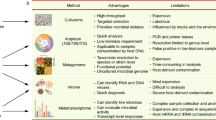
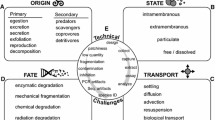
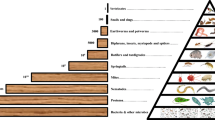
Abstract
Microbes are vital to the earth because of their enormous numbers and instinct function maintaining the natural balance. Since the microbiology was applied in environmental science and engineering more than a century ago, researchers desire for more and more information concerning the microbial spatio-temporal variations in almost every fields from contaminated soil to wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). For the past 30 years, molecular biologic techniques explored for environmental microbial community (EMC) have spanned a broad range of approaches to facilitate the researches with the assistance of computer science: faster, more accurate and more sensitive. In this feature article, we outlined several current and emerging molecular biologic techniques applied in detection of EMC, and presented and assessed in detail the application of three promising tools.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tiedje J, Donohue T. Microbes in the energy grid. Science, 2008, 320(5879): 985
Lemaire R, Webb R I, Yuan Z G. Micro-scale observations of the structure of aerobic microbial granules used for the treatment of nutrient-rich industrial wastewater. ISME J, 2008, 2(5): 528–541
Kartal B, Kuenen J G, van Loosdrecht M C M. Sewage treatment with anammox. Science, 2010, 328(5979): 702–703
Xu M Y, Wu W M, Wu L Y, He Z L, van Nostrand J D, Deng Y, Luo J A, Carley J, Ginder-Vogel M, Gentry T J, Gu B H, Watson D, Jardine P M, Marsh T L, Tiedje J M, Hazen T, Criddle C S, Zhou J Z. Responses of microbial community functional structures to pilot-scale uranium in situ bioremediation. ISME J, 2010, 4(8): 1060–1070
Fuhrman J A. Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature, 2009, 459(7244): 193–199
Hori T, Haruta S, Ueno Y, Ishii M, Igarashi Y. Dynamic transition of a methanogenic population in response to the concentration of volatile fatty acids in a thermophilic anaerobic digester. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(2): 1623–1630
Ikeda S, Rallos L E E, Okubo T, Eda S, Inaba S, Mitsui H, Minamisawa K. Microbial community analysis of field-grown soybeans with different nodulation phenotypes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(18): 5704–5709
Wood S A, Rueckert A, Cowan D A, Cary S C. Sources of edaphic cyanobacterial diversity in the Dry Valleys of Eastern Antarctica. ISME J, 2008, 2(3): 308–320
Kvennefors E C E, Sampayo E, Ridgway T, Barnes A C, Hoegh-Guldberg O. Bacterial communities of two ubiquitous Great Barrier Reef corals reveals both site- and species-specificity of common bacterial associates. PLOS ONE, 2010, 5(4):1–14
Mikkelsen D, Kappler U, McEwan A G, Sly L I. Probing the archaeal diversity of a mixed thermophilic bioleaching culture by TGGE and FISH. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2009, 32(7): 501–513
Xue D W, Feng S G, Zhao H Y, Jiang H, Shen B, Shi N N, Lu J J, Liu J J, Wang H Z. The linkage maps of Dendrobium species based on RAPD and SRAP markers. Journal of Genetics and Genomics = Yi Chuan Xue Bao, 2010, 37(3): 197–204
Rodas A M, Ferrer S, Pardo I. 16S-ARDRA, a tool for identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from grape must and wine. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2003, 26(3): 412–422
Deiglmayr K, Philippot L, Tscherko D, Kandeler E. Microbial succession of nitrate-reducing bacteria in the rhizosphere of Poa alpina across a glacier foreland in the Central Alps. Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 8(9): 1600–1612
Alvarado P, Manjón J L. Selection of enzymes for terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of fungal internally transcribed spacer sequences. Applied and Environ-mental Microbiology, 2009, 75(14): 4747–4752
Talbot G, Roy C S, Topp E, Beaulieu C, Palin M F, Massé D I. Multivariate statistical analyses of rDNA and rRNA fingerprint data to differentiate microbial communities in swine manure. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2009, 70(3): 540–552
Chandler D P, Kukhtin A, Mokhiber R, Knickerbocker C, Ogles D, Rudy G, Golova J, Long P, Peacock A. Monitoring microbial community structure and dynamics during in situ U(VI) bioremediation with a field-portable microarray analysis system. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(14): 5516–5522
Brulc J M, Antonopoulos D A, Berg Miller M E, Wilson M K, Yannarell A C, Dinsdale E A, Edwards R E, Frank E D, Emerson J B, Wacklin P, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B, Nelson K E, White B A. Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(6): 1948–1953
