Abstract
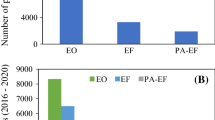
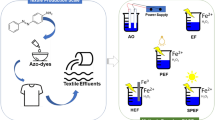
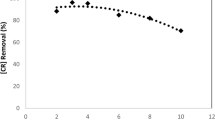
The threat of organic dye-rich wastewaters on the environment and health has risen as a major problem. The situation is becoming worsened as legislation on dye effluent discharge is more and more rigorous. Over the last three decades, many efforts have been intensified to the implementation of EAOPs as effective technologies for recalcitrant dye pollutants. It was found that the main factors governing these processes are electrode material, current intensity, initial pH and dye structure. Heterogeneous AO was found very sensitive to anode material. The best performance was achieved by costly BDD anodes. Homogenous processes were observed to be very efficient in decolorization. The oxidizing ability was in the following order AO–H2O2 < EF < PEF < SPEF. Combining EAOPs with similar processes or other technologies significantly improves mineralization. Adopting PV panels as energy source shows to be a promising option to reduce drawbacks related to EAOPs high costs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACF:
-
Activated carbon fiber
- AO:
-
Anodic oxidation
- AO–H2O2:
-
Anodic oxidation with electrogenerated H2O2
- AOP:
-
Advanced oxidation process
- BDD:
-
Boron-doped diamond
- BEF:
-
Bioelectro-Fenton
- CB:
-
Conductive band
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- CPC:
-
Compound parabolic collector
- CV:
-
Crystal violet; compound parabolic collector
- DOC:
-
Dissolved organic carbon
- DSA:
-
Dimensionally stable anode
- EAOP:
-
Electrochemical advanced oxidation process
- EF:
-
Electro-Fenton
- FCF:
-
Fast green
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- M:
-
Anode surface
- MCE:
-
Mineralization current efficiency
- MEC:
-
Microbial electrolysis cells
- MeG:
-
Methyl green
- MFC:
-
Microbial fuel cell
- MG:
-
Malachite green
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- OER:
-
Oxygen evolution reaction
- PC:
-
Peroxi-coagulation
- PEC:
-
Photoelectrocatalysis
- PEF:
-
Photoelectro-Fenton
- POP:
-
Persistent organic pollutant
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- PV:
-
Photovoltaic
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RVC:
-
Reticulated vitreous carbon
- SEF:
-
Sonoelectro-Fenton
- SHE:
-
Standard hydrogen electrode
- SPEF:
-
Solar photoelectro-Fenton
- SS:
-
Stainless steel
- TCE:
-
Total current efficiency
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
- UHPLC:
-
Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- UVA:
-
Ultraviolet A (315–400 nm)
- UVB:
-
Ultraviolet B (280–315 nm)
- UVC:
-
Ultraviolet C
- VB:
-
Valence band
- E:
-
Electrode potential (V)
- E°:
-
Standard redox potential (V/SHE)
- eV:
-
Electron-Volt
- hν :
-
Light radiation
- I:
-
Current intensity (mA)
- j:
-
Current density (mA cm−2)
- T:
-
Temperature (℃)
- V:
-
Volume (L)
- •OH:
-
Hydroxyl radical
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- TPM:
-
Triphenylmethane
References
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA, Rodrigo MA, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow-a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8336–8367
Garcia-Segura S, Ocon JD, Nan Chong M (2018) Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents-a review. Process Saf Environ 113:48–67
Nidheesh P, Zhou M, Oturan MA (2018) An overview on the removal of synthetic dyes from water by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 197:210–227
Barrera-Díaz C, Cañizares P, Fernández FJ, Natividad R, Rodrigo MA (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes-an overview of the current applications to actual industrial effluents. J Mex Chem Soc 58:256–275
Kapałka A, Fóti G, Comninellis C (2008) Kinetic modeling of the electrochemical mineralization of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. J Appl Electrochem 38:7–16
da Costa Soares IC, da Silva ÁRL, de Moura Santos ECM, dos Santos EV, da Silva DR, Martínez-Huitle CA (2020) Understanding the electrochemical oxidation of dyes on platinum and boron–doped diamond electrode surfaces: experimental and computational study. J Solid State Electr 24:3245–3256s
Comninellis C (1994) Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim Acta 39:1857–1862
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods-an updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166–167:603–643
