Abstract
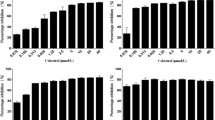
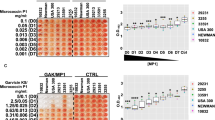
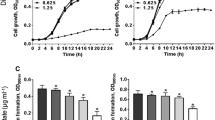
The emergence of microbial resistance to conventional antibiotics, partially attributed to biofilm formation, has urged for new antimicrobial compounds. Here, we reported two novel low molecular weight (LMW) compounds from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SJ33 and evaluated their biofilm inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus aureus. The compounds C1 and C2 were purified by RP-HPLC and structurally identified as 3-amino-5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(1-hydroxyprop-2-yn-1-yl)-3,3a,4,5,6,7a-hexahydro-7H-indazol-7-one and 1-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-3-((2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)oxy)-1-(methylamino)-butan-2-one by spectroscopic techniques. High ESI–MS data confirmed the molecular weight of C1 and C2 as 254.1141 and 234.1658 Da, respectively. Time-kill assay demonstrated bactericidal action of compounds, whereas scanning electron microscopy revealed morphological changes in treated S. aureus MTCC96 and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) cells. The antibacterial compounds reduced biofilm formation in S. aureus MTCC96 and MRSA by crystal violet assay. Further, fluorescence and scanning electron microscopic images exhibited biofilm formation by pathogens and biofilm inhibition by compounds treatment. The Quantitative RT PCR revealed the down-regulation of icaC and icaD genes involved in intercellular adhesion of biofilms. The results confirmed the anti-biofilm activity of novel LMW compounds by eliminating preformed biofilms formed by S. aureus MTCC96 and MRSA.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allam NG (2017) Correlation between biofilm production and bacterial urinary tract infections: new therapeutic approach. Egypt J Microbiol 48:39–48
Ausbacher D, Fallarero A, Kujala J et al (2014) Staphylococcus aureus biofilm susceptibility to small and potent β2,2-amino acid derivatives. Biofouling 30:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.847924
Bilokin YV, Gella IM (1998) A facile stereoselective synthesis of novel heterocycles with hexahydro-2H-indazole, thiazole, and coumarin moieties. Heterocycl Commun 4:339–340. https://doi.org/10.1515/HC.1998.4.4.339
Blanco AR, Sudano-Roccaro A, Spoto GC et al (2005) Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits biofilm formation by ocular Staphylococcal isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:4339–4343. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.49.10.4339-4343.2005
Costa GA, Rossatto FCP, Medeiros AW, F ANAP, (2018) Evaluation antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of the antimicrobial peptide P34 against Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. An Acad Bras Cienc 90:73–84
Crispim SM, Nascimento AMA, Costa PS et al (2013) Molecular identification of Lactobacillus spp. associated with puba, a Brazilian fermented cassava food. Braz J Microbiol 21:15–21
Eftekhar F, Dadaei T (2011) Biofilm formation and detection of IcaAB genes in clinical isolates of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Iran J Pathol 14:132–136
Faidallah HM, Khan KA, Rostom SAF, Asiri AM (2013) Synthesis and in vitro antitumor and antimicrobial activity of some 2,3-diaryl-7-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydroindazole and 3,3a,4,5,6,7- hexahydroindazole derivatives. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 28:495–508. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2011.653354
Fisher LE, Hook AL, Ashraf W et al (2015) Biomaterial modification of urinary catheters with antimicrobials to give long-term broadspectrum antibiofilm activity. J Control Release 202:57–64
Fleming D, Rumbaugh KP (2017) Approaches to dispersing medical biofilms. Microorganisms 5:15
Furno F, Morley KS, Wong B et al (2004) Silver nanoparticles and polymeric medical devices: a new approach to prevention of infection? J Antimicrob Chemother 54:1019–1024
Gerits E, Blommaert E, Lippell A et al (2016) Elucidation of the mode of action of a new antibacterial compound active against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 11:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155139
Haddadin RNS, Saleh S, Al-Adham ISI et al (2010) The effect of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on virulence factors expressed by Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 108:1281–1291. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04529.x
Haroun MF, Al-Kayali RS (2016) Synergistic effect of Thymbra spicata L. Extracts with antibiotics against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. Iran J Basic Med Sci 19:1193–1200
Jeevaratnam K, Vidhyasagar V, Agaliya PJ, Saraniya A, Umaiyaparvathy M (2015) Characterization of an antibacterial compound, 2-hydroxyl Indole-3-propanamide, produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented batter. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177(1):137–147
Jiang L, Wang F, Han F et al (2013) Evaluation of diffusion and dilution methods to determine the antimicrobial activity of water-soluble chitosan derivatives. J Appl Microbiol 114:956–963
