Abstract
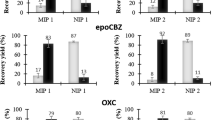
A novel method is described for trace determination of sotalol, a β-blocker drug, using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction (MISPE) coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection (HPLC/UV). The synthesis of the molecularly imprinted polymer was performed using acrylamide, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, dimethylformamide, 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile and sotalol as a functional monomer, cross-linker monomer, solvent, initiator, and target drug, respectively. Scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy were used for characterizing the synthesized polymers. Also, a central composite design under response surface methodology and chemometrics applied to investigate and optimize the molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction procedure parameters such as pH, loading and eluent solvent flow-rate, eluent solvent volume and sorbent mass, that probably influence the extraction process, to achieve the highest sotalol extraction efficiency. Batch rebinding capacity of sotalol was determined from the derived Langmuir isotherm and was found to be 20.08 mg/g. At above specified conditions, the proposed MISPE-HPLC/UV method used for the separation of trace amounts of sotalol in human urine samples with acceptable high recoveries (97–102%) and RSD% lower than 5%. The limit of detection and limit of quantification of the method were 0.01 and 0.04 μg/mL, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIBN :
-
2,2azobisisobutyronitrile
- AM :
-
acrylamide
- CCD :
-
central composite design
- DMF :
-
dimethylformamide
- EGDMA :
-
ethylene glycol dimethacrylate
- LLE :
-
liquid-liquid extraction
- MIP :
-
molecularly imprinted polymer
- MISPE :
-
molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction
- NIP :
-
nonimprinted polymer
- SPE :
-
solid phase extraction
References
Abdel Razeq SA, Abel Salam KM, Fouad MM, Mohamed TF (2014) Stability-indicating densitometric, fluorimetric and difference absorbance (∆A) methods for the determination of sotalol-HCl. World J Pharm Res 3:1–13
Abirami G, Kumar KA, Veterichelvan T, Muvva A (2013) Analytical method development and validation of estimation method for sotalol hydrochloride tablets by using RP-HPLC. Indian J Res Pharm Biotechnol 1:736–740
Ak D, Gül Dal A, Tuncel M (2007) Determination of sotalol in tablets and serum by CZE. Chromatographia 66:159–163
Ansari S (2017a) Application of hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymer using K2Ti4O9 coupled with SPE–HPLC for the determination of celecoxib in human urine samples: optimization by central composite design (CCD). Anal Methods 9:3200–3212
Ansari S (2017b) Application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as a versatile and highly selective tool in food and environmental analysis: Recent developments and trends. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 90:89–106
Ansari S (2017c) Combination of molecularly imprinted polymers and carbon nanomaterials as a versatile biosensing tool in sample analysis: Recent applications and challenges. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2017.05.015
Ansari S, Karimi M (2017a) Novel developments and trends of analytical methods for drug analysis in biological and environmental samples by molecularly imprinted polymers. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 89:146–162
Ansari S, Karimi M (2017b) Recent configurations and progressive uses of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for drug analysis. Talanta 167:470–485
Ansari S, Karimi M (2017c) Recent progress, challenges and trends in trace determination of drug analysis using molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction technology. Talanta 164:612–625
Baranowska I, Wilczek A (2009) Simultaneous RP-HPLC determination of sotalol, metoprolol, alpha-hydroxymetoprolol, paracetamol and its glucuronide and sulfate metabolites in human urine. Anal Sci 25:769–772
Du B, Qu T, Chen Z, Cao X, Han S, Shen G, Wang L (2014) A novel restricted access material combined to molecularly imprinted polymers for selective solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography determination of 2-methoxyestradiol in plasma samples. Talanta 129:465–472
Garcia R, Cabrita MJ, Costa Freitas AM (2011) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of pesticide residues in food-a highly selective and innovative approach. Am J Anal Chem 2:16–25
Hanyok JJ (1993) Clinical pharmacokinetics of sotalol. Am J Cardiol 72:19A–26A