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B Environ 202:217–261
He Y, Lin H, Guo Z, Zhang W, Li H, Huang W (2019) Recent developments and advances in boron-doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants. Sep Purif Technol 212:802–821
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem Rev 109:6541–6569
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Aoudj S, Drouiche N, Khelifa A (2019) Emerging contaminants remediation by heterogeneous photocatalysis, Book Chapter 9. In: Emerging and nanomaterial contaminants in wastewater, advanced treatment technologies. Elsevier Inc., pp 245–275
Orimolade BO, Arotiba OA (2020) Bismuth vanadate in photoelectrocatalytic water treatment systems for the degradation of organics: a review on recent trends. J Electroanal Chem 878:114724
Daghrir R, Drogui P, Robert D (2012) Photoelectrocatalytic technologies for environmental applications. J Photoch Photobio A 238:41–52
Qiu S, He D, Ma J, Liu T, Waite TD (2015) Kinetic modeling of the electro-Fenton process: quantification of reactive oxygen species generation. Electrochim Acta 176:51–58
Ghime D, Ghosh P (2019) Removal of organic compounds found in the wastewater through electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review. Russ J Electrochem 55:591–620
Thiam A, Sirés I, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E (2015) Decolorization and mineralization of Allura Red AC aqueous solutions by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 290:34–42
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimath R (2012) Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: an overview. Desalination 299:1–15
Zhao Z, Dong W, Wang H, Chen G, Tang J, Wu Y (2018) Simultaneous decomplexation in blended Cu(II)/Ni(II)-EDTA systems by electro-Fenton process using iron sacrificing electrodes. J Hazard Mater 350:128–135
Oturan MA, Brillas E (2007) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) for environmental applications. Port Electrochimica Acta 25:1–18
Kubo D, Kawase Y (2018) Hydroxyl radical generation in electro-Fenton process with in situ electro-chemical production of Fenton reagents by gas-diffusion-electrode cathode and sacrificial iron anode. J Clean Prod 203:685–695
Brillas E, Sauleda R, Casado J (1997) Peroxi-coagulation of aniline in acidic medium using an oxygen diffusion cathode. J Electrochem Soc 144:2374–2379
Aoudj S, Khelifa A, Zemmouri H, Hamadas I, Yatoui S, Zabchi N, Drouiche N (2018) Degradation of EDTA in H2O2-containing wastewater by photo-electrochemical peroxidation. Chemosphere 208:984–990
Rondán V, Ramírez B, Silva-Martínez S, Hernández JA, Tiwari MK, Alvarez-Gallegos A (2020) High removal efficiency of dye pollutants by anodic Fenton treatment. Int J Electrochem Sci 15:52–67
Wang Q, Lemley AT (2002) Oxidation of diazinon by anodic Fenton treatment. Water Res 36:3237–3244s
Brillas E (2014) A review on the degradation of organic pollutants in waters by UV photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton. J Braz Chem Soc 25:393–417
Brillas E (2020) A review on the photoelectro-Fenton process as efficient electrochemical advanced oxidation for wastewater remediation. Treatment with UV light, sunlight, and coupling with conventional and other photo-assisted advanced technologies. Chemosphere 250:126–198
Flox C, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Arias C, Brillas E (2007) Solar photoelectro-Fenton degradation of cresols using a flow reactor with a boron-doped diamond anode. Appl Catal B Environ 75:17–28
Oturan MA, Sires I, Oturan N, Pérocheau S, Laborde J-L, Trévin S (2008) Sonoelectro-Fenton proces: a novel hybrid technique for the destruction of organic pollutants in water. J Electroanal Chem 624:329–332
Chakma S, Moholkar VS (2013) Physical mechanism of sono-Fenton process. AIChE J 59:4303–4313
Suslick KS (1989) The chemical effects of ultrasound. Sci Am 260:80–87
Garbellini GS, Salazar-Banda GR, Avaca LA (2008) Ultrasound applications in electrochemical systems: theoretical and experimental aspects. Quim Nova 31:123–133
Pradhan AA, Gogate PR (2010) Degradation of p-nitrophenol using acoustic cavitation and Fenton chemistry. J Hazard Mater 173:517–522
Zhu X, Ni J (2009) Simultaneous processes of electricity generation and p-nitrophenol degradation in a microbial fuel cell. Electrochem Commun 11:274–277