Kannappan A, Durgadevi R, Srinivasan R et al (2020) 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde from Hemidesmus indicus is antagonistic to Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. Biofouling 36:549–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2020.1777989
Kavitha S, Harikrishnan A, Jeevaratnam K (2020) Characterization and evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of a novel antibiotic-type compound from a probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum KJB23 against food-borne pathogens. Lwt 118:108759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108759
Kȩpa M, Miklasińska-Majdanik M, Wojtyczka RD et al (2018) Antimicrobial potential of caffeic acid against Staphylococcus aureus clinical strains. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7413504
Kim M, Lee SJ et al (2009) Characterization of antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus paraplantarum KNUC25 isolated from kimchi. Korean J Microbiol Biotechnol 37:24–32
Lakshmanan D, Harikrishnan A, Kumari J et al (2019) A compound isolated from Alpinia officinarum Hance. inhibits swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and down regulates virulence genes. J Appl Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14563
Lerch MF, Schoenfelder SMK, Marincola G et al (2019) A non-coding RNA from the intercellular adhesion (ica) locus of Staphylococcus epidermidis controls polysaccharide intercellular adhesion (PIA)-mediated biofilm formation. Mol Microbiol 111:1571–1591. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14238
Lin TH, Pan TM (2019) Characterization of an antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus plantarum NTU 102. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 52:409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2017.08.003
Liu H, Zhao Y, Zhao D et al (2015) Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of thiazolidione derivatives against clinical Staphylococcus strains. Emerg Microbes Infect 4:e1. https://doi.org/10.1038/emi.2015.1
Liu J, Yi L, Wang X et al (2017) A novel antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus rhamnous LS8. Food Control 73:754–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.09.028
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Man NYT, Knight DR, Stewart SG et al (2018) Spectrum of antibacterial activity and mode of action of a novel tris-stilbene bacteriostatic compound. Sci Rep 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25080-w
Melo PDC, Ferreira LM, Filho AN et al (2013) Comparison of methods for the detection of biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine subclinical mastitis. Braz J Microbiol 44:119–124
Mohamed MF, Abdelkhalek A, Seleem MN (2016) Evaluation of short synthetic antimicrobial peptides for treatment of drug-resistant and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 6:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29707
Mohammad H, Mayhoub AS, Cushman M, Seleem MN (2015) Anti-biofilm activity and synergism of novel thiazole compounds with glycopeptide antibiotics against multidrug-resistant Staphylococci. J Antibiot (tokyo) 68:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.142
Morais IMC, Cordeiro AL, Teixeira GS et al (2017) Biological and physicochemical properties of biosurfactants produced by Lactobacillus jensenii P6A and Lactobacillus gasseri P65. Microb Cell Fact 16:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0769-7
Niku-Paavola ML, Laitila A, Mattila-Sandholm T, Haikara A (1999) New types of antimicrobial compounds produced by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Appl Microbiol 86:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00632.x
Ong TH, Chitra E, Ramamurthy S et al (2019) Cationic chitosan-propolis nanoparticles alter the zeta potential of S. epidermidis, inhibit biofilm formation by modulating gene expression and exhibit synergism with antibiotics. PLoS ONE 14:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213079
Parente E, Brienza C, Moles M, Ricciardi A (1995) A comparision of methods for the measurement of bacteriocin activity. J Microbiol Methods 22:95–108
Paudel A, Hamamoto H, Kobayashi Y et al (2011) Identification of novel deoxyribofuranosyl indole antimicrobial agents. J Antibiot (tokyo) 65:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2011.110
Rachid S, Ohlsen K, Witte W et al (2000) Effect of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations on polysaccharide intercellular adhesin expression in biofilm-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:3357–3363. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.44.12.3357-3363.2000
Saba T, Sajid M, Khan AA, Zahra R (2018) Role of intracellular adhesion icaAD and agr genes in biofilm formation in clinical S. aureus isolates and assessment of two phenotypic methods. Pakistan J Med Sci 34:633–637
Sahoo TK, Jena PK, Patel AK, Seshadri S (2015) Purification and molecular characterization of the novel highly potent bacteriocin TSU4 produced by Lactobacillus animalis TSU4. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1730-z