Mou X Z, Sun S L, Edwards R A, Hodson R E, Moran M A. Bacterial carbon processing by generalist species in the coastal ocean. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 708–711
Poitelon J B, Joyeux M, Welté B, Duguet J P, Prestel E, Lespinet O, DuBow M S. Assessment of phylogenetic diversity of bacterial microflora in drinking water using serial analysis of ribosomal sequence tags. Water Research, 2009, 43(17): 4197–4206
Sahl J W, Schmidt R H, Swanner E D, Mandernack K W, Templeton A S, Kieft T L, Smith R L, Sanford W E, Callaghan R L, Mitton J B, Spear J R. Subsurface microbial diversity in deepgranitic-fracture water in Colorado. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(1): 143–152
Burkhardt E M, Akob D M, Bischoff S, Sitte J, Kostka J E, Banerjee D, Scheinost A C, Küsel K. Impact of biostimulated redox processes on metal dynamics in an iron-rich creek soil of a former uranium mining area. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(1): 177–183
Foley M E, Sigler V, Gruden C L. A multiphasic characterization of the impact of the herbicide acetochlor on freshwater bacterial communities. ISME J, 2008, 2(1): 56–66
Kim J M, Lee H J, Kim S Y, Song J J, Park W, Jeon C O. Analysis of the fine-scale population structure of “Candidatus accumulibacter phosphatis” in enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludge, using fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometric sorting. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(12): 3825–3835
Hesselsoe M, Füreder S, Schloter M, Bodrossy L, Iversen N, Roslev P, Nielsen P H, Wagner M, Loy A. Isotope array analysis of Rhodocyclales uncovers functional redundancy and versatility in an activated sludge. ISME J, 2009, 3(12): 1349–1364
White D C, Davis W M, Nickels J S, King J D, Bobbie R J. Determination of the sedimentary microbial biomass by extractible lipid phosphate. Oecologia, 1979, 40(1): 51–62
Yergeau E, Bezemer T M, Hedlund K, Mortimer S R, Kowalchuk G A, van der Putten W H, Influences of space, soil, nematodes and plants on microbial community composition of chalk grassland soils. Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 12(8): 2096–2106
Yao H Y, Wu F Z. Soil microbial community structure in cucumber rhizosphere of different resistance cultivars to fusarium wilt. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2010, 72(3): 456–463
Schütz K, Nagel P, Vetter W, Kandeler E, Ruess L. Flooding forested groundwater recharge areas modifies microbial communities from top soil to groundwater table. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2009, 67(1): 171–182
Björk R G, Ernfors M, Sikström U, Nilsson M B, Andersson M X, Rütting T, Klemedtsson L. Contrasting effects of wood ash application on microbial community structure, biomass and processes in drained forested peatlands. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2010, 73(3): 550–562
Wang MC, Liu Y H, Wang Q, Gong M, Hua XM, Pang Y J, Hu S, Yang Y H. Impacts of methamidophos on the biochemical, catabolic, and genetic characteristics of soil microbial communities. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2008, 40(3): 778–788
Muyzer G, de Waal E C, Uitterlinden A G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(3): 695–700
Fromin N, Hamelin J, Tarnawski S, Roesti D, Jourdain-Miserez K, Forestier N, Teyssier-Cuvelle S, Gillet F, Aragno M, Rossi P. Statistical analysis of denaturing gel electrophoresis (DGE) fingerprinting patterns. Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 4(11): 634–643
Hjort K, Bergström M, Adesina M F, Jansson J K, Smalla K, Sjöling S. Chitinase genes revealed and compared in bacterial isolates, DNA extracts and a metagenomic library from a phytopathogen-suppressive soil. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2010, 71(2): 197–207
Parkes R J, Cragg B A, Banning N, Brock F, Webster G, Fry J C, Hornibrook E, Pancost R D, Kelly S, Knab N, Jørgensen B B, Rinna J, Weightman A J. Biogeochemistry and biodiversity of methane cycling in subsurface marine sediments (Skagerrak, Denmark). Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 9(5): 1146–1161
Wang X H, Wen X H, Criddle C, Wells G, Zhang J, Zhao Y. Community analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge of eight wastewater treatment systems. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2010, 22(4): 627–634
