited by compound 3b makes it as a potential therapeutic molecule in the treatment of S. aureus infections.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral MM, Coelho LR, Flores RP, Souza RR, Silva-Carvalho MC, Teixeira LA, Ferreira-Carvalho BT, Figueiredo AM (2005) The predominant variant of the Brazilian epidemic clonal complex of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus has an enhanced ability to produce biofilm and to adhere to and invade airway epithelial cells. J Infect Dis 192:801–810
Aoki Y, Sundqvist M, Hooker AC, Gennemark P, Pop ED L (2016) An optimal design software for preclinical pharmacokinetic and pharmaco dynamic studies. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 127:126–143
Archer NK, Mazaitis MJ, Costerton JW, Leid JG, Powers ME, Shirtliff ME (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms properties, regulation and roles in human disease. Virulence 2(5):445–459
Basarab GS, Manchester JI, Bist S, Boriack-Sjodin PA, Dangel B, Illingworth R, Sherer BA, Sriram S, Uria-Nickelsen M, Eakin AE (2013) Fragment-to-hit-to-lead discovery of a novel pyridylurea scaffold of ATP competitive dual targeting type II topoisomerase inhibiting antibacterial agents. J Med Chem.14; 56(21):8712–8735
Bordi C, de Bentzmann S (2011) Hacking into bacterial biofilms: a new therapeutic challenge. Ann Intensive Care 1(1):19
Brvar M, Perdih A, Hodnik V, Renko M, Anderluh G, Jerala R, Solmajer T (2012) In silico discovery and biophysical evaluation of novel 5-(2-hydroxybenzylidene) rhodanine inhibitors of DNA gyrase B. Bioorg Med Chem.15 20(8):2572–2580
Cardot Martin E, Michel A, Raynal B, Badiou C, Laurent F, Vandenesch F, Etienne J, Lina G, Dumitrescu O (2015) Community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300 resists staphylococcal protein A modulation by antibiotics and antimicrobial peptides. Int J Antimicrob Agents 45(1):9–24
Chagnon F, Guay I, Bonin MA, Mitchell G, Bouarab K, Malouin F, Marsault É (2014) Unraveling the structure-activity relationship of tomatidine, a steroid alkaloid with unique antibiotic properties against persistent forms of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Med Chem 10(80):605–620
Coico R, Kowalik T, Quarles J, Stevenson B, Taylor R (eds) (2005) Current protocols in microbiolgy. Wiley, New York
Craigen B, Dashiff A, Kadouri DE (2011) The Use of Commercially Available Alpha- Amylase Compounds to Inhibit and Remove Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Open Microbiol J 5:21–31
Cramton ES, Ulrich M, Gotz F, doring G (2001) Anaerobic conditions induce expression of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun 69(6):4079–4085
Cramton SE, Gerke C, Schnell NF, Nichols WW, Gotz F (1999) The intercellular adhesion (ica) locus is present in Staphylococcus aureus and is required for biofilm formation. Infect Immun 67(10):5427–5433
Drake, GL, Calamari, TA (1983) Industrial Uses of Phosphonates. In: Hilderbrand RL (ed) Chapter. 7, RC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Drescher M, Hammerschmidt F, Kahlig H (1995) Synthesis of Alpha-hydroxy and Fluoro Phosphonates and cyclic ether containing Natural products. 1267
Eakin AE, Green O, Hales N, Walkup GK, Bist S, Singh A, Mullen G, Bryant J, Embrey K, Gao N, Breeze A, Timms D, Andrews B, Uria-Nickelsen M, Demeritt J, Loch 3rd JT, Hull K, Blodgett A, Illingworth RN, Prince B, Boriack-Sjodin PA, Hauck S, MacPherson LJ, Ni H, Sherer B, Pyrrolamide (2012) DNA gyrase inhibitors: fragment-based nuclear magnetic resonance screening to identify antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 56:1240
Ginzburg E, Namias N, Brown M, Ball S, Hameed SM, Cohn SM (2000) Gram positive infection in trauma patients: new strategies to decrease emerging Gram-positive resistance and vancomycin toxicity. Int J Antimicrob Agent 16:39
Hammerschmidt F, Hanbauer (2000) Transformation of Arylmethylamines into α-Aminophosphonic Acids via Metalated Phosphoramidates: Rearrangement of Partly Configurationally Stable N-Phosphorylated α-Aminocarbanions. J Org Chem 65(19):6121–6131
Herman-Bausier P, El-Kirat-Chatel S, Foster TJ2, Geoghegan JA, Dufrêne YF (2015) Staphylococcus aureus Fibronectin-Binding Protein A Mediates Cell-Cell Adhesion through Low-Affinity Homophilic Bonds. MBio. 26 6(3):e00413–e00415
