Abstract
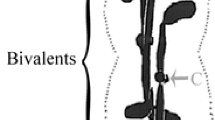
In spermatogonial mitoses of Dysdercus intermedius, chromosomal spindle microtubules insert in discrete kinetochores. The latter consist of two electron dense plates of about 0,3 μm diameter located at opposite sites at the poleward surfaces of the daughter chromatids. The evidence presented permits the interpretation that a localized kinetochore owes its layered substructure to successive binding sites for kinetochore material at the ends of bundled microtubules. A working hypothesis, based upon different distributions of genetic loci for kinetochore material in species with localized and diffuse kinetochores is proposed. In Dysdercus, holokinetic chromosome behavior in mitotic anaphase movement is not due to truly diffuse kinetochores but to chromosomal interconnections which are established at prometaphase. Such interconnections are absent in the first meiotic division when each bivalent is enclosed by a sheath of endoplasmic reticulum. Spindle microtubules penetrate through terminal openings in this sheath and end singly in dense spots of kinetochore material.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bajer, A.: Chromosome movement and fine structure of the mitotic spindle. In: Aspects of cell motility (22. Sym. Soc. Exptl. Biol.), p. 286–310. New York: Columbia Univ. Press 1968.
Bauer, H.: Die kinetische Organisation der Lepidopteren-Chromosomen. Chromosoma (Berl.) 22, 101–125 (1967).
Braselton, J. P.: The ultrastruoture of the non-localized kinetochores of Luzula and Cyperus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 36, 89–99 (1971).
Brinkley, B. R., and Hsu, T.C.: The effects of colcemid inhibition and reversal on the fine structure of the mitotic apparatus of Chinese hamster cells in vitro. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 19, 1–18 (1967).
Brinkley, B. R., Stubblefield, E.: Ultrastructure and interaction of the kinetochore and centriole in mitosis and meiosis. In: Advanc. Cell Biol. 1, 119–185 (1970).
Brown, S. W.: Mitosis and Meiosis in Luzula campestris Dc. Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot. 27, 231–278 (1954).
Buck, R. C.: Mitosis and meiosis in Rhodnius prolixus: the fine structure of the spindle and diffuse kinetochore. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 18, 489–501 (1967).
Callan, H. G., Lloyd, L.: Lamprush chromosomes of crested newts Triturus cristatus. Phil. Trans. B 243, 135–219 (1960).
Fuge, H.: Spindelbau, Mikrotubuliverteilung und Chromosomenstruktur während der I. meiotischen Teilung der Spermatocyten von Pales ferruginea. Eine elektronenmikroskopische Analyse. Z. Zellforsch. 120, 579–599 (1971).
Godward, M. B. E.: The ‚'diffuse“ centromere or polycentric chromosomes of Spirogyra. Ann. Bot. 18, 143–156 (1954).
Håkansson, A.: Holocentric chromosomes in Eleocharis. Hereditag (Lund) 44, 531–540 (1958).
Hughes-Schrader, S., Ris, H.: The diffuse spindle attachment of coccids, verified by the mitotic behavior of induced chromosome fragments. J. exp. Zool. 87, 429–456 (1941).
Hughes-Schrader, S., Schrader, F.: The kinetochore of the Hemiptera. Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 327–350 (1961).
Jokelainen, P. T.: The ultrastructure and spatial organization of the metaphase kinetochore in mitotic rat cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 19, 19–44 (1967).
Lima-de-Faria, A.: The role of the kinetochore in chromosome organization. Hereditas (Lund) 42, 85–160 (1956).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Luykx, P.: Cellular mechanisms of chromosome distribution. Int. Rev. Cytol. Suppl. 2, 1–173 (1970).
Malheiros, N., DeCastro, D.: Chromosome number and behavior in Luzula purpura Link. Nature (Lond.) 160, 156 (1949).
Mendes, L.O. T.: Observacoes citologicas em Dysdercus. Bragantica 9, 53–57 (1949).
Parshad, R.: Cytological studies in Heteroptera II. Cytologia (Tokyo) 22, 127–135 (1957).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Ris, H.: A cytological and experimental analysis of the meiotic behavior of the univalent × chromosome in the bearberry aphid Tamalia (=Phyllaphis) coweni (Ckll.), J. exp. Zool. 90, 267–330 (1942).
Roth, L. E., Pihlaja, D. J., Shigenaka, J.: Microtubules in the heliozoan axopodium I. The gradion hypothesis of allosterism in structural proteins. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 30, 7–37 (1970).
Schrader, F.: Notes on the mitotic behavior of long chromosomes. Cytologia (Tokyo) 6, 422–430 (1935).
Trump, B. F., Smuckler, E. A., Benditt, E. P.: A method for staining epoxy sections for ligth microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 5, 343–348 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruthmann, A., Permantier, Y. Spindel und kinetochoren in der Mitose und Meiose der Baumwollwanze Dysdercus intermedius (Heteroptera). Chromosoma 41, 271–288 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344022
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344022