Suzuki M, Rappe MS, Giovannoni S J. Kinetic bias in estimates of coastal picoplankton community structure obtained by measurements of small-subunit rRNA gene PCR amplicon length heterogeneity. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(11): 4522–4529
Bulgari D, Casati P, Brusetti L, Quaglino F, Brasca M, Daffonchio D, Bianco P A. Endophytic bacterial diversity in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) leaves described by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis and length heterogeneity-PCR. Journal of Microbiology (Seoul, Korea), 2009, 47(4): 393–401
Ahn C, Peralta R M. Soil bacterial community structure and physicochemical properties in mitigation wetlands created in the Piedmont region of Virginia (USA). Ecological Engineering, 2009, 35(7): 1036–1042
Taipale S, Jones R I, Tiirola M. Vertical diversity of bacteria in an oxygen-stratified humic lake, evaluated using DNA and phospholipid analyses. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2009, 55(1): 1–16
Mills D K, Fitzgerald K, Litchfield C D, Gillevet P M. A comparison of DNA profiling techniques for monitoring nutrient impact on microbial community composition during bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soils. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2003, 54(1): 57–74
Ritchie N J, Schutter M E, Dick R P, Myrold D D. Use of length heterogeneity PCR and fatty acid methyl ester profiles to characterize microbial communities in soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(4): 1668–1675
Tiirola M A, Suvilampi J E, Kulomaa M S, Rintala J A. Microbial diversity in a thermophilic aerobic biofilm process: analysis by length heterogeneity PCR (LH-PCR). Water Research, 2003, 37(10): 2259–2268
Suzuki M T. Effect of protistan bacterivory on coastal bacterioplankton diversity. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 1999, 20(3): 261–272
Dorigo U, Volatier L, Humbert J F. Molecular approaches to the assessment of biodiversity in aquatic microbial communities. Water Research, 2005, 39(11): 2207–2218
Fisher M M, Triplett E W. Automated approach for ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of microbial diversity and its application to freshwater bacterial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(10): 4630–4636
Manter D K, Delgado J A, Holm D G, Stong R A. Pyrosequencing reveals a highly diverse and cultivar-specific bacterial endophyte community in potato roots. Microbial Ecology, 2010, 60(1): 157–166
Knief C, Ramette A, Frances L, Alonso-Blanco C, Vorholt J A. Site and plant species are important determinants of the Methylobacterium community composition in the plant phyllosphere. ISME J, 2010, 4(6): 719–728
Ranjard L, Poly F, Lata J C, Mougel C, Thioulouse J, Nazaret S. Characterization of bacterial and fungal soil communities by automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis fingerprints: biological and methodological variability. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(10): 4479–4487
Sanz J L, Kochling T. Molecular biology techniques used in wastewater treatment: an overview. Process Biochemistry, 2007, 42(2): 119–133
Brinkmeyer R, Knittel K, Jürgens J, Weyland H, Amann R, Helmke E. Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(11): 6610–6619
Glöckner F O, Fuchs B M, Amann R. Bacterioplankton compositions of lakes and oceans: a first comparison based on fluorescence in situ hybridization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(8): 3721–3726
Knittel K, Lösekann T, Boetius A, Kort R, Amann R. Diversity and distribution of methanotrophic archaea at cold seeps. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(1): 467–479
Eilers H, Pernthaler J, Glöckner F O, Amann R. Culturability and In situ abundance of pelagic bacteria from the North Sea. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(7): 3044–3051
Schramm A, de Beer D, van den Heuvel J C, Ottengraf S, Amann R. Microscale distribution of populations and activities of Nitrosospira and Nitrospira spp. along a macroscale gradient in a nitrifying bioreactor: quantification by in situ hybridization and the use of microsensors. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(8): 3690–3696
Gieseke A, Purkhold U, Wagner M, Amann R, Schramm A. Community structure and activity dynamics of nitrifying bacteria in a phosphate-removing biofilm. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(3): 1351–1362
Altmann D, Stief P, Amann R, de Beer D. Distribution and activity of nitrifying bacteria in natural stream sediment versus laboratory sediment microcosms. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2004, 36(1): 73–81