Johannes A-S (2015) The art of destruction: revealing the proteolytic capacity of bacterial caspase homologs. Mol Microbiol 98(1):1–6
Lei MG, Cue D, Roux CM, Dunman PM, Lee CY (2011) Rsp Inhibits Attachment and Biofilm Formation by Repressing fnbA in Staphylococcus aureus MW2. J Bacteriol 193(19):5231–5241
McAdam PR, Templeton KE, Edwards GF, Holden MT, Feil EJ, Aanensen DM, Bargawi HJ, Spratt BG, Bentley SD, Parkhill (2012) Molecular tracing of the mergence, adaptation, and transmission of hospital-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109:9107
Mitchell G, Séguin DL, Asselin AE, Déziel E, Cantin AM, Frost EH, Michaud S, Malouin F (2010) Staphylococcus aureus sigma B-dependent emergence of small-colony variants and biofilm production following exposure to Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline-N-oxide. BMC Microbiol 30(10):33
Nanda Kumar Y, Navya A, Kalpana K, Ravendra Babu K, Jhansi Rani V, Hariprasad O, Nagaraju C, Sarma PVGK, Bhaskar M (2014) Design, synthesis, in silico, and in vitro evaluation of novel pyrimidine phosphonates with cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells. Med Chem Res 23:317–328
Oprea TI, Matter H (2004) Integrating virtual screening in lead discovery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:349–358
Osmon DR, Berbari EF (2002) Outpatient intravenous antimicrobial therapy for the practicing orthopaedic surgeon. Clin Orthop Relat Res 403:80–86
O’Toole G, Kaplan HB, Kolter R (2000) Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:49–79
Pokalwar RU, Hangarge RV, Maskeb aPrakashV, Shingare MS (2006) Synthesis and antibacterial activities of α-hydroxyphosphonates and α acetyloxyphosphonates derived from 2-chloroquinoline-3-carbaldehyde. ARKIVOC 11:196–204
Prasad UV, Vasu D, Yeswanth S, Swarupa V, Sunitha MM, Choudhary A, Sarma PV (2015) Phosphorylation controls the functioning of Staphylococcus aureus isocitrate dehydrogenase--favours biofilm formation. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 30(4):655–661
Proctor RA, von Eiff C, Kahl BC, Becker K, McNamara P, Herrmann M, Peters G (2006) Small colony variants: a pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:295–305
Renuka J, Jeankumar VU, Bobesh KA, Soni V, Devi PB, Sriram D (2014) Structure-guided design and development of novel benzimidazole class of compounds targeting DNA gyraseB enzyme of Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg Med Chem 22:5970–5987
Venkateswara Prasad U, Vasu D, Nanda Kumar Y, Santhosh Kumar P, Yeswanth S, Swarupa V, Phaneendra BV, Chaudhary A, Sarma PVGK (2013) Cloning, Expression and Characterization of NADP-Dependent Isocitrate Dehydrogenase from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:862–869
Vuong C, Kidder JB, Jacobson ER, Proctor MOAR, Somerville GA (2005) Staphylococcus epidermidis polysaccharide intercellular adhesin production significantly increases during tricarboxylic acid cycle stress. J Bacteriol 187:2967–2973
Waters EM, Rudkin JK, Schaeffer CR, Lohan AJ, Tong P, Loftus BJ, Fey PD, Massey RC, O’Gara JP, Pozzi C (2012) Methicillin resistance alters the biofilm phenotype and attenuates virulence in Staphylococcus aureus device-associated infections. PLoS Pathog 8:1002626
Yeswanth S, Nanda Kumar Y, Venkateswara Prasad U, Swarupa V, Koteswara rao V, Venkata Gurunadha Krishna Sarma P (2013) Cloning and characterization of L-lactate dehydrogenase gene of Staphylococcus aureus. Anaerobe 24:43–48
Zhang Y, Li J-F, Yuan C-Y (2003) Enzymatic synthesis of optically active trifluoromethylated 1- and 2-hydroxyalkanephosphonates. Tetrahedron 59(4):473–479
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, INDIA under Grant of Major Research Project of ICMR—SRF (Senior Research Fellowship), File No.80/849/2014-ECD-I, dated: 7-5-2014.; Sri Venkateswara Institute of Medical Sciences and University, under SBAVP scheme (SBAVP/Ph.D/03) dated: 9-10- 2012. This paper forms a part of Ph.D. thesis work going to be submitted to SVIMS University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeswanth, S., Chandra Sekhar, K., Chaudhary, A. et al. Anti-microbial and Anti-biofilm activity of a novel Dibenzyl (benzo[d] thiazol-2-yl (hydroxy) methyl) phosphonate by inducing protease expression in Staphylococcus aureus . Med Chem Res 27, 785–795 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2102-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2102-8