Li X, Chen S, Angelidaki I, Zhang Y (2018) Bio-electro-Fenton processes for wastewater treatment: advances and prospects. Chem Eng J 354:492–506
Kahoush M, Behary N, Cayla A, Nierstrasz V (2018) Bio-Fenton and Bio-electro-Fenton as sustainable methods for degrading organic pollutants in wastewater. Process Biochem 64:237–247
Zou R, Angelidaki I, Jin B, Zhang Y (2020) Feasibility and applicability of the scaling-up of bio-electro-Fenton system for textile wastewater treatment. Environ Int 134:105352
Weng M, Zhou Z, Zhang Q (2013) Electrochemical degradation of typical dyeing wastewater in aqueous solution: performance and mechanism. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:290–296
de Oliveira GR, Fernandes NS, de Melo JV, da Silva DR, Urgeghe C, Martinez-Huitle CA (2011) Electrocatalytic properties of Ti-supported Pt for decolorizing and removing dye from synthetic textile wastewaters. Chem Eng J 168:208–214
Peralta-Hernandez JM, Mendez-Tovar M, Guerra-Sanchez R, Martinez-Huitle CA, Nava JL (2012) A brief review on environmental application of boron doped diamond electrodes as a new way for electrochemical incineration of synthetic dyes. Int J Electrochem 2012:1–18
Martínez-Huitle CA, dos Santos EV, de Araújo DM, Panizza M (2012) Applicability of diamond electrode/anode to the electrochemical treatment of a real textile effluent. J Electroanal Chem 674:103–107
Faouzi AM, Nasr B, Abdellatif G (2007) Electrochemical degradation of anthraquinone dye Alizarin Red S by anodic oxidation on boron-doped diamond. Dyes Pigments 73:86–89
Panizza M, Barbucci A, Ricotti R, Cerisola G (2007) Electrochemical degradation of methylene blue. Sep Purif Technol 54:382–387
Palma-Goyes RE, Guzmán-Duque FL, Penuela G, González I, Nava JL, Torres-Palma RA (2010) Electrochemical degradation of crystal violet with BDD electrodes: effect of electrochemical parameters and identification of organic by-products. Chemosphere 81:26–32
Martinez-Huitle CA, dos Santos EV, Medeiros de Araujo D, Panizza M (2012) Applicability of diamond electrode/anode to the electrochemical treatment of a real textile effluent. J Electroanal Chem 674:103–107
Osugi ME, Zanoni MVB, Chenthamarakshan CR, de Tacconi NR, Woldemariam GA, Mandal SS, Rajeshwar K (2008) Toxicity assessment and degradation of disperse azo dyes by photoelectrocatalytic oxidation on Ti/TiO2 nanotubular array electrodes. J Adv Oxid Technol 11:425–434
Zhang A, Zhou M, Liu L, Wang W, Jiao Y, Zhou Q (2010) A novel photoelectrocatalytic system for organic contaminant degradation on a TiO2 nanotube (TNT)/Ti electrode. Electrochim Acta 55:5091–5099
Olvera-Vargas H, Oturan N, Aravindakumar CT, Sunil Paul MM, Sharma VK, Oturan MA (2014) Electro-oxidation of the dye azure B: kinetics, mechanism, and by-products. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8379–8386
Lahkimi A, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Chaouch M (2007) Removal of textile dyes from water by the electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 5:35–39
Yu FK, Zhou MH, Yu XM (2015) Cost-effective electro-Fenton using modified graphite felt that dramatically enhanced on H2O2 electro-generation without external aeration. Electrochim Acta 163:182–189
Lei Y, Liu H, Shen Z, Wang W (2013) Development of a trickle bed reactor of electro-Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 261:570–576
Almeida LC, Garcia-Segura S, Arias C, Bocchi N, Brillas E (2012) Electrochemical mineralization of the azo dye Acid Red 29 (Chromotrope 2R) by photoelectro-Fenton process. Chemosphere 89:751–758
Feng C-H, Li F-B, Mai H-J, Li X-Z (2010) Bio-electro-Fenton process driven by microbial fuel cell for wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 44:1875–1880
Fernández de Dios MÁ, González del Campo A, Fernández FJ, Rodrigo M, Pazos M, Sanromán MÁ (2013) Bacterial-fungal interactions enhance power generation in microbial fuel cells and drive dye decolourisation by an ex situ and in situ electro-Fenton process. Bioresource Technol 148C:39–46
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Angelidaki I (2015) Alternate switching between microbial fuel cell and microbial electrolysis cell operation as a new method to control H2O2 level in Bioelectro-Fenton system. J Power Sources 291:108–116
Zarei M, Niaei A, Salari D, Khataee A (2010) Removal of four dyes from aqueous medium by the peroxi-coagulation method using carbon nanotube PTFE cathode and neural network modeling. J Electroanal Chem 639:167–174