Ravenschlag K, Sahm K, Knoblauch C, Jørgensen B B, Amann R. Community structure, cellular rRNA content, and activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in marine arctic sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(8): 3592–3602
Llobet-Brossa E, Rabus R, Bottcher M E, Konneke M, Finke N, Schramm A, Meyer R L, Grotzschel S, Rossello-Mora R, Amann R. Community structure and activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in an intertidal surface sediment: a multi-method approach. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2002, 29(3): 211–226
Christensson M, Blackall L L, Welander T. Metabolic transformations and characterisation of the sludge community in an enhanced biological phosphorus removal system. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1998, 49(2): 226–234
Strous M, Kuenen J G, Jetten MS M. Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(7): 3248–3250
Tran H T, Park Y J, Cho M K, Kim D J, Ahn D H. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation process in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor with granular sludge selected from an anaerobic digestor. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2006, 11(3): 199–204
Miura Y, Watanabe Y, Okabe S. Significance of Chloroflexi in performance of submerged membrane bioreactors (MBR) treating municipal wastewater. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(22): 7787–7794
Webster G, Blazejak A, Cragg B A, Schippers A, Sass H, Rinna J, Tang X H, Mathes F, Ferdelman T G, Fry J C, Weightman A J, Parkes R J. Subsurface microbiology and biogeochemistry of a deep, cold-water carbonate mound from the Porcupine Seabight (IODP Expedition 307). Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 11(1): 239–257
Lee N, Nielsen P H, Andreasen K H, Juretschko S, Nielsen J L, Schleifer K H, Wagner M. Combination of fluorescent in situ hybridization and microautoradiography-a new tool for structurefunction analyses in microbial ecology. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(3): 1289–1297
Ouverney C C, Fuhrman J A. Combined microautoradiography-16S rRNA probe technique for determination of radioisotope uptake by specific microbial cell types in situ. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(4): 1746–1752
Wagner M, Nielsen P H, Loy A, Nielsen J L, Daims H. Linking microbial community structure with function: fluorescence in situ hybridization-microautoradiography and isotope arrays. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2006, 17(1): 83–91
Nielsen J L, Christensen D, Kloppenborg M, Nielsen P H. Quantification of cell-specific substrate uptake by probe-defined bacteria under in situ conditions by microautoradiography and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 5(3): 202–211
Neufeld J D, Wagner M, Murrell J C. Who eats what, where and when? Isotope-labelling experiments are coming of age. ISME J, 2007, 1(2): 103–110
Boschker H T S, Nold S C, Wellsbury P, Bos D, de Graaf W, Pel R, Parkes R J, Cappenberg T E. Direct linking of microbial populations to specific biogeochemical processes by 13C-labelling of biomarkers. Nature, 1998, 392(6678): 801–805
Radajewski S, Ineson P, Parekh N R, Murrell J C. Stable-isotope probing as a tool in microbial ecology. Nature, 2000, 403(6770): 646–649
Manefield M, Whiteley A S, Griffiths R I, Bailey M J. RNA stable isotope probing, a novel means of linking microbial community function to phylogeny. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(11): 5367–5373
Friedrich M W. Stable-isotope probing of DNA: insights into the function of uncultivated microorganisms from isotopically labeled metagenomes. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2006, 17(1): 59–66
Whiteley A S, Manefield M, Lueders T. Unlocking the ‘microbial black box’ using RNA-based stable isotope probing technologies. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2006, 17(1): 67–71
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis R W, Brown P O. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science, 1995, 270(5235): 467–470
Roh S W, Abell G C J, Kim K H, Nam Y D, Bae J W. Comparing microarrays and next-generation sequencing technologies for microbial ecology research. Trends in Biotechnology, 2010, 28(6): 291–299
Gentry T J, Wickham G S, Schadt C W, He Z, Zhou J. Microarray applications in microbial ecology research. Microbial Ecology, 2006, 52(2): 159–175
Duc L, Neuenschwander S, Rehrauer H, Wagner U, Sobek J, Schlapbach R, Zeyer J. Development and experimental validation of a nifH oligonucleotide microarray to study diazotrophic communities in a glacier forefield. Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 11(8): 2179–2189
