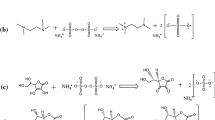
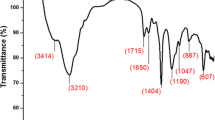
Abstract
The main objective of this research work is to reveal the detailed and extensive rheological characterization of terpolymeric hydrogel formulations using a variety of monomers having different concentrations of acrylic acid and applying a range of temperatures. The hydrogels with the different concentrations of acrylic acid were prepared in the absence of air using three different monomers, by free radical polymerization, gradually increasing the temperature up to polymerization point, using ethyl alcohol as solvent. Different shear measurements were performed to study rheological properties, temperature dependence, and yield strength of acrylic acid pharmaceutical hydrogels. Various models were applied to analyze the rheological behavior of the gels. The acrylic acid pharmaceutical gels having physical cross links in the gel networks, exhibit remarkable temperature dependence especially with relatively higher concentration of acrylic acid at greater shear rate. Flow curves plotted at various temperatures indicate that these gels exhibit a reasonable pseudoplastic behavior. All these hydrogels require appropriate yield strength to break their network structures. The gel samples exhibit the best fit to the Modified Bingham model, which can explain the overall flow behavior of these topical gels. The rheological analysis indicates that these gels may be used as topical gels for targeted and controlled drug delivery at a specific site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alina, O., D. P. Christina, V. G. Mihaela, M. P. Laidia, and I. Lucian, 2011, Rheological study of a liposomal hydrogel based on carbapol, Roman, Biotech. Lett. 16, 47–54.
Attapatu, D. D., R. P. Chhabara, and D. H. T. UhCherr, 1990, Wall effect for spheres falling at small Reynolds-number in a viscoplastic medium, J, Non-Newtonian Fluid. Mech. 38, 31–42.
Barners, H. A., 1999, A brief history of the yield stress, Appl. Rheol. 9, 262–266.
Bird, R. B., R. C. Armstrong, and O. Hassager, Dynamics of polymer liquids, 2nd Ed. Wiley, New York (1987).
Boss, G. W., J. J. L. Jacobs, S. R. van Tomme, T. F. J. Veldhuis, C. F. van Nostrum, W. D. Otter, and E. E. Hennik, 2004, In situ cross linked biodegradable hydrogels loaded with 1L -2 are effective tools for local 1L-2 therapy, Eur. J. Phar. Sci. 21, 561–567.
Chang, J. Y., Y. K. Oh, H. G. Choi, Y. B. Kim, and C. K. Kim, 2002, Rheological evaluation of thermosensitive and mucoadhesive vaginal gels in physiological conditions, Int. J. Pharm. 241, 155–163.
Chatterjee, S. and H. B. Bohidar, 2006, Effect of salt and temperature on viscoelasticity of gelatin hydrogels, J. Surface Sci. Technol. 22, 1–13.
Chen, T. H., H. D. Embree, E. M. Brown, M. M. Taylor, and G. F. Payne, 2003, Enzyme-catalyzed gel formulation of gelatin and chitosan: Potential for in situ applications, Biomaterials. 24, 2831–2847.
Dodov, M. G., E. F. Kumbaradzi, K. Goracinova, S. Calis, M. Simonoska, and A. A. Hincal, 2003, 5-Fluorouracil in topical liposomal gels for anticancer treatment-formation and evaluation, Acta. Pharm. 53, 241–250.
Drury, J. L. and D. J. Mooney, 2003, Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications, Biomaterials. 24, 4337–4351.
Fergusen, J. and Z. Kemblowski, Applied fluid rheology, Elsevier Applied Science, London and New York (1992).
Guan, L., H. Xu, and D. Huang, 2010, The effect of ions on thermal behaviors of poly (acrylic acid)/water mixtures, Polym. (Korea) 34, 386–389.
Hatefi, A. and B. Amsden, 2002, Biodegradable injectable in situ formatting drug delivery systems, J. Control. Release. 80, 9–28.
Hennik, W. E. and C. F. van Nostrum, 2002, Novel cross linking methods to design hydrogels, Adv. Drug Deliver 54, 13–36.
Islam, M. T., N. R. Hornido, S, Ciotti, and C, Ackermann, 2004, Rheological characterization of topical carbomer gels neutralized to different pH, Pharm. Research. 21, 1192–1199.