Salari D, Niaei A, Khataee A, Zarei M (2009) Electrochemical treatment of dye solution containing C.I. basic yellow 2 by the peroxi-coagulation method and modeling of experimental results by artificial neural networks. J Electroanal Chem 629:117–125
Eslami A, Moradi M, Ghanbari F, Mehdipour F (2013) Decolorization and COD removal from real textile wastewater by chemical and electrochemical Fenton processes: a comparative study. J Environ Health Sci Eng 11:31
Khataee AR, Vahid B, Behjati B, Safarpour M, Joo SW (2014) Kinetic modeling of a triarylmethane dye decolorization by photoelectro-Fenton process in a recirculating system: nonlinear regression analysis. Chem Eng Res Des 92:362–367
Li H, Lei H, Yu Q, Li Z, Feng X, Yang B (2010) Effect of low frequency ultrasonic irradiation on the sonoelectro-Fenton degradation of cationic red X-GRL. Chem Eng J 160(2010):417–422
Martínez SS, Uribe EV (2012) Enhanced sonochemical degradation of azure B dye by the electroFenton process. Ultrason Sonochem 19:174–178
Wang A, Qu J, Liu H, Ru J (2008) Mineralization of an azo dye Acid Red 14 by photoelectro-Fenton process using an activated carbon fiber cathode. Appl Catal B Environ 84:393–399
Peralta-Hernández JM, Meas-Vong Y, Rodríguez FJ, Chapman TW, Maldonado MI, Godínez LA (2008) Comparison of hydrogen peroxide-based processes for treating dye-containing wastewater: decolorization and destruction of Orange II azo dye in dilute solution. Dyes Pigments 76:656–662
Diagne M, Sharma VK, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2014) Depollution of indigo dye by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton using B-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 12:219–224
Garcia-Segura S, El-Ghenymy A, Centellas F, Rodríguez RM, Arias C, Garrido JA, Cabot PL, Brillas E (2012) Comparative degradation of the diazo dye Direct Yellow 4 by electro-Fenton, photoelectro-Fenton and photo-assisted electro-Fenton. J Electroanal Chem 681:36–43
El-Ghenymy A, Centellas F, Rodríguez RM, Cabot PL, Garrido JA, Sirés I, Brillas E (2015) Comparative use of anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton with Pt or boron-doped diamond anode to decolorize and mineralize Malachite Green oxalate dye. Electrochim Acta 182:247–256
Thiam A, Brillas E, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Sirés I (2016) Routes for the electrochemical degradation of the artificial food azo-colour Ponceau 4R by advanced oxidation processes. Appl Catal B 180:227–236
Moreira FC, Garcia-Segura S, Vilar VJP, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E (2013) Decolorization and mineralization of Sunset Yellow FCF azo dye by anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton, UVA photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton processes. Appl Catal B 142–143:877–890
Alcocer S, Picos A, Uribe AR, Perez T, Peralta-Hernandez JM (2018) Comparative study for degradation of industrial dyes by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes with BDD anode in a laboratory stirred tank reactor. Chemosphere 205:682–689
Rocha JHB, Gomes MMS, Santos EVD, Moura ECMD, Silva DRD, Quiroz MA, Martínez-Huitle CA (2014) Electrochemical degradation of Novacron Yellow C-RG using boron-doped diamond and platinum anodes: direct and Indirect oxidation. Electrochim Acta 140:419–426
Hmani E, Samet Y, Abdelhédi R (2012) Electrochemical degradation of auramine-O dye at boron-doped diamond and lead dioxide electrodes. Diam Relat Mater 30:1–8
Song S, Fan J, He Z, Zhan L, Liu Z, Chen J, Xu X (2010) Electrochemical degradation of azo dye C.I. Reactive Red 195 by anodic oxidation on Ti/SnO2-Sb/PbO2 electrodes. Electrochim Acta 55:3606–3613
Liu CF, Huang CP, Hu CC, Huang C (2019) A dual TiO2/Ti-stainless steel anode for the degradation of Orange G in a coupling photoelectrochemical and photo-electro-Fenton system. Sci Total Environ 659:221–229
Saez C, Panizza M, Rodrigo MA, Cerisola G (2007) Electrochemical incineration of dyes using a boron-doped diamond anode. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82:575–581
Sires I, Guivarch E, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2008) Efficient removal of triphenylmethane dyes from aqueous medium by in situ electrogenerated Fenton’s reagent at carbon-felt cathode. Chemosphere 72:592–600