He Z L, Gentry T J, Schadt C W, Wu L Y, Liebich J, Chong S C, Huang Z J, Wu W M, Gu B H, Jardine P, Criddle C, Zhou J. GeoChip: a comprehensive microarray for investigating biogeochemical, ecological and environmental processes. ISME J, 2007, 1(1): 67–77
Zhou J H. Microarrays for bacterial detection and microbial community analysis. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2003, 6(3): 288–294
Rivas L A, García-Villadangos M, Moreno-Paz M, Cruz-Gil P, Gómez-Elvira J, Parro V. A 200-antibody microarray biochip for environmental monitoring: searching for universal microbial biomarkers through immunoprofiling. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(21): 7970–7979
Rich V I, Konstantinidis K, DeLong E F. Design and testing of ‘genome-proxy’ microarrays to profile marine microbial communities. Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 10(2): 506–521
Raes J, Bork P. Molecular eco-systems biology: towards an understanding of community function. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(9): 693–699
Hultman J, Ritari J, Romantschuk M, Paulin L, Auvinen P. Universal ligation-detection-reaction microarray applied for compost microbes. BMC Microbiology, 2008, 8:237–251.
Nyberg L, Turco R F, Nies L. Assessing the impact of nanomaterials on anaerobic microbial communities. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(6): 1938–1943
Drees K P, Neilson J W, Betancourt J L, Quade J, Henderson D A, Pryor B M, Maier R M. Bacterial community structure in the hyperarid core of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(12): 7902–7908
Duineveld B M, Rosado A S, van Elsas J D, van Veen J A. Analysis of the dynamics of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of the chrysanthemum via denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and substrate utilization patterns. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(12): 4950–4957
Weidler G W, Gerbl F W, Stan-Lotter H. Crenarchaeota and their role in the nitrogen cycle in a subsurface radioactive thermal spring in the Austrian Central Alps. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(19): 5934–5942
Otawa K, Asano R, Ohba Y, Sasaki T, Kawamura E, Koyama F, Nakamura S, Nakai Y. Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria community in intermittent aeration sequencing batch reactors used for animal wastewater treatment. Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 8(11): 1985–1996
Chen X P, Zhu Y G, Xia Y, Shen J P, He J Z. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea: important players in paddy rhizosphere soil? Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 10(8): 1978–1987
Weinert N, Meincke R, Gottwald C, Heuer H, Gomes N C M, Schloter M, Berg G, Smalla K. Rhizosphere communities of genetically modified zeaxanthin-accumulating potato plants and their parent cultivar differ less than those of different potato cultivars. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(12): 3859–3865
Kowalchuk G A, Stienstra A W, Heilig G H J, Stephen J R, Woldendorp J W. Changes in the community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria during secondary succession of calcareous grasslands. Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 2(1): 99–110
Henckel T, Friedrich M, Conrad R. Molecular analyses of the methane-oxidizing microbial community in rice field soil by targeting the genes of the 16S rRNA, particulate methane monooxygenase, and methanol dehydrogenase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(5): 1980–1990
Wertz S, Dandie C E, Goyer C, Trevors J T, Patten C L. Diversity of nirK denitrifying genes and transcripts in an agricultural soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(23): 7365–7377
Glausiusz J. Extreme culture. Nature, 2007, 447(7147): 905–906
Meroth C B, Hammes WP, Hertel C. Identification and population dynamics of yeasts in sourdough fermentation processes by PCRdenaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(12): 7453–7461
Crump B C, Koch E W. Attached bacterial populations shared by four species of aquatic angiosperms. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(19): 5948–5957
Cébron A, Coci M, Garnier J, Laanbroek H J. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoretic analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial community structure in the lower Seine River: impact of Paris wastewater effluents. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(11): 6726–6737