Jeong, B., S.W. Kim, and Y. H. Bae, 2002, Thermo-sensitive solgel reversible hydrogels, Adv. Drug Deliver 54, 37–51.
Keiweg, S. L., A. R. Geonnotti, and D. F. Katz, 2004, Gravityinduced coating films of vaginal gel formulations: in vitro experimental analysis, J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 2941–2952.
Khutoryanskiy, V. V., A. V. Dubolazov, Z. S. Nurkeeva, and G. A. Mun, 2004, pH effects in complex formation and blending of poly (acrylic acid) with poly (ethylene oxide), Langmuir 20, 3785–3790.
Kim, J. Y., J. Y. Song, E. J. Lee, and S. K. Park, 2003, Rheological properties and microstructures of carbopol gel nerwork system, Colloid Polym. Sci. 281, 614–623.
Larson, R. J., The structure and rheology of complex fluids, oxford University Press, New York (1999).
Levy, M. C. and M. C. Andry, 1991, Mixed-walled microcapsules made of cross linked proteins and poly sacchrides-Preparation and properties, J. Microencapsule. 8, 335–347.
Li, S. M. and M. Vert, 2003, Synthesis, characterization and stereocomplex-induced gelation of block copolymers prepared by ring opening polymerization of L (D) -lactide in the presence of poly (ethylene glycol), Macromolecules 36, 8008–8014.
Nae, H. N. and W. W. Reichert, 1992, Rheological properties of lightly cross linked carboxy copolymers in aqueous solutions, Rheol. Acta 31, 351–361.
Nguyen, Q. D. and D. V. Boger, 1983, Yield stress measurement for concentrated suspensions, J. Rheol. 27, 321–349.
Okay, O. and C. Gurun, 1992, Synthesis and formation mechanism of porous 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate ethylene-glycoldimethacrylate copolymer beads, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 46, 401–4110.
Owen, D. H., J. J. Peters, and D. F. Katz, 2001, Comparison of the rheological properties of Advantage-S and Replens, Contraception 64, 393–396.
Ramirez, A., M. J. Fresno, M. M. Jimenenz, and E. Selles, 1999, Rheological study of Carbopoly (R) Ultrez (TM) 10 hydroalcoholic gels, I: Flow and thixotropic behavior as a function of pH and polymer concentration, Pharmazei. 54, 444–447.
Rudraraju, V. S. and C. M. Wyandt, 2005, Rheology of microcrystalline cellulose and sodiumcarboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels using a controlled stress rheometer: part II. Int. J. Pharm. 292, 63–73.
Tamburic, S. and D. Q. M. Craig, 1996, The effects of aging on the rheological, dielectric and mucoadhesive properties of poly (acrylic acid) gel systems, Pharm. Res. 13, 279–283.
Thor Geirs Dottier, T. O., A. L. Kjoniksen, K. D. Knudsen, T. Kristmunds Dottier, and B. Nystrom, 2005, Viscoelastic and structural properties of pharmaceutical hydrogels containing monocaprin, Europ. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 59, 333–392.
Tomme, S. R. V., M. J. V. Steenbergen, S. C. D. Smedth, C. F. V. Nostrum, and W. E. Hennik, 2005, Self-gelling hydrogels based on opposite charged dextrin microspheres, Biomaterials. 26, 2129–2135.
Vyanahare, N. and J. Kohn, 1994, Photocrosslinked hydrogels based on copolymers of poly (ethylene glycol) and lysine, J. Polym. Sci: Part A Polym. Chem. 32, 1271–1281.
Yahia, A. and K. H. Khayat, 2001, Analytical models for estimating yield stress of high-performance pseudo plastic grout, Cement Concrete Research. 31, 731–738.
Zafar, Z. I., M.A. Malana, H. Pervez, M. A. Shad, and K. Momina, 2008, Synthesis and swelling kinetics of a cross linked pH-sensitive ternary co-polymer gel system, Polym. (Korea) 32, 1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malana, M.A., Zohra, R. & Khan, M.S. Rheological characterization of novel physically crosslinked terpolymeric hydrogels at different temperatures. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 24, 155–162 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-012-0019-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-012-0019-9