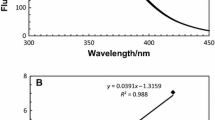
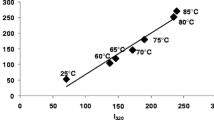
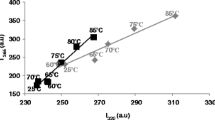
Abstract
Bovine α-lactalbumin (α-LA) is able to interact with fatty acids, resulting in structural changes that are potentially responsible for the HAMLET/BAMLET role. Different states of α-LA induced by pH, temperature and fatty acid binding have been examined. Evidences of the structural changes of α-LA in molten globule and native states in correlation with oleic acid (OA) binding are shown using fluorescence spectroscopy and in silico approach. In addition, the α-LA was subjected to automated docking analysis, to better understand the interaction with oleic acid, using the PatchDock algorithm. The experimental results demonstrate a more flexible conformation of the protein at pH 2.5 when compared to neutral pH, thus facilitating the oleic acid binding to α-LA. The quenching experiments indicate the remarkable increase in the content of molten globule state at pH 2.5 and a more compact and rigid structure for α-LA–OA complexes at pH 7.0. The docking results are consistent with the experimental data concerning the thermal stability of the α-LA–OA complex. α-LA in different conformations/complexes was sensitive to pH and temperature. Several different molecular species induced by pH, heat treatment and oleic acid binding were suggested. The structure of the protein was more flexible at acidic pH, therefore favoring the hydrophobic exposure.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mercer N, Ramakrishnan B, Boeggeman E, Qasba PK (2011) Applications of site-specific labeling to study HAMLET, a tumoricidal complex of α-lactalbumin and oleic acid. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26093
Noyelle K, Dael H (2000) Kinetics of conformational changes induced by the binding of various metal ions to bovine α-lactalbumin. J Inorg Biochem 88:69–76
Permyakov EA, Berliner LJ (2000) α-Lactalbumin: structure and function. FEBS Lett 473:269–274
Bañuelos S, Muga A (1995) Binding of molten globule-like conformations to lipid bilayers: structure of native and partially folded α-lactalbumin bound to model membranes. J Biol Chem 270(5):29910–29915
Das UN, Vaddadi KS (2004) Essential fatty acids in Huntington’s disease. Nutrition 20:942–947
Barbana C, Pérez MD, Sánchez L, Dalgalarrondo M, Chobert JM, Haertlé T, Calvo M (2006) Interaction of bovine α-lactalbumin with fatty acids as determined by partition equilibrium and fluorescence spectroscopy. Int Dairy J 16:18–25
Yang F Jr, Zhang M, Zhou BR, Chen J, Liang Y (2006) Structural changes of α-lactalbumin induced by low pH and oleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764:1389–1396
Svensson M, Hakansson A, Mossberg AK, Linse S, Svanborg C (2000) Conversion of alpha-lactalbumin to a protein inducing apoptosis. PNAS 97:4221–4226
Svensson M, Fast J, Mossberg AK, Duringer C, Gustafsson L, Hallgren O, Brooks CL, Berliner L, Linse S, Svanborg C (2003) α-Lactalbumin unfolding is not sufficient to cause apoptosis, but is required for the conversion to HAMLET (human alpha-lactalbumin made lethal to tumor cells. Prot Sci 12:2794–2804
Köhler C, Gogvadze V, Håkansson A, Svanborg C, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2001) A folding variant of human α-lactalbumin induces mitochondrial permeability transition in isolated mitochondria. Eur J Biochem 268:186–191
Aits S, Gustafsson L, Hallgren O, Brest P, Gustafsson M, Trulsson M, Mossberg AK, Simon HU, Mograbi B, Svanborg C (2009) HAMLET (human alpha-lactalbumin made lethal to tumor cells) triggers autophagic tumor cell death. Int J Cancer 124:1008–1019
Mossberg AK, Puchades M, Halskau Ø, Baumann A, Lanekoff I, Chao Y, Martinez A, Svanborg C, Karlsson R (2010) HAMLET interacts with lipid membranes and perturbs their structure and integrity. PLoS ONE 5:e9384
Veprintsev DB, Permyakov SE, Permyakov EA, Rogov VV, Cawthern KM, Berliner LJ (1997) Cooperative thermal transitions of bovine and human apo-alphalactalbumins: evidence for a new intermediate state. FEBS Lett 412:625–628
Kamijima T, Ohmura A, Sato T, Akimoto K, Itabashi M, Mizuguchi M, Kamiya M, Kikukawa T, Aizawa T, Takahashi M, Kawano K, Demura M (2008) Heat treatment method for producing fatty acid-bound α-lactalbumin that induces tumor cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:211–214
Aprodu A, Stănciuc N, Banu I, Bahrim G, Probing thermal behaviour of microbial transglutaminase with fluorescence and in silico methods. J Sci Food Agric. doi:10.1002/jsfa.5799
Chrysina ED, Brew K, Acharya KR (2000) Crystal structures of apo- and holo-bovine α-lactalbumin at 2.2-Å resolution reveal an effect of calcium on inter-lobe interactions. J Biol Chem 275:37021–37029
Hyperchem-Computational Chemistry (2002) Hyperchem®. Hypercube, Canada
Schneidman-Duhovny D, Inbar Y, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ (2005) PatchDock and SymmDock: servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W363–W367