Haupt K, Dzgoey A, Mosbach K (1998) Assay system for the herbicide 2,4-dichiorophenoxyacetic acid using a molecularly imprinted polymer as an artificial recognition element. Anal Chem 70:628–631
Hua L, Dan L (2015) Preparation of a pipette tip-based molecularly imprinted solid-phase micro-extraction monolith by epitope approach and its application for determination of enkephalins in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Pharm Biomed Anal 115:330–338
Javanbakht M, Eynollahi Fard S, Mohammadi A, Abdouss M, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Safaraliee L (2008) Molecularly imprinted polymer based potentiometric sensor for the determination of hydroxyzine in tablets and biological fluids. Anal Chim Acta 612:65–74
Jiao-Jiao D, Rui-Xia G, Hu Y, Xiao-Jing L, Hui M (2015) Selective extraction of dimethoate from cucumber samples by use of molecularly imprinted microspheres. J Pharm Anal 5:200–206
Jin Y, Row KH (2005) Adsorption isotherm of ibuprofen on molecular imprinted polymer. Korean J Chem Eng 22:264–267
Kolaei M, Dashtian K, Rafiee Z, Ghaedi M (2016) Ultrasonic-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of morphine in urine samples by new imprinted polymer-supported on MWCNT-Fe3O4-NPs: Central composite design optimization. Ultrason Sonochem 33:240–248
Koohpaei AR, Shahtaheri SJ, Ganjali MR, Rahimi Forushani A, Golbabaei F (2008) Application of multivariate analysis to the screening of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) for ametryn. Talanta 75:978–986
Läer S, Wauer I, Scholz H (2001) Small blood volumes from children for quantitative sotalol determination using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 753:421–425
Lanzhe Y, Yanbin Y, Weijun Zh, Lihua W (2011) Preparation, recognition characteristics and properties for quercetin molecularly imprinted polymers. Desalination Water Treat 34:309–314
Lefebvre MA, Girault J, Saux MCl, Fourtillan JB (1980) Fluorometric high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of sotalol in biological fluids. J Pharm Sci 69:1216–1217
Liu QS, Zheng T, Li N, Wang P, Abulikemu G (2010) Modification of bamboo-based activated carbon using microwave radiation and its effects on the adsorption of methylene blue. Appl Surf Sci 256:3309–3315
Matysova L, Zahalkova O, Klovrzova S, Sklubalova Z, Solich P, Zahalka L (2015) Development of a gradient HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of sotalol and sorbate in oral liquid preparations using solid core stationary phase. J Anal Methods Chem. doi:10.1155/2015/806736
Najafi M, Yousefi Y, Rafati AA (2012) Synthesis, Characterization and adsorption studies of several heavy metal ions on amino-functionalized silica nano hollow sphere and silica gel. Sep Purif Tech 85:193–205
Omidi F, Behbahani M, Sadeghi Abandansari H, Sedighi A (2014) Application of molecular imprinted polymer nanoparticles as a selective solid phase extraction for preconcentration and trace determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in the human urine and different water samples. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:137–138
Rao RN, Maurya PK, Khalid S (2011) Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction followed by liquid chromatographic determination of sitagliptin in rat plasma and urine. Talanta 85:950–957
Sharma PS, Dabrowski M, D’Souza F, Kutner W (2013) Surface development of molecularly imprinted polymer films to enhance sensing signals. Trends Anal Chem 51:146–157
Shoufang X, Jinhua L, Lingxin C (2011) Molecularly imprinted polymers by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer precipitation polymerization for preconcentration of atrazine in food matrices. Talanta 85:282–289
Song XL, Li JH, Wang JT, Chen LX (2009) Quercetin molecularly imprinted polymers: Preparation, recognition, characteristics and properties as sorbent for solid-phase extraction. Talanta 80:694–702
Udaykumar P (2010) Textbook of medical pharmacology. CBS publishers & Distributors LTD, New Delhi
Zhang HM, Yang JY, Du LM, Lia CF, Wua H (2011) Determination of sotalol by fluorescence quenching method. Anal Methods 3:1156–1162
Zhong Lan S, Dong Y, Qing S (2011) Selective solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for analysis of methamidophos in water and soil samples. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:473–479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, S., Karimi, M. Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective solid phase extraction trace amount of sotalol from human urine samples: Optimization by central composite design (CCD). Med Chem Res 26, 2477–2490 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1947-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1947-1