da Costa Soares IC, da Silva DR, Oliveira do Nascimento JH, Garcia-Segura S, Martínez-Huitle CA (2017) Functional group influences on the reactive azo dye decolorization performance by electrochemical oxidation and electro-Fenton technologies. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:24167–24176
Garcia-Segura S, Centellas F, Arias C, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Cabot PL, Brillas E (2011) Comparative decolorization of monoazo, diazo and triazo dyes by electro-Fenton process. Electrochim Acta 58:303–311
Aquino JM, Rodrigo MA, Rocha-Filho RC, Saez C, Canizares P (2012) Influence of the supporting electrolyte on the electrolyses of dyes with conductive diamond anodes. Chem Eng J 184:221–227
Fan Y, Ai Z, Zhang L (2010) Design of an electro-Fenton system with a novel sandwich film cathode for wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 176:678–684
Thiam A, Sires I, Brillas E (2015) Treatment of a mixture of food color additives (E122, E124 and E129) in different water matrices by UVA and solar photoelectro-Fenton. Water Res 81:178–187
Sales Solano AM, Costa de Araújo CK, Vieira de Melo J, Peralta-Hernandez JM, Ribeiro da Silva D, Martínez-Huitle CA (2013) Decontamination of real textile industrial effluent by strong oxidant species electrogenerated on diamond electrode: viability and disadvantages of this electrochemical technology. Appl Catal B 130–131:112–120
Wang A, Qu J, Ru J, Liu H, Ge J (2005) Mineralization of an azo dye Acid Red 14 by electro-Fenton’s reagent using an activated carbon fiber cathode. Dyes Pigments 65:227–233
Wang CT, Chou WL, Chung MH, Kuo YM (2010) COD removal from real dyeing wastewater by electro-Fenton technology using an activated carbon fiber cathode. Desalination 253:129–134
Wang SB (2008) A comparative study of Fenton and Fenton-like reaction kinetics in decolourisation of wastewater. Dyes Pigments 76:714–720
Ruiz EJ, Hernández-Ramírez A, Peralta-Hernández JM, Arias C, Brillas E (2011) Application of solar photoelectro-Fenton technology to azo dyes mineralization: effect of current density, Fe2+ and dye concentrations. Chem Eng J 171:385–392
Espinoza C, Romero J, Villegas L, Cornejo-Ponce L, Salazar R (2016) Mineralization of the textile dye acid yellow 42 by solar photoelectro-Fenton in a lab-pilot plant. J Hazard Mater 319:24–33
Almeida LC, Silva BF, Zanoni MVB (2014) Combined photoelectrocatalytic/electro-Fenton process using a Pt/TiO2NTs photoanode for enhanced degradation of an azo dye: a mechanistic study. J Electroanal Chem 734:43–52
Roshini PS, Gandhimathi R, Ramesh ST, Nidheesh PV (2017) Combined electro-Fenton and biological processes for the treatment of industrial textile effluent: mineralization and toxicity analysis. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 21:04017016
Zhu X, Ni J, Wei J, Xing X, Li H (2011) Destination of organic pollutants during electrochemical oxidation of biologically-pretreated dye wastewater using boron doped diamond anode. J Hazard Mater 189:127–133
Alvarez-Guerra E, Dominguez-Ramos A, Irabien A (2011) Design of the Photovoltaic Solar Electro-Oxidation (PSEO) process for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng Res Des 89:2679–2685
Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E (2016) Combustion of textile monoazo, diazo and triazo dyes by solar photoelectro-Fenton: decolorization, kinetics and degradation routes. Appl Catal B 181:681–691
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Research Fund from DGRSDT/MESRS (Algeria).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
S1: Appendix
S1: Appendix
S1: Different chemical formulas of dyes used in the study of Oliveira do Nascimento et al. [77]
Name | Formula |
|---|---|
Reactive Orange 16 (RO16) |
|
Reactive Violet 4 (RV4) |
|
Reactive Red 228 (RR228) |
|
Reactive Black 5 (RB5) |
|
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Aoudj, S., Bahloul, K., Khelifa, A. (2021). Degradation of Dyes by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. In: Muthu, S.S., Khadir, A. (eds) Advanced Removal Techniques for Dye-containing Wastewaters. Sustainable Textiles: Production, Processing, Manufacturing & Chemistry. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3164-1_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3164-1_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-3163-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-3164-1
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)