Abstract
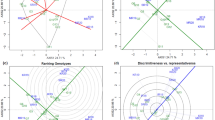
Increasing attention is being paid to environment characterisation as a means of identifying the environmental factors determining grain protein content (GPC) in durum wheat. New insights in crop physiology and agronomy have led to the development of crop simulation models. Those models can reconstruct plant development for past cropping seasons. One major advantage of these models is that they can also indicate the intensity of limiting factors affecting plants during particular developmental stages. The main environmental factors determining GPC in durum wheat can be investigated by introducing the intensity of limiting factors into genotype × environment (G×E) models. In our case, limiting factors corresponding to water deficit and nitrogen availability were calculated for the development period between booting and heading. These variables were then introduced into a clustering model. This model is an extension of factorial regression applied to discrete environment and genotypic variables. This procedure effectively described the environment main effect: around 30.9% of the sum of squares of the environment main effect was accounted for, using less than 33% of the degrees of freedom. It also partially accounted for G×E interaction. Our methodology, coupling the use of crop simulation and G×E analysis models, is of potential value for improving our understanding of the main development stages and identification of environmental limiting factors for the development of GPC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brancourt-Hulmel M, Biarnès-Dumoulin V, Denis J-B (1997) Points de repère dans l’analyse de la stabilité et de l’interaction génotype-milieu en amélioration des plantes. Agronomie 17:219–246
Brancourt-Hulmel M, Denis J-B, Lecomte C (2000) Determining environmental covariates which explain genotype environment interaction in winter wheat through probe genotypes and biadditive factorial regression. Theor Appl Genet 100:285–298
Brancourt-Hulmel M, Lecomte C, Denis J-B (2001) Choosing probe genotypes for the analysis of genotype-environment interaction in winter wheat trials. Theor Appl Genet 103:371–382
Brancourt-Hulmel M, Lecomte C (2003) Effect of environmental variates on genotype x environment interaction of winter wheat: a comparison of biadditive factorial regression to AMMI. Crop Sci 43:608–617
Decoux G, Denis J-B (1991) Intera. Logiciels pour l’interprétation statistique de l’interaction entre deux facteurs. Laboratoire de biométrie, INRA, 78026 Versailles cedex
Denis J-B (1989) Two-way analysis using covariates. Statistics 19:123–132
Denis J-B (1991) Ajustement de modèles linéaires et bilinéaires sous contraintes linéaires avec données manquantes. Rev Stat Appl 34:5–24
Denis J-B, Vincourt P (1982) Panorama des méthodes statistiques d’analyse des interaction génotype X milieu. Agronomie 2(3):219–230
Desclaux D (1996) De l’intérêt de génotypes révélateurs de facteurs limitants dans l’analyse des interaction génotype x milieu chez le soja (Glycine max. L. Merrill). Thèse de doctorat, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse
Finlay KW, Wilkinson GN (1963) The analysis of adaptation in plant-breeding programme. Aust J Agric Res 14:742–754
Foucteau V, El Daouk M, Baril C (2001) Interpretation of genotype by environment interaction in two sunflower experimental networks. Theor Appl Genet 102:327–334
Gate P (1995) Ecophysiologie du blé-de la plante à la culture, techniques and Documentation. Lavoisier, Paris, p429
Gauch HG (1992) Statistical analysis of regional yield trials: AMMI analysis of factorial designs. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gollob HF (1968) A statistical model which combines features of factor analytic and analysis of variance techniques. Psychometrika 3:73–116
Mandel J (1969) The partitioning of interaction in analysis of variance. J Res Nat Bur Stand (US) 738(4):309–327
Ottman MJ, Doerge TA, Martin EC (2000) Durum grain quality as affected by nitrogen fertilization near anthesis and irrigation during grain fill. Agron J 92:1035–1041
Reynolds MP, Trethowan R, Crossa J, Vargas M, Sayre KD (2002) Physiological factors associated with genotype by environment interaction in wheat. Field Crops Res 75:139–160
SAS Institute (1996) SAS/STAT User’s Guide, 2nd edn. SAS Institute Inc., Cary
Soltner D (2000) Les bases de la production végétale, Tome1, Le sol et son amélioration, Sciences et techniques agricoles, Saintes-Gemmes-Sur-Loire, p472
Strong WM (1982) Effect of late application of nitrogen on the yield and protein content of wheat. Aust J Exp Agric Anim Husb 22:54–61
Vargas M, Crossa J, Eeuwijk FA van, Ramirez ME, Sayre K (1999) Using partial least squares, factorial regression, and AMMI models for interpreting genotype × environment interaction. Crop Sci 39:955–967
Wuest SB, Cassman KG (1992) Fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigates wheat: I. Uptake efficiency of preplant versus late-season application. Agron J 84:682–688
Yates F, Cochran WG (1938) The analysis of groups of experiments. J Agric Sci (Camb) 28:556–580
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Philippe Gate for his active participation and the Arvalis Institut du Végétal for providing the climatic data and software necessary for the analysis. We also thank Christelle Crespin for providing the experimental data from the CTPS network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.C. Becker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacaze, X., Roumet, P. Environment characterisation for the interpretation of environmental effect and genotype × environment interaction. Theor Appl Genet 109, 1632–1640 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1786-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1786-6