Hallin S, Lydmark P, Kokalj S, Hermansson M, Sörensson F, Jarvis A, Lindgren P E. Community survey of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in full-scale activated sludge processes with different solids retention time. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2005, 99(3): 629–640
Cardenas E, Wu W M, Leigh M B, Carley J, Carroll S, Gentry T, Luo J, Watson D, Gu B, Ginder-Vogel M, Kitanidis P K, Jardine P M, Zhou J, Criddle C S, Marsh T L, Tiedje J M. Microbial communities in contaminated sediments, associated with bioremediation of uranium to submicromolar levels. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(12): 3718–3729
Wu W M, Carley J, Luo J, Ginder-Vogel M A, Cardenas E, Leigh M B, Hwang C, Kelly S D, Ruan C, Wu L, van Nostrand J, Gentry T, Lowe K, Mehlhorn T, Carroll S, Luo W, Fields M W, Gu B, Watson D, Kemner K M, Marsh T, Tiedje J, Zhou J, Fendorf S, Kitanidis P K, Jardine P M, Criddle C S. In situ bioreduction of uranium (VI) to submicromolar levels and reoxidation by dissolved oxygen. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(16): 5716–5723
Gao DW, Fu Y, Tao Y, Li X, Xing M, Gao X H, Ren N Q, Linking microbial community structure to membrane biofouling associated with varying dissolved oxygen. Bioresource Technology, 2010 DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech. 2011.02.039
White H K, Reimers C E, Cordes E E, Dilly G F, Girguis P R. Quantitative population dynamics of microbial communities in plankton-fed microbial fuel cells. ISME J, 2009, 3(6): 635–646
Jong B C, Kim B H, Chang I S, Liew PWY, Choo Y F, Kang G S. Enrichment, performance, and microbial diversity of a thermophilic mediatorless microbial fuel cell. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(20): 6449–6454
Cytryn E, Minz D, Gelfand I, Neori A, Gieseke A, de Beer D, van Rijn J. Sulfide-oxidizing activity and bacterial community structure in a fluidized bed reactor from a zero-discharge mariculture system. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(6): 1802–1810
Martineau C, Whyte L G, Greer C W. Stable isotope probing analysis of the diversity and activity of methanotrophic bacteria in soils from the Canadian high Arctic. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(17): 5773–5784
Lukow T 1, Dunfield P F, Liesack W. Use of the T-RFLP technique to assess spatial and temporal changes in the bacterial community structure within an agricultural soil planted with transgenic and non-transgenic potato plants. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2000, 32(3): 241–247
Dunbar J, Ticknor L O, Kuske C R. Assessment of microbial diversity in four southwestern United States soils by 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(7): 2943–2950
Tom-Petersen A, Leser T D, Marsh T L, Nybroe O. Effects of copper amendment on the bacterial community in agricultural soil analyzed by the T-RFLP technique. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2003, 46(1): 53–62
Morales S E, Mouser P J, Ward N, Hudman S P, Gotelli N J, Ross D S, Lewis T A. Comparison of bacterial communities in New England Sphagnum bogs using terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP). Microbial Ecology, 2006, 52(1): 34–44
Lepère C, Boucher D, Jardillier L, Domaizon I, Debroas D. Succession and regulation factors of small eukaryote community composition in a lacustrine ecosystem (Lake Pavin). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(4): 2971–2981
Mills H J, Hunter E, Humphrys M, Kerkhof L, McGuinness L, Huettel M, Kostka J E. Characterization of nitrifying, denitrifying, and overall bacterial communities in permeable marine sediments of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(14): 4440–4453
Swan B K, Ehrhardt C J, Reifel K M, Moreno L I, Valentine D L. Archaeal and bacterial communities respond differently to environmental gradients in anoxic sediments of a California hypersaline lake, the Salton Sea. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(3): 757–768
Whang L M, Chien I C, Yuan S L, Wu Y J. Nitrifying community structures and nitrification performance of full-scale municipal and swine wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(2): 234–242
Collins G, Woods A, McHugh S, Carton M W, O’Flaherty V. Microbial community structure and methanogenic activity during start-up of psychrophilic anaerobic digesters treating synthetic industrial wastewaters. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2003, 46(2): 159–170