Saising J, Dube L, Ziebandt AK et al (2012) Activity of gallidermin on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5804–5810. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01296-12
Sakoulas G, Nam SJ, Loesgen S et al (2012) Novel bacterial metabolite merochlorin a demonstrates in vitro activity against Multi-Drug resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 7:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029439
Saraniya A, Jeevaratnam K (2012) Molecular characterization of bacteriocinogenic Lactobacillus species isolated from fermented Uttapam batter. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 9:417–421
Saraniya A, Jeevaratnam K (2014a) Optimization of nutritional and non-nutritional factors involved for production of antimicrobial compounds from Lactobacillus pentosus SJ65 using response surface methodology. Brazilian J Microbiol 45:81–88
Saraniya A, Jeevaratnam K (2014b) Purification and mode of action of antilisterial bacteriocins produced by Lactobacillus pentosus SJ65 isolated from Uttapam batter. J Food Biochem 38:612–619
Schaefer L, Auchtung TA, Hermans KE et al (2010) The antimicrobial compound reuterin (3-hydroxypropionaldehyde) induces oxidative stress via interaction with thiol groups. Microbiology 156:1589–1599. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.035642-0
Schwenninger SM, Lacroix C, Truttmann S et al (2008) Characterization of low-molecular-weight antiyeast metabolites produced by a food-protective Lactobacillus-Propionibacterium coculture. J Food Prot 71:2481–2487. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-71.12.2481
Su S, Yin P, Li J et al (2020) In vitro and in vivo anti-biofilm activity of pyran derivative against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Public Health 13:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2019.10.010
Sun W, Weingarten RA, Xu M et al (2016) Rapid antimicrobial susceptibility test for identifi cation of new therapeutics and drug combinations against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Emerg Microbes Infect 5:e116–e211. https://doi.org/10.1038/emi.2016.123
Tagg J, McGiven AR (1971) Assay system for bacteriocins. Appl Microbiol 21:943
Tong Z, Zhang L, Ling J et al (2014) An in vitro study on the effect of free amino acids alone or in combination with nisin on biofilms as well as on planktonic bacteria of Streptococcus mutans. PLoS ONE 9:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099513
Valgas C, de Souza SM, Smânia EFA, Smânia A Jr (2007) Screening methods to determine antibacterial activity of natural products. Braz J Microbiol 38:369–380
Vidhyasagar V, Jeevaratnam K (2013) Bacteriocin activity against various pathogens produced by Pediococcus pentosaceus VJ13 isolated from Idly batter. Biomed Chromatogr 27:1497–1502. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.2948
Wang Q, Sun FJ, Liu Y et al (2010) Enhancement of biofilm formation by subinhibitory concentrations of macrolides in icaADBC-positive and -negative clinical isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:2707–2711. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01565-09
Wu S, Liu G, Jin W et al (2016) Antibiofilm and anti-infection of a marine bacterial exopolysaccharide against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00102
Yang Z, Suomalainen T, Mayra-makinen A, Huttunenl E (1997) Antimicrobial activity of 2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic produced by lactic acid bacteria acid. J Food Prot 60:786–790
Yang EJ, Kim Y-S, Chang HC (2011) Purification and characterization of antifungal δ-dodecalactone from Lactobacillus plantarum AF1 isolated from kimchi. J Food Prot 74:651–657
Yang H, Zhang Y, Huang Y et al (2014) Degradation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms using a chimeric lysin. Biofouling 30:667–674. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2014.905927
Yu K, Lo JCY, Yan M et al (2017) Biomaterials Anti-adhesive antimicrobial peptide coating prevents catheter associated infection in a mouse urinary infection model. Biomaterials 116:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.11.047
Zgoda JR, Porter JR (2001) A convenient microdilution method for screening natural products against bacteria and fungi. Pharm Biol 39:221–225
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute (MGMCRI), Pondicherry, India for providing clinical strains for this study. We are grateful to SAIF, IIT Madras, Chennai for SEM analysis, Central instrumentation facility (CIF), Pondicherry University for NMR and FT-IR analysis and Department of Chemistry, Pondicherry University, Pondicherry for providing the HR ESI-MS data.
Funding
The work was not supported by any external or internal funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray Mohapatra, A., Harikrishnan, A., Lakshmanan, D. et al. Targeting Staphylococcus aureus and its biofilms with novel antibacterial compounds produced by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SJ33. Arch Microbiol 204, 20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02630-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02630-x