Andrusier N, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ (2007) FireDock: fast interaction refinement in molecular docking. Proteins 69:139–159
Laskowski RA (2009) PDBsum new things. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D355–D359
Arai M, Kuwajima K (1996) Rapid formation of a molten globule intermediate in refolding of α-lactalbumin. Fold Des 1(4):275–287
Stănciuc N, Râpeanu G, Bahrim G, Aprodu I (2012) pH and heat-induced structural changes of bovine apo-α-lactalbumin. Food Chem 131:956–963
Yang F Jr, Zhang M, Zhou BR, Chen J, Liang Y (2006) Oleic acid inhibits amyloid formation of the intermediate of α-lactalbumin at moderately acidic pH. J Mol Biol 362(4):821–834
Wehbi Z, Pérez MD, Sánchez L, Pocovi C, Barbana C, Calvo M (2005) Effect of heat treatment on denaturation of bovine α-lactalbumin: determination of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters. J Agric Food Chem 53:9730–9736
Gautieri A, Ionita M, Silvestri D, Votta E, Vesentini S, Fiore B, Barbani N, Ciardelli G, Redaelli A (2010) Computer-aided molecular modeling and experimental validation of water permeability properties biosynthetic materials. J Comput Theor Nanosci 7:1–7
Pan CP, Callis PR, Barkley MD (2006) Dependence of tryptophan emission wavelength on conformation in cyclic hexapeptides. J Phys Chem B 110(13):7009–7016
Demarest SJ, Boice JA, Fairman R, Raleigh DP (1999) Defining the core structure of the α-lactalbumin molten globule state. J Mol Biol 294:213–221
Hendrix T, Griko YV, Privalov PL (2000) A calorimetric study of the influence of calcium on the stability of bovine α-lactalbumin. Biophys Chem 84:27–34
Vanderheeren G, Hanssens I, Meijberg W, Van Aerschot A (1996) Thermodynamic characterization of the partially unfolded state of Ca2+-loaded α-lactalbumin: evidence that partial unfolding can precede Ca2+ release. Biochem 35:16753–16759
Vanderheeren G, Hanssens I (1999) Spectroscopic study of the thermal unfolding of α-lactalbumin. Recent Res Dev Anal Biochem 1:45–61
Zhang M, Yang F Jr, Yang F, Chen J, Zheng CY, Liang Y (2009) Cytotoxic aggregates of α-lactalbumin induced by unsaturated fatty acid induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Chem Biol Inter 180(2):131–142
Otzen DE, Sehgal P, Westh P (2009) α-Lactalbumin is unfolded by all classes of surfactants but by different mechanisms. J Coll Int Sci 329:273–283
Svensson M, Mossberg AK, Pettersson J, Linse S, Svanborg C (2003) Lipids as cofactors in protein folding: stereo-specific lipid–protein interactions are required to form HAMLET (human alpha-lactalbumin made lethal to tumor cells). Prot Sci 12:2805–2814
Wijesinha-Bettoni R, Dobson CM, Redfield C (2001) Comparison of the denaturant-induced unfolding of the bovine and human alpha-lactalbumin molten globules. J Mol Biol 312:261–273
Torta F, Dyuysekina A, Cavazzini D, Fantuzzi A, Bychkova V, Rossi G (2004) Solvent-induced ligand dissociation and conformational states of cellular retinol-binding protein type I. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:21–29
Casbarra A, Birolo L, Infusini G, Dal Piaz F, Svensson M, Pucci P et al (2004) Conformational analysis of HAMLET, the folding variant of human alpha-lactalbumin associated with apoptosis. Protein Sci 13:1322–1330
Kehoe JJ, Brodkorb A (2012) Interactions between sodium oleate and a-lactalbumin: the effect of temperature and concentration on complex formation. Food Hydrocoll. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.09.009
Brodkorb A, Liskova K (2010) A process for producing a biologically active globular protein complex. International Patent No. WO2010131237
Muresan S, van der Vent A, de Wolf FA (2001) Interaction of β-lactoglobulin with small hydrophobic ligands as monitored by fluorometry and equilibrium dialysis: nonlinear quenching effects related to protein–protein association. J Agric Food Chem 49:609–2618
Peters T (1996) All about albumin. Academic Press, London
Lakowicz JR (1986) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Plenum Press, New York
Chadborn N, Bryant J, Bain AJ, O’Shea P (1999) Ligand-dependent conformational equilibria of serum albumin revealed by tryptophan fluorescence quenching. Biophys J 76:2198–2207
Barbana C, Pérez MD, Pocovi C, Sánchez L, Wehbi Z (2008) Interaction of human α-lactalbumin with fatty acids: determination of binding parameters. Biochemistry (Moscow) 73(6):711–716
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 2010 POSDRU/89/1.5/S/52432 project, Organizing the national interest postdoctoral school of applied biotechnologies with impact on Romanian bioeconomy, project co-financed by the European Social Fund through the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development 2007-2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stănciuc, N., Aprodu, I., Râpeanu, G. et al. pH- and heat-induced structural changes of bovine α-lactalbumin in response to oleic acid binding. Eur Food Res Technol 236, 257–266 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1882-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1882-9