Gao D, Zhang T, Tang C Y, Wu WM, Wong C Y, Lee Y H, Yeh D H, Criddle C S. Membrane fouling in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor: differences in relative abundance of bacterial species in the membrane foulant layer and insuspension. Journal ofMembrane Science, 2010
Pang C M, Liu W T. Community structure analysis of reverse osmosis membrane biofilms and the significance of Rhizobiales bacteria in biofouling. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(13): 4728–4734
Saikaly P E, Stroot P G, Oerther D B. Use of 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis to assess the impact of solids retention time on the bacterial diversity of activated sludge. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(10): 5814–5822
Madden A S, Smith A C, Balkwill D L, Fagan L A, Phelps T J. Microbial uranium immobilization independent of nitrate reduction. Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 9(9): 2321–2330
Kennedy N, Edwards S, Clipson N. Soil bacterial and fungal community structure across a range of unimproved and semi-improved upland grasslands. Microbial Ecology, 2005, 50(3): 463–473
Hidri Y, Bouziri L, Maron P A, Anane M, Jedidi N, Hassan A, Ranjard L. Soil DNA evidence for altered microbial diversity after long-term application of municipal wastewater. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2010, 30(2): 423–431
Kent A D, Jones S E, Yannarell A C, Graham J M, Lauster G H, Kratz T K, Triplett E W. Annual patterns in bacterioplankton community variability in a humic lake. Microbial Ecology, 2004, 48(4): 550–560
Graham J M, Kent A D, Lauster G H, Yannarell A C, Graham L E, Triplett E W. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton and planktonic protozoan communities in a northern temperate humic lake: diversity in a dinoflagellate dominated system. Microbial Ecology, 2004, 48(4): 528–540
Wood S A, Jentzsch K, Rueckert A, Hamilton D P, Cary S C. Hindcasting cyanobacterial communities in Lake Okaro with germination experiments and genetic analyses. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2009, 67(2): 252–260
Nold S C, Pangborn J B, Zajack H A, Kendall S T, Rediske R R, Biddanda B A. Benthic bacterial diversity in submerged sinkhole ecosystems. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(1): 347–351
Borin S, Marzorati M, Cavalca L, Sorlini C, Daffonchio D, Zilli M, Converti A, Cherif H, Hassen A. Diversity of the microflora of a compost-packed biofilter treating benzene-contaminated air. European Symposium on Environmental Biotechnology, Eseb 2004, 2004: 75–79
Steele J A, Ozis F, Fuhrman J A, Devinny J S. Structure of microbial communities in ethanol biofilters. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2005, 113(2–3): 135–143
Vanysacker L, Declerck S A J, Hellemans B, de Meester L, Vankelecom I, Declerck P. Bacterial community analysis of activated sludge: an evaluation of four commonly used DNA extraction methods. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 88(1): 299–307
Zhang X, Brussee K, Coutinho C T, Rooney-Varga J N. Chemical stress induced by copper: examination of a biofilm system. Water Science and Technology, 2006, 54(9): 191–199
Hewson I, Fuhrman J A. Richness and diversity of bacterioplankton species along an estuarine gradient in Moreton Bay, Australia. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(6): 3425–3433
Popa R, Popa R, Mashall M J, Nguyen H, Tebo B M, Brauer S. Limitations and benefits of ARISA intra-genomic diversity fingerprinting. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2009, 78(2): 111–118
Kovacs A, Yacoby K, Gophna U. A systematic assessment of automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis (ARISA) as a tool for estimating bacterial richness. Research in Microbiology, 2010, 161(3): 192–197
de Vero L, Gala E, Gullo M, Solieri L, Landi S, Giudici P. Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis to evaluate acetic acid bacteria in traditional balsamic vinegar. Food Microbiology, 2006, 23(8): 809–813
Meays C L, Broersma K, Nordin R, Mazumder A. Source tracking fecal bacteria in water: a critical review of current methods. Journal of Environmental Management, 2004, 73(1): 71–79
Middleton S A, Anzenberger G, Knapp L A. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) screening of clones prior to sequencing. Molecular Ecology Notes, 2004, 4(4): 776–778
Talbot G, Topp E, Palin M F, Massé D I. Evaluation of molecular methods used for establishing the interactions and functions of microorganisms in anaerobic bioreactors. Water Research, 2008, 42(3): 513–537
