Abstract
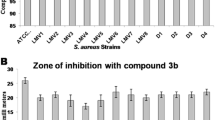
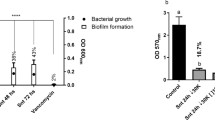
Staphylococcus aureus biofilms are the pathogenic factor in the spread of infection and are more pronounced in multidrug-resistant strains of S. aureus, where high expression of proteases is observed. Among various proteases, Serine protease (SspA) and cysteine protease Staphopain B (SspB) are known to play a key role in the biofilm formation and removal of biofilms. In earlier studies, we have reported Dibenzyl (benzo [d] thiazol-2-yl (hydroxy) methyl) phosphonate (DBTMP) exhibits anti-S. aureus and anti-biofilm properties by elevating the expression of the protease. In this study, the effect of DBTMP on the activities of SspA, and SspB of S. aureus was evaluated. The SspA and SspB genes of S. aureus ATCC12600 were sequenced (Genbank accession numbers: MZ456982 and MW574006). In S. aureus active SspA is formed by proteolytic cleavage of immature SspA, to get this mature SspA (mSspA), we have PCR amplified the mSspA sequence from the SspA gene. The mSspA and SspB genes were cloned, expressed, and characterized. The pure recombinant proteins rSspB and rmSspA exhibited a single band in SDS–PAGE with a molecular weight of 40 and 30 KD, respectively. The activities of rmSspA and rSspB are 32.33 and 35.45 Units/mL correspondingly. DBTMP elevated the activities of rmSspA and rSspB by docking with respective enzymes. This compound disrupted the biofilms formed by the multidrug-resistant strains of S. aureus and further prevented biofilm formation. These findings explain that DBTMP possesses anti-S. aureus and anti-biofilm features.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SspA:
-
Staphylococcal serine protease A
- SspB:
-
Staphylococcal staphopain B
- DBTMP:
-
Dibenzyl (benzo [d] thiazol-2-yl (hydroxy) methyl) phosphonate
- mSspA:
-
Mature SspA
- ATCC:
-
American type cell culture
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- SDS–PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- KD:
-
Kilodalton
- EPS:
-
Extracellular polymeric substances
- MSCRAMMs:
-
Microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules
- icaADBC:
-
Intercellular adhesion ADBC
- PIA:
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin
- Fnbp:
-
Fibronectin-binding protein
- SpA:
-
Surface protein A
- Agr:
-
Accessory gene regulator
- SarA:
-
Staphylococcal accessory regulator
- LMV:
-
Local milk vendor
- D:
-
Dairy herds
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani
- BHI:
-
Brain–Heart infusion
- TLC:
-
Thin layer chromatography
- SMA:
-
Skim milk agar
- CFU:
-
Colony forming units
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl ß-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
References
Ali MM, Mansoor R, Zahra QA, Liangliang L, Gangguo W, Ali R, Kazmi A, Khan MI (2021) Frequency and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human pus samples at holy family hospital Rawalpindi. Open Access J Microbiol Biotechnol 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.23880/oajmb-16000189
Archer NK, Mazaitis MJ, Costerton JW, Leid JG, Powers ME, Shirtliff ME (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence 2(5):445–459. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.2.5.17724
Beenken KE, Mrak LN, Griffin LM, Zielinska AK, Shaw LN, Rice KC, Horswill AR, Bayles KW, Smeltzer MS (2010) Epistatic relationships between sarA and agr in Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10790. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010790
Bobofchak KM, Pineda AO, Mathews FS, Di Cera E (2005) Energetic and structural consequences of perturbing Gly-193 in the oxyanion hole of serine proteases. J Biol Chem 280(27):25644–25650. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M503499200
Boles BR, Horswill AR (2008) Agr-mediated dispersal of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS Pathog 4(4):e1000052. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000052
Boles B, Thoendel R, Roth AJ, Horswill AR (2010) Identification of genes involved in polysaccharide-independent Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 5(4):e10146. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010146
Brown ED (2006) Microbiology: antibiotic stops “ping-pong” match. Nature 441(7091):293–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/441293a
Cassat JE, Hammer ND, Campbell JP, Benson MA, Perrien DS, Mrak LN, Smeltzer MS, Torres VJ, Skaar EP (2013) A secreted bacterial protease tailors the Staphylococcus aureus virulence repertoire to modulate bone remodeling during osteomyelitis. Cell Host Microbe 13(6):759–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2013.05.003
Charney J, Tomarelli RM (1947) A colorimetric method for the determination of the proteolytic activity of duodenal juice. J Biol Chem 171(2):501–505
Chen C, Krishnan V, Macon K, Manne K, Narayana SV, Schneewind O (2013) Secreted proteases control autolysin-mediated biofilm growth of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem 288(41):29440–29452. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.502039
Cheung AL, Eberhardt K, Heinrichs JH (1997) Regulation of protein A synthesis by the sar and agr loci of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 65(6):2243–2249. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.65.6.2243-2249.1997
Cramton SE, Gerke C, Schnell NF, Nichols WW, Götz F (1999) The intercellular adhesion (ica) locus is present in Staphylococcus aureus and is required for biofilm formation. Infect Immun 67(10):5427–5433. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.67.10.5427-5433.1999
