Abstract
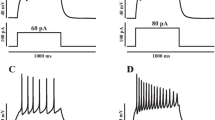
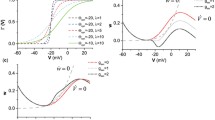
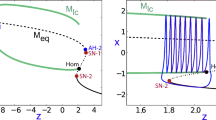
Neurons show diverse firing patterns. Even neurons belonging to a single chemical or morphological class, or the same identified neuron, can display different types of electrical activity. For example, motor neuron MN5, which innervates a flight muscle of adult Drosophila, can show distinct firing patterns under the same recording conditions. We developed a two-dimensional biophysical model and show that a core complement of just two voltage-gated channels is sufficient to generate firing pattern diversity. We propose Shab and DmNa v to be two candidate genes that could encode these core currents, and find that changes in Shab channel expression in the model can reproduce activity resembling the main firing patterns observed in MN5 recordings. We use bifurcation analysis to describe the different transitions between rest and spiking states that result from variations in Shab channel expression, exposing a connection between ion channel expression, bifurcation structure, and firing patterns in models of membrane potential dynamics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arhem, P., & Blomberg, C. (2007). Ion channel density and threshold dynamics of repetitive firing in a cortical neuron model. Biosystems, 89(1–3), 117–125.
Av-Ron, E., Parnas, H., Segel, L. (1991). A minimal biophysical model for an excitable and oscillatory neuron. Biological Cybernetics, 65(6), 487–500.
Av-Ron, E., Parnas, H., Segel, L.A. (1993). A basic biophysical model for bursting neurons. Biological Cybernetics, 69, 87–95.
Baines, R., Uhler, J., Thompson, A., Sweeney, S., Bate, M. (2001). Altered electrical properties in Drosophila neurons developing without synaptic transmission. Journal of Neuroscience, 21(5), 1523–1531.
Baranauskas, G., & Martina, M. (2006). Sodium currents activate without a hodgkin and huxley-type delay in central mammalian neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(2), 671–684.
Baro, D., Quinones, L., Lanning, C., Harris-Warrick, R., Ruiz, M. (2001). Alternate splicing of the Shal gene and the origin of IA diversity among neurons in a dynamic motor network. Neuroscience, 106(2), 419–432.
Brembs, B., Christiansen, F., Pflüger, H., Duch, C. (2007). Flight initiation and maintenance deficits in flies with genetically altered biogenic amine levels. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(41), 11122–11131.
Chay, T., & Kang, H. (1988). Role of single-channel stochastic noise on bursting clusters of pancreatic beta-cells. Biophysical Journal, 54(3), 427–435.
Choi, J., Park, D., Griffith, L. (2004). Electrophysiological and morphological characterization of identified motor neurons in the Drosophila third instar larva central nervous system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 91(5), 2353–2365.
Coetzee, W., Amarillo, Y., Chiu, J., Chow, A., Lau, D., McCormack, T., et al. (1999). Molecular diversity of K + channels. Annals of New York Academy of Sciences, 868, 233–285.
Connor, J., & Stevens, C. (1971). Inward and delayed outward membrane currents in isolated neural somata under voltage clamp. Journal of Physiology, 213(1), 1–19.
Connors, B., & Gutnick, M. (1990). Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons. Trends in Neurosciences, 13(3), 99–104.
Covarrubias, M., Wei, A., Salkoff, L. (1991). Shaker, Shal, Shab, and Shaw express independent K-current systems. Neuron, 7(5), 763–773.
Dickinson, M., & Tu, M. (1997). The function of dipteran flight muscle. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology, 116(3), 223–238.
Duch, C., Vonhoff, F., Ryglewski, S. (2008). Dendrite elongation and dendritic branching are affected separately by different forms of intrinsic motoneuron excitability. Journal of Neurophysiology, 100(5), 2525–2536.
Eberwine, J., Yeh, H., Miyashiro, K., Cao, Y., Nair, S., Finnell, R., et al. (1992). Analysis of gene expression in single live neurons. PNAS, 89(7), 3010–3014.
Endresen, L.P., Hall, K., Hoye, J.S., Myrheim, J. (2000). A theory for the membrane potential of living cells. European Journal of Biophysics, 29, 90–103.
Ermentrout, B. (2006). PPAUT. Scholarpedia, 2(1), 1399.
Ermentrout, G., & Terman, D. (2010). Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience. Springer.
Ewing, A. (1977). The neuromuscular basis of courtship song in Drosophila: the role of the indirect flight muscles. Journal of Comparative Physiology A: Neuroethology, Sensory, Neural, and Behavioral Physiology, 119(3), 249–265.