Gilbride K A, Lee D Y, Beaudette L A. Molecular techniques in wastewater: understanding microbial communities, detecting pathogens, and real-time process control. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2006, 66(1): 1–20
Bernhard A E, Colbert D, McManus J, Field K G. Microbial community dynamics based on 16S rRNA gene profiles in a Pacific Northwest estuary and its tributaries. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2005, 52(1): 115–128
Kan J, Suzuki M T, Wang K, Evans S E, Chen F. High temporal but low spatial heterogeneity of bacterioplankton in the Chesapeake Bay. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(21): 6776–6789
Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia A M, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D. Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(10): 6147–6156
Tiirola M, Lahtinen T, Vuento M, Oker-Blom C. Early succession of bacterial biofilms in paper machines. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2009, 36(7): 929–937
Okubo A, Sugiyama S. Comparison of molecular fingerprinting methods for analysis of soil microbial community structure. Ecological Research, 2009, 24(6): 1399–1405
Danovaro R, Luna G M, Dell’anno A, Pietrangeli B. Comparison of two fingerprinting techniques, terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism and automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis, for determination of bacterial diversity in aquatic environments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(9): 5982–5989
Ramette A. Quantitative community fingerprinting methods for estimating the abundance of operational taxonomic units in natural microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(8): 2495–2505
Yannarell A C, Triplett E W. Within- and between-lake variability in the composition of bacterioplankton communities: investigations using multiple spatial scales. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(1): 214–223
Wilderer P A, Bungartz H J, Lemmer H, Wagner M, Keller J, Wuertz S. Modern scientific methods and their potential in wastewater science and technology. Water Research, 2002, 36(2): 370–393
Sekar R, Pernthaler A, Pernthaler J, Warnecke F, Posch T, Amann R. An improved protocol for quantification of freshwater Actinobacteria by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(5): 2928–2935
Miura Y, Okabe S. Quantification of cell specific uptake activity of microbial products by uncultured Chloroflexi by microautoradiography combined with fluorescence in situ hybridization. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(19): 7380–7386
Nielsen J L, Christensen D, Kloppenborg M, Nielsen P H. Quantification of cell-specific substrate uptake by probe-defined bacteria under in situ conditions by microautoradiography and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 5(3): 202–211
Nielsen J L, Nielsen P H. Advances in microscopy: microautor-adiography of single cells. Methods in Enzymology, 2005, 397: 237–256
Yin H Q, Cao L H, Qiu G Z, Wang D Z, Kellogg L, Zhou J Z, Dai Z M, Liu X D. Development and evaluation of 50-mer oligonucleotide arrays for detecting microbial populations in Acid Mine Drainages and bioleaching systems. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2007, 70(1): 165–178
Wilson K H, Wilson W J, Radosevich J L, DeSantis T Z, Viswanathan V S, Kuczmarski T A, Andersen G L. High-density microarray of small-subunit ribosomal DNA probes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(5): 2535–2541
Wu L Y, Thompson D K, Liu X D, Fields M W, Bagwell C E, Tiedje J M, Zhou J Z. Development and evaluation of microarraybased whole-genome hybridization for detection of microorganisms within the context of environmental applications. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(24): 6775–6782
Wu L Y, Thompson D K, Li G S, Hurt R A, Tiedje J M, Zhou J Z. Development and evaluation of functional gene arrays for detection of selected genes in the environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(12): 5780–5790
Shalon D, Smith S J, Brown P O. A DNA microarray system for analyzing complex DNA samples using two-color fluorescent probe hybridization. Genome Research, 1996, 6(7): 639–645
Bent S J, Forney L J. The tragedy of the uncommon: understanding limitations in the analysis of microbial diversity. ISME J, 2008, 2(7): 689–695
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, D., Tao, Y. Current molecular biologic techniques for characterizing environmental microbial community. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 6, 82–97 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0306-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0306-6