Abstract
Background and aims
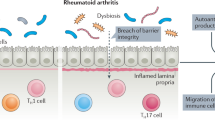
The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is to be further elucidated. The present study aims to investigate the role of oral antigen in the induction of RA-like inflammation in the articular joints of rats.
Methods
An RA animal model was developed by gavage-feeding with antigen and aspirin, and lipopolysaccharide intraperitoneal injection. The gut epithelial barrier function was assessed by the absorption of mannitol and lactose. The absorption of the specific antigen was observed by the immune fluorescent method. The frequency of antigen specific CD4+ T cells in the peripheral system was assessed by flow cytometry. The inflammation in the ankle joints was evaluated by light microscopy and immunohistochemistry.
Results
Rats treated with aspirin showed intestinal barrier dysfunction; high contents of the specific antigen were absorbed into the lamina propria. The antigen specific CD4+ T cells were detected in the spleen that could be activated by exposure to the specific antigen as well as the extracts of joint tissue. High levels of proinflammatory cytokines were detected in the sera. Antigen specific immune complexes were localized in the ankle joints. Heavy extravasation was observed in the synovial cavity. The histology showed an inflammatory feature in the ankle joints.
Conclusions
Oral antigen can induce RA-like inflammation in the articular joints under certain environment such as gut epithelial barrier dysfunction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hazes JMW, Luime JJ. The epidemiology of early inflammatory arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:381–90.
Carmona L, Cross M, Williams B, Lassere M, March L. Rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24:733–45.
Isaacs JD. The changing face of rheumatoid arthritis: sustained remission for all? Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:605–11.
Kyung Chang S, Gu Z, Brenner MB. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammatory arthritis pathology: the emerging role of cadherin-11. Immunol Rev. 2010;233:256–66.
Walsh NC, Gravallese EM. Bone remodeling in rheumatic disease: a question of balance. Immunol Rev. 2010;233:301–12.
Weissmann G. Rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus as immune complex diseases. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67:251.
Choi S, Lee YA, Hong SJ, Lee GJ, Kang S, Park JH, et al. Evaluation of inflammatory change and bone erosion using a murine type II collagen-induced arthritis model. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31:595–603.
He S-H, Chen X, Song C-H, Liu Z-Q, Zhou L-F, Ma W-J, et al. Interferon-lambda mediates oral tolerance and inhibits antigen-specific, T-helper 2 cell-mediated inflammation in mouse intestine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:249–58.
Burton OT, Oettgen HC. Beyond immediate hypersensitivity: evolving roles for IgE antibodies in immune homeostasis and allergic diseases. Immunol Rev. 2011;242:128–43.
Muraki M, Gleich GJ, Kita H. Antigen-specific IgG and IgA, but not IgE, activate the effector functions of eosinophils in the presence of antigen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011;154:119–27.
Kattah NH, Kattah MG, Utz PJ. The U1-snRNP complex: structural properties relating to autoimmune pathogenesis in rheumatic diseases. Immunol Rev. 2010;233:126–45.
Turnbull JA. Food allergens in connection with arthritis. Boston Med Surg J. 1924;82:438–40.
Turnbull JA. The relation of anaphylactic disturbances to arthritis. JAMA. 1924;82:1757–9.
Weatherbee M. Chronic arthritis. The clinical analysis of three hundred and fifty cases. Arch Intern Med. 1932;50:926–44.
Zeller M. Rheumatoid arthritis-food allergy as a factor. Ann Allergy. 1949;7:200–5.
Kokkonen J, Arvonen M, Vähäsalo P, Karttunen TJ. Intestinal immune activation in juvenile idiopathic arthritis and connective tissue disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2007;36:386–9.
Murphy H, Cogan T, Hughes R, Humphrey T. Porcine intestinal epithelial responses to campylobacter infection. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;34:489–95.
Yang PC, Jury J, Soderholm JD, Sherman PM, McKay DM, Perdue MH. Chronic psychological stress in rats induces intestinal sensitization to luminal antigens. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:104–14.
Farhadi A, Keshavarzian A, Kwasny MJ, Shaikh M, Fogg L, Lau C, et al. Effects of aspirin on gastroduodenal permeability in alcoholics and controls. Alcohol. 2010;44:447–56.
Ivey KJ. Drugs, gastritis, and peptic ulcer. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981;3(Suppl 2):29–34.
Yang PC, Berin MC, Yu L, Perdue MH. Mucosal pathophysiology and inflammatory changes in the late phase of the intestinal allergic reaction in the rat. Am J Pathol. 2001;158:681–90.
Monach PA, Hueber W, Kessler B, Tomooka BH, BenBarak M, Simmons BP, et al. A broad screen for targets of immune complexes decorating arthritic joints highlights deposition of nucleosomes in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:15867–72.
Monach PA, Nigrovic PA, Chen M, Hock H, Lee DM, Benoist C, et al. Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte functionΓêÆassociated antigen 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:753–64.
Spadaro A, Scrivo R, Riccieri V, Valesini G. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75:87–9.
Kim HR, Kim KW, Yoon SY, Kim SH, Lee SH. Serum pro-hepcidin could reflect disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:348–52.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 30871752, 31101280), Postdoctoral Scholarship of China (No. 20060390196), Shenzhen-Hong Kong Scientific Invention Foundation (CX Q2008026), Shenzhen Municipal Key Research Laboratory Support (SW201110010). Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR; #191063, #177843 and #220058), Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (#371268).
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
D. Wu, X. Liu and H. Su are contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Liu, X., Su, H. et al. Oral antigens induce rheumatoid arthritis-like inflammation in a rat model. Inflamm. Res. 62, 291–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-012-0577-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-012-0577-9