Fernandes, J., & Keshishian, H. (1998). Nerve-muscle interactions during flight muscle development in Drosophila. Development, 125(9), 1769–1779.
Fitz-Hugh, R. (1961). Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophysical Journal, 1, 445–466.
Fleshman, J., Munson, J., Sypert, G., Friedman, W. (1981). Rheobase, input resistance, and motor-unit type in medial gastrocnemius motoneurons in the cat. Journal of Neurophysiology, 46(6), 1326–1338.
Golomb, D., Donner, K., Shacham, L., Shlosberg, D., Amitai, Y., Hansel, D. (2007). Mechanisms of firing patterns in fast-spiking cortical interneurons. PLoS Computational Biology, 3(8), e156.
Gordon, S., & Dickinson, M. (2006). Role of calcium in the regulation of mechanical power in insect flight. PNAS, 103(11), 4311–4315.
Guckenheimer, J., Harris-Warrick, R., Peck, J., Willms, A. (1997). Bifurcation, bursting, and spike frequency adaptation. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 4(3), 257–277.
Guckenheimer, J., & Holmes, P. (1990). Nonlinear oscillations, dynamical systems, and bifurcations of vector fields. Springer.
Günay, C., Edgerton, J., Jaeger, D. (2008). Channel density distributions explain spiking variability in the globus pallidus: a combined physiology and computer simulation database approach. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(30), 7476–7491.
Harcombe, E., & Wyman, R. (1977). Output pattern generation by drosophila flight motoneurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 40(5), 1066–1077.
Hardie, R., & Minke, B. (1994). Spontaneous activation of light-sensitive channels in Drosophila photoreceptors. Journal of general physiology, 103(3), 389–407.
Heinemann, S., Rettig, J., Graack, H., Pongs, O. (1996). Functional characterization of Kv channel β-subunits from rat brain. Journal of Physiology, 493(3), 625.
Herrera-Valdez, M. (2012). Membranes with the same ion channel populations but different excitabilities. PLoS ONE, 7(4), e34636.
Herrera-Valdez, M.A., & Lega, J. (2011). Reduced models for the pacemaker dynamics of cardiac cells. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 270(1), 164–176.
Hille, B. (2001). Ionic channels of excitable membranes (3rd ed.). Sinauer.
Hindmarsh, J., & Rose, R. (1984). A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B. Biological Sciences, 221(1222), 87–102.
Hodgkin, A. (1948). The local electric changes associated with repetitive action in a nonmedulated axon. Journal of Physiology, 107, 165–181.
Hodgkin, A., & Huxley, A. (1952a). A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. Journal of Physiology, 117, 500–544.
Hodgkin, A., & Huxley, A. (1952b). The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. Journal of Physiology, 116(4), 473–496.
Hunter, J., Dale, D., Droettboom, M. (2008). Matplotlib: a Python 2D plotting library. http://matplotlib.sourceforge.net/.
Ikeda, K., & Koenig, J. (1988). Morphological identification of the motor neurons innervating the dorsal longitudinal flight muscle of Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 273(3), 436–444.
Isacoff, E., Jan, Y., Jan, L., et al. (1990). Evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric potassium channels in xenopus oocytes. Nature, 345(6275), 530–534.
Izhikevich, E. (2007). Dynamical systems in neuroscience. MIT Press.
Izhikevich, E.M. (2003). Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 14(6), 1569–1572.
Jan, L., & Jan, Y. (1976). Properties of the larval neuromuscular junction in Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Physiology, 262(1), 189–214.
Jan, L., & Jan, Y. (1990). How might the diversity of potassium channels be generated? Trends in Neurosciences, 13(10), 415–419.
Jan, L., & Jan, Y. (1997). Voltage-gated and inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Journal of Physiology, 505(2), 267–282.
Jones, E., Oliphant, T., Peterson, P., et al. (2001). SciPy: open source scientific tools for Python. http://www.scipy.org/.
Kim, J., Wei, D., Hoffman, D. (2005). Kv4 potassium channel subunits control action potential repolarization and frequency-dependent broadening in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones. Journal of Physiology, 569(1), 41–57.
Levine, J., & R. Wyman (1973). Neurophysiology of flight in wild-type and a mutant Drosophila. PNAS, 70(4), 1050–1054.
Lin, W., Wright, D., Muraro, N., Baines, R. (2009). Alternative splicing in the voltage-gated sodium channel DmNav regulates activation, inactivation, and persistent current. Journal of Neurophysiology, 102(3), 1994–2006.
