Abstract
Objective
The higher signal at 3.0-T allows spatial resolution to be increased without loss in image quality. We evaluated a T2-weighted turbo spin-echo sequence with high spatial resolution (3T-HR) to determine whether this provides clinically useful pelvic MRI.
Materials and methods
We designed a sequence with high spatial resolution (3T-HR) (0.45×0.46×4 mm) that was combined with parallel imaging and the variable refocusing angle technique (8.06 min). We examined 23 patients with gynecological disorders using 3T-HR and a standard sequence (3T-SP; 4.03 min; equivalent to 1.5 T). Two radiologists analyzed tissue contrast, signal to noise, detail delineation and artifact level.
Results
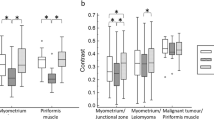
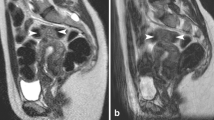
Tissue contrasts and signal to noise were rated equal. Motion artifacts occurred more often with 3T-SP despite the longer scanning time of 3T-HR. The higher spatial resolution provided additional information in four patients. In two patients small myomas were detected, in one patient a lymph node metastasis was apparent, and in one patient 3T-HR excluded tumor invasion.
Conclusions
High spatial resolution pelvic studies with high image quality can be obtained at 3 T in acceptable scan time. The higher spatial resolution that is feasible at 3 T also provides more clinically relevant information.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willinek WA, Gieseke J, von Falkenhausen M, Born M, Hadizadeh D, Manka C, Textor HJ, Schild HH, Kuhl CK (2004) Sensitivity encoding (SENSE) for high spatial resolution time-of-flight MR angiography of the intracranial arteries at 3.0 T. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 176:21–26
Scarabino T, Nemore F, Giannatempo GM, Bertolino A, Di Salle F, Salvolini U (2003) 3.0 T magnetic resonance in neuroradiology. Eur J Radiol 48:154–164
Berg A, Singer T, Moser E (2003) High-resolution diffusivity imaging at 3.0 T for the detection of degenerative changes: a trypsin-based arthritis model. Invest Radiol 38:460–466
Chen W, Ugurbil K (1999) High spatial resolution functional magnetic resonance imaging at very-high-magnetic field. Top Magn Reson Imaging 10:63–78
Yoneka Y, Kwee IL, Fujii Y, Nakada T (2002) Criteria for normal cavities observed within the adult hippocampus: high resolution magnetic resonance imaging study on a 3.0 T-system. J Neuroimaging 12:231–235
Lutterbey G, Gieseke J, von Falkenhausen M, Morakkabati N, Schild H (2005) Lung MRI at 3.0 tesla: a comparison of helical CT and high field MRI in the detection of lund disease. Eur Radiol 15:324–328
Greenman RL, Shirosky JE, Mulkern RV, Rofsky NM (2003) Double inversion black-blood fast spin-echo imaging of the human heart: a comparison between 1.5 T and 3.0 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:648–655
Stuber M, Botnar RF, Fischer SE, Lamerichs R, Smink J, Harvey P, Manning WJ (2002) Preliminary report on in vivo coronary MRA at 3.0 T in humans. Magn Reson Med 48:425–429
Peterson DM, Carruthers CE, Wolverton BL et al (1999) Application of a bird-cage coil at 3 tesla to imaging of the human knee using MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:215–221
Fischbach F, Thormann M, Ricke J (2004) 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the liver and hepatic malignant tumors at 3.0 tesla. Radiologe 44:1192–1196
Futterer JJ, Scheenen TW, Huisman HJ, Klomp DW, van Dorsten FA, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, Witjes JA, Heerschap A, Barentsz JO (2004) Initial experience of 3 tesla endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging and 1H-spectroscopic imaging of the prostate. Invest Radiol 39:671–680
Sosna J, Pedrosa I, Dewolf WC, Mahallati H, Lenkinski RE, Rofsky NM (2004) MR imaging of the prostate at 3 tesla: comparison of an external phased-array coil to imaging with an endorectal coil at 1.5 tesla. Acad Radiol 11:857–862
