Abstract
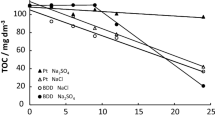
Hazardous wastes are generated in the synthesis of dyes and pigments applied in industries. Efficient methods are thus needed to clean wastewaters. Here, we use anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton with B-doped diamond anode to degrade the synthetic dye indigo in aqueous sodium dithionite. Results show the near-complete mineralization of the dye within 80 min at 500 mA. Mineralization was faster by electro-Fenton than anodic oxidation. The second-order rate constant (k) for the reaction of indigo with ·OH was measured as 4.03 × 109 M−1 s−1 at pH 3.0 and was compared with the rate constants of reactions between dyes and ·OH. The results clearly demonstrate that both electro-Fenton and anodic oxidation can be used to depollute dyes in textile effluent with high efficiency and low cost. The main oxidant, ·OH, being a non-selective reagent, the method could be applied to degrade other organic pollutants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammar S, Asma M, Oturan N, Abdelhédi R, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical degradation of anthraquinone dye alizarin red: role of the electrode material. Curr Org Chem 16:1978–1985
Beltran De Heredia J, Torregrosa J, Dominguez JR, Peres JA (2001) Kinetic model for phenolic compound oxidation by Fenton’s reagent. Chemosphere 45:85–90
Boufia-Chergui S, Oturan N, Khalaf H, Oturan MA (2010) Parametric study on the effect of the ratio [H2O2]/[Fe3+] on the photo-Fenton degradation of Basic Blue 41 cationic azo dye. J Environ Sci Heal A 45:622–629
Brillas E, Sirés I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109:6570–6631
Dirany A, Sirés I, Oturan N, Özcan A, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical treatment of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine: kinetics, reaction pathways, and toxicity evolution. Environ Sci Technol 46:4074–4082
Fonovich TM (2013) Sudan dyes: are they dangerous for human health. Drug Chem Toxicol 36:343–352
Garcia-Segura S, Dosta S, Guilemany JM, Brillas E (2013) Solar photoelectrocatalytic degradation of Acid Orange 7 azo dye using a highly stable TiO2 photoanode synthesized by atmospheric plasma spray. Appl Catal B Environ 132–133:142–150
Guivarch E, Oturan MA (2004) The problem of the contamination of waters by synthetic dyes: how to destroy them? Application of the electro-Fenton process. Actual Chim 277–278:65–69
Guivarch E, Trévin S, Lahitte C