Liss, B., Franz, O., Sewing, S., Bruns, R., Neuhoff, H., Roeper, J. (2001). Tuning pacemaker frequency of individual dopaminergic neurons by Kv4.3L and KChip3.1 transcription. The EMBO Journal, 20(20), 5715–5724.
Machin, K., & Pringle, J. (1959). The physiology of insect fibrillar muscle. ii. mechanical properties of a beetle flight muscle. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B. Biological Sciences, 151(943), 204–225.
Mo, Z., Adamson, C., Davis, R. (2002). Dendrotoxin-sensitive k+ currents contribute to accommodation in murine spiral ganglion neurons. The Journal of physiology, 542(3), 763–778.
Murbartián, J., Arias, J., Perez-Reyes, E., (2004). Functional impact of alternative splicing of human T-type Cav3.3 calcium channels. Journal of Neurophysiology, 92(6), 3399–3407.
Nagumo, J., Arimoto, S., Yoshizawa, S. (1962). An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proceedings of the IRE, 50(10), 2061–2070.
Neher, E. (1971). Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. Journal of General Physiology, 58(1), 36–53.
O’Donnell Olson, R., Liu, Z., Nomura, Y., Song, W., Dong, K. (2008). Molecular and functional characterization of voltage-gated sodium channel variants from Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 38(5), 604–610.
Pan, Z., Selyanko, A., Hadley, J., Brown, D., Dixon, J., McKinnon, D. (2001). Alternative splicing of KCNQ2 potassium channel transcripts contributes to the functional diversity of M-currents. Journal of Physiology, 531(2), 347–358.
Peng, I.-F., & Wu, C.-F. (2007). Differential contributions of Shaker and Shab K + currents to neuronal firing patterns in Drosophila. Journal of Neurophysiology, 97(1), 780–794.
Ping, Y., Waro, G., Licursi, A., Smith, S., Vo-Ba, D., Tsunoda, S. (2011). Shal/Kv4 channels are required for maintaining excitability during repetitive firing and normal locomotion in Drosophila. PloS ONE, 6(1), e16043.
Pongs, O., & Schwarz, J. (2010). Ancillary subunits associated with voltage-dependent K + channels. Physiological Reviews, 90(2), 755–796.
Prescott, S., De Koninck, Y., Sejnowski, T. (2008). Biophysical basis for three distinct dynamical mechanisms of action potential initiation. PLoS Computational Biology, 4(10), e1000198.
Prinz, A., Billimoria, C., Marder, E. (2003). Alternative to hand-tuning conductance-based models: construction and analysis of databases of model neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 90(6), 3998–4015.
Rinzel, J. (1985). Excitation dynamics: insights from simplified membrane models. Federation Proceedings, 44(15), 2944–2946.
Rinzel, J., & Ermentrout, G. (1989). Analysis of neural excitability and oscillations. In C. Koch & I. Segev (Eds.), Methods in neuronal modelling: from synapses to networks (pp. 251–291). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Ryan, M., Maloney, R., Reenan, R., Horn, R. (2008). Characterization of five RNA editing sites in Shab potassium channels. Channels (Austin, Tex.), 2(3), 202–209.
Ryglewski, S., & Duch, C. (2009). Shaker and Shal mediate transient calcium-independent potassium current in a Drosophila flight motoneuron. Journal of Neurophysiology, 102(6), 3673–3688.
Ryglewski, S., & Duch, C. (2012). Preparation of Drosophila central neurons for in situ patch clamping. Journal of Visualized Experiments, in press
Ryglewski, S., Lance, K., Levine, R., Duch, C. (2012). Cav2 channels mediate low and high voltage-activated calcium currents in drosophila motoneurons. Journal of Physiology, 590(4), 809–825.
Saito, M., Nelson, C., Salkoff, L., Lingle, C., (1997). A cysteine-rich domain defined by a novel exon in a Slo variant in rat adrenal chromaffin cells and PC12 cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272(18), 11710–11717.
Saito, M., & Wu, C. (1991). Expression of ion channels and mutational effects in giant Drosophila neurons differentiated from cell division-arrested embryonic neuroblasts. Journal of Neuroscience, 11(7), 2135–2150.
Salkoff, L., Baker, K., Butler, A., Covarrubias, M., Pak, M., Wei, A. (1992). An essential set of K + channels conserved in flies, mice and humans. Trends in Neurosciences, 15(5), 161–166.
Sanyal, S., Narayanan, R., Consoulas, C., Ramiswami, M. (2003). Evidence for cell autonomous ap1 function in regulation of drosophila motor-neuron plasticity. BMC Neuroscience, 4, 20.