Dancer SJ, Garratt R, Saldanha J, Jhoti H, Evans R (1990) The epidermolytic toxins are serine proteases. FEBS Lett 268(1):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(90)80990-z
Drapeau GR (1978) The primary structure of staphylococcal protease. Can J Biochem 56(6):534–544. https://doi.org/10.1139/o78-082
Dubin G (2003) Defense against own arms: staphylococcal cysteine proteases and their inhibitors. Acta Biochim Pol 50(3):715–724
Foster TJ (2019) The MSCRAMM family of cell-wall-anchored surface proteins of gram-positive cocci. Trends Microbiol 27(11):927–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2019.06.007
Gimza BD, Larias MI, Budny BG, Shaw LN (2019) Mapping the global network of extracellular protease regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. mSphere 4(5):e00676-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00676-19
Guo Y, Song G, Sun M, Wang J, Wang Y (2020) Prevalence and therapies of antibiotic-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:107. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00107
Hassoun A, Linden PK, Friedman B (2017) Incidence, prevalence, and management of MRSA bacteremia across patient populations—a review of recent developments in MRSA management and treatment. Crit Care (Lond, Engl) 21(1):211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-017-1801-3
Izano EA, Amarante MA, Kher WB, Kaplan JB (2008) Differential roles of poly-N-acetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(2):470–476. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02073-07
Jenul C, Horswill AR (2019) Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Microbiol Spectrum 7(2). https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0031-2018
Kantyka T, Shaw LN, Potempa J (2011) Papain-like proteases of Staphylococcus aureus. Adv Exp Med Biol 712:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8414-2_1
Khan MI, Xua S, Ali MM, Ali R, Kazmi A, Akhtar N, Bilal M, Hua Y, Li F (2020) Assessment of multidrug resistance in bacterial isolates from urinary tract-infected patients. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 13(1):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/16878507.2020.1730579
Kisil OV, Efimenko TA, Gabrielyan NI, Efremenkova OV (2020) Development of antimicrobial therapy methods to overcome the antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii. Acta Nat 12(3):34–45. https://doi.org/10.32607/actanaturae.10955
Kwon K, Hasseman J, Latham S, Grose C, Do Y, Fleischmann RD, Pieper R, Peterson SN (2011) Recombinant expression and functional analysis of proteases from Streptococcus pneumoniae, Bacillus anthracis, and Yersinia pestis. BMC Biochem 12:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2091-12-17
Lakhundi S, Zhang K (2018) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: molecular characterization, evolution, and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 31(4):e00020-e118. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00020-18
Lim Y, Jana M, Luong TT, Lee CY (2004) Control of glucose- and NaCl-induced biofilm formation by rbf in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 186(3):722–729. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.3.722-729.2004
Mann EE, Rice KC, Boles BR, Endres JL, Ranjit D, Chandramohan L, Tsang LH, Smeltzer MS, Horswill AR, Bayles KW (2009) Modulation of eDNA release and degradation affects Staphylococcus aureus biofilm maturation. PLoS ONE 4(6):e5822. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005822
Mantravadi PK, Kalesh KA, Dobson R, Hudson AO, Parthasarathy A (2019) The quest for novel antimicrobial compounds: emerging trends in research, development, and technologies. Antibiotics (Basel, Switzerland) 8(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8010008
Martí M, Trotonda MP, Tormo-Más MA, Vergara-Irigaray M, Cheung AL, Lasa I, Penadés JR (2010) Extracellular proteases inhibit protein-dependent biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbes Infect 12(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2009.10.005
McGavin MJ, Zahradka C, Rice K, Scott JE (1997) Modification of the Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin binding phenotype by V8 protease. Infect Immun 65(7):2621–2628. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.65.7.2621-2628.1997
Miedzobrodzki J, Kaszycki P, Bialecka A, Kasprowicz A (2002) Proteolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from the colonized skin of patients with acute-phase atopic dermatitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Inf Dis Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol 21(4):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0706-4
Mootz JM, Malone CL, Shaw LN, Horswill AR (2013) Staphopains modulate Staphylococcus aureus biofilm integrity. Infect Immun 81(9):3227–3238. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00377-13
Nguyen H, Nguyen TH, Otto M (2020) The staphylococcal exopolysaccharide PIA—biosynthesis and role in biofilm formation, colonization, and infection. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 18:3324–3334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2020.10.027
Nickerson NN, Prasad L, Jacob L, Delbaere LT, McGavin MJ (2007) Activation of the SspA serine protease zymogen of Staphylococcus aureus proceeds through unique variations of a trypsinogen-like mechanism and is dependent on both autocatalytic and metalloprotease-specific processing. J Biol Chem 282(47):34129–34138. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705672200