Bloch BN, Rofsky NM, Baroni RH, Marquis RP, Pedrosa I, Lenkinski RE (2004) 3 tesla magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate with combined pelvic phased-array and endorectal coils; initial experience (1). Acad Radiol 11:863–867
Morakkabati-Spitz N, Gieseke J, Kuhl C, Lutterbey G, von Falkenhausen M, Traeber F, Zivanovic O, Schild HH (2005) 3.0-T high-field magnetic resonance imaging of the female pelvis: preliminary experiences. Eur Radiol 15:639–644
Schick F (2005) Whole-body MRI at high field: technical limits and clinical potential. Eur Radiol 15:946–959
Femlee JP, MA Bernstein MA, Huston J (2000) Analysis of RF heating at 3.0 T. ISMRM, p 2002
Lin C, Bernstein M, Huston J, Fain S (2001) In-vivo and in-vitro measurements of T1 relaxation at 3.0 T. In: Proceedings of the 9th Meeting ISMRM, p 1391
Wansapura JP, Holland SK, Dunn RS, Ball WS Jr (1999) NMR relaxation times in human brain at 3.0 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:531–538
Al Kwifi O, Emery DJ, Wilman AH (2002) Vessel contrast at three tesla in time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography of the intracranial and carotid arteries. Magn Reson Imaging 20:181–187
Thomas SD, Al Kwifi O, Emery DJ, Wilman AH (2002) Application of magnetization transfer at 3.0 T in three-dimensional time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography of the intracranial arteries. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:479–483
von Falkenhausen M, Gieseke J, Morakkabati N, Lutterbey G, Blömer R, Kuhl CK, Schild HH (2004) 3T MRI of the liver after SPIO application. A comparison to 1.5T. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 11:904
Hennig J, Scheffler K (2001) Hyperechos. Magn Reson Med 46:6–12
Hennig J, Weigel M, Scheffler K (2003) Multi echo sequences with variable refocussing flip angles: optimization of signal behaviour using smooth transitions between pseudo steady states (TRAPS). Magn Reson Med 49:527–535
Gieseke J, Wattjes M, Lutterbey G, von Falkenhausen M, Blömer R Gür-O, Manka C, Schild H Kuhl CK (2004) Ultra fast T2-weighted TSE sequences using flip angle sweep with half-fourier and SENSE at 3T. Neuroradiology 46(Suppl 1):122
Gieseke J, Kuhl CK, von Falkenhausen M, Blömer R, Gür O, van Yperen G, Schild HH, Lutterbey G (2004) Ultra fast T2-weighted TSE sequences with flip angle sweep and SENSE at 3T. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 11:74
Sheu MH, Chang CY, Wang JH, Yen MS (2001) Preoperative staging of cervical carcinoma with MR imaging: a reappraisal of diagnostic accuracy and pitfalls. Eur Radiol 11:1828–1833
Sironi S, Belloni C, Taccagni GL et al (1991) Carcinoma of the cervix: value of MR imaging in detecting parametrial involvement. AJR Am J Roentgenol 156:753–756
Togashi K, Nishimura K, Sagoh T et al (1989) Carcinoma of the cervix: staging with MR imaging. Radiology 171:245–251
Okamoto Y, Tanaka YO, Nishida M, Tsunoda H, Yoshikawa H, Itai Y (2003) MR imaging of the uterine cervix: imaging-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 425–45:534–535
Gieseke J, Morakkabati-Spitz N, Kuhl CK, Lutterbey G, von-Falkenhausen M, Schild HH (2004) SAR-Reduktion mit variabler HF-Refokussierung und paralleler Bildgebung bei 3T: Neue Technik ermöglicht hohe räumliche Auflösung des weiblichen Beckens in akzeptabler Messzeit. Fortschr Roentgenstr 176(Suppl 222)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morakkabati-Spitz, N., Gieseke, J., Kuhl, C. et al. MRI of the pelvis at 3 T: very high spatial resolution with sensitivity encoding and flip-angle sweep technique in clinically acceptable scan time. Eur Radiol 16, 634–641 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0016-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0016-1