Schaefer, J., Worrell, J., Levine, R. (2010). Role of intrinsic properties in Drosophila motoneuron recruitment during fictive crawling. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104(3), 1257–1266.
Schilcher, F.v. (1976). The behavior of cacophony, a courtship song mutant in drosophila melanogaster. Behavioral Biology, 17(2), 187–196.
Schulz, D., Goaillard, J., Marder, E. (2006). Variable channel expression in identified single and electrically coupled neurons in different animals. Nature Neuroscience, 9(3), 356–362.
Schulz, D., Goaillard, J., Marder, E. (2007). Quantitative expression profiling of identified neurons reveals cell-specific constraints on highly variable levels of gene expression. PNAS, 104(32), 13187–13191.
Schulz, D., Temporal, S., Barry, D., Garcia, M. (2008). Mechanisms of voltage-gated ion channel regulation: from gene expression to localization. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 65(14), 2215–2231.
Shibata, R., Nakahira, K., Shibasaki, K., Wakazono, Y., Imoto, K., Ikenaka, K. (2000). A-type K + current mediated by the Kv4 channel regulates the generation of action potential in developing cerebellar granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 20(11), 4145–4155.
Sonders, M., & Amara, S. (1996). Channels in transporters. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 6(3), 294–302.
Steriade, M. (2001). The intact and sliced brain. MIT Press.
Steriade, M., Timofeev, I., Durmuller, N., Grenier, F. (1998). Dynamic properties of corticothalamic neurons and local cortical interneurons generating fast rhythmic (30–40 Hz) spike bursts. Journal of Neurophysiology, 79(1), 483–490.
Swensen, A., & Bean, B. (2005). Robustness of burst firing in dissociated Purkinje neurons with acute or long-term reductions in sodium conductance. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(14), 3509–3520.
Tan, M., Theeuwes, H., Feenstra, L., Borst, J. (2007). Membrane properties and firing patterns of inferior colliculus neurons: an in vivo patch-clamp study in rodents. Journal of neurophysiology, 98(1), 443–453.
Timpe, L., Jan, Y., Jan, L. (1988). Four cdna clones from the shaker locus of drosophila induce kinetically distinct a-type potassium currents in xenopus oocytes. Neuron, 1(8), 659–667.
Tobin, A., Cruz-Bermúdez, N., Marder, E., Schulz, D. (2009). Correlations in ion channel mRNA in rhythmically active neurons. PLoS ONE, 4(8), e6742.
Trimmer, J., & Rhodes, K. (2004). Localization of voltage-gated ion channels in mammalian brain. Annual Reviews of Physiology, 66, 477–519.
Tsunoda, S., & Salkoff, L. (1995a). Genetic Analysis of Drosophila Neurons: Shal, Shaw, and Shab Encode Most Embryonic Potassium Currents. Journal of Neuroscience, 15(3), 1741–1754.
Tsunoda, S., & Salkoff, L. (1995b). The major delayed rectifier in both Drosophila neurons and muscle is encoded by Shab. Journal of Neuroscience, 15(7), 5209–5221.
Watanabe, I., Wang, H., Sutachan, J., Zhu, J., Recio-Pinto, E., Thornhill, W. (2003). Glycosylation affects rat Kv1.1 potassium channel gating by a combined surface potential and cooperative subunit interaction mechanism. Journal of Physiology, 550(1), 51–66.
Willms, A., Baro, D., Harris-Warrick, R., Guckenheimer, J. (1999). An improved parameter estimation method for Hodgkin-Huxley models. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 6(2), 145–168.
Acknowledgements
MAHV, SDB, SR, CD, and SC were supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF IIS 0613404). MAHV and ECM were supported in part by the Building Research Infrastructure and Capacity (BRIC) program at UPR-Cayey (P20 MD006144) through the National Institute of Minority Health and Health Disparities. Support for SDB was also provided by the Interdisciplinary Graduate Program in Neuroscience at Arizona State University. Additional support for SR was provided by the German Research Foundation (DFG RY 117/1-1). We thank Cengiz Günay, Martin Strube, and Joceline Lega for their challenging and insightful feedback. We also thank two anonymous reviewers whose suggestions greatly improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: David Golomb
M. A. Herrera-Valdez and E. C. McKiernan contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera-Valdez, M.A., McKiernan, E.C., Berger, S.D. et al. Relating ion channel expression, bifurcation structure, and diverse firing patterns in a model of an identified motor neuron. J Comput Neurosci 34, 211–229 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-012-0416-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-012-0416-6