Oleksy A, Golonka E, Bańbuła A, Szmyd G, Moon J, Kubica M, Greenbaum D, Bogyo M, Foster TJ, Travis J, Potempa J (2004) Growth phase-dependent production of a cell wall-associated elastinolytic cysteine proteinase by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biol Chem 385(6):525–535. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2004.062
O’Neill E, Pozzi C, Houston P, Smyth D, Humphreys H, Robinson DA, O’Gara JP (2007) Association between methicillin susceptibility and biofilm regulation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from device-related infections. J Clin Microbiol 45(5):1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02280-06
Park H, Lee J, Lee S (2006) Critical assessment of the automated AutoDock as a new docking tool for virtual screening. Proteins 65(3):549–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21183
Pietrocola G, Nobile G, Rindi S, Speziale P (2017) Staphylococcus aureus manipulates innate immunity through own and host-expressed proteases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00166
Prasad UV, Vasu D, Yeswanth S, Swarupa V, Sunitha MM, Choudhary A, Sarma PV (2015) Phosphorylation controls the functioning of Staphylococcus aureus isocitrate dehydrogenase–favours biofilm formation. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 30(4):655–661. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2014.959945
Pustelny K, Zdzalik M, Stach N, Stec-Niemczyk J, Cichon P, Czarna A, Popowicz G, Mak P, Drag M, Salvesen GS, Wladyka B, Potempa J, Dubin A, Dubin G (2014) Staphylococcal SplB serine protease utilizes a novel molecular mechanism of activation. J Biol Chem 289(22):15544–15553. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.507616
Ramírez-Larrota JS, Eckhard U (2022) An introduction to bacterial biofilms and their proteases, and their roles in host infection and immune evasion. Biomolecules 12(2):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020306
Rice K, Peralta R, de Bast D, Azavedo J, McGavin MJ (2001) Description of staphylococcus serine protease (ssp) operon in Staphylococcus aureus and nonpolar inactivation of sspA-encoded serine protease. Infect Immun 69(1):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.69.1.159-169.2001
Rom JS, Beenken KE, Ramirez AM, Walker CM, Echols EJ, Smeltzer MS (2021) Limiting protease production plays a key role in the pathogenesis of the divergent clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus LAC and UAMS-1. Virulence 12(1):584–600. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2021.1879550
Shaw L, Golonka E, Potempa J, Foster SJ (2004) The role and regulation of the extracellular proteases of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology (Reading, Engl) 150(Pt 1):217–228. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.26634-0
Swarupa V, Chaudhury A, Sarma P (2018) Iron enhances the peptidyl deformylase activity and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. 3 Biotech 8(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1050-9
Taylor TA, Unakal CG (2022) Staphylococcus aureus [Updated 2022 Feb 14]. In: Stat Pearls [Internet]. Stat Pearls Publishing, Treasure Island, FL. Available from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441868/
Turner NA, Sharma-Kuinkel BK, Maskarinec SA, Eichenberger EM, Shah PP, Carugati M, Holland TL, Fowler VG Jr (2019) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an overview of basic and clinical research. Nat Rev Microbiol 17(4):203–218. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0147-4
VudhyaGowrisankar YM, Mudhu S, Pasupuleti SK, Suthi S, Chaudhury A, Sarma P (2021) Staphylococcus aureus grown in anaerobic conditions exhibits elevated glutamine biosynthesis and biofilm units. Can J Microbiol 67(4):323–331. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2020-0434
Yeswanth S, Nanda Kumar Y, Venkateswara Prasad U, Swarupa V, Koteswararao V, Sarma VGK (2013) Cloning and characterization of l-lactate dehydrogenase gene of Staphylococcus aureus. Anaerobe 24:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2013.09.003
Yeswanth S, Chaudhury A, Sarma P (2017) Quantitative expression analysis of SpA, FnbA and Rsp genes in Staphylococcus aureus: actively associated in the formation of biofilms. Curr Microbiol 74(12):1394–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1331-x
Yeswanth S, Sekhar KC, Chaudhury A, Sarma PVGK (2018) Anti-microbial and antibiofilm activity of a novel dibenzyl (benzo[d] thiazol-2-yl (hydroxy) methyl) phosphonate by inducing protease expression in Staphylococcus aureus. Med Chem Res 27:785–795
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Sri Venkateswara Institute of Medical Sciences and University, under the SBAVP scheme for providing funds and facilities to carry out this research work. This paper forms a part of my Ph.D. thesis work to be submitted to SVIMS University, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Funding
This work was funded by Sri Balaji Arogya Vara Prasadini Scheme (SBAVP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PVGKS, AC, and GD: Designed the work. SSR and GD conducted the experiments, PVGKS, AC, and GD analyzed the results, and prepared and edited the manuscript. All the authors concurred with the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deepika, G., Subbarayadu, S., Chaudhary, A. et al. Dibenzyl (benzo [d] thiazol-2-yl (hydroxy) methyl) phosphonate (DBTMP) showing anti-S. aureus and anti-biofilm properties by elevating activities of serine protease (SspA) and cysteine protease staphopain B (SspB). Arch Microbiol 204, 397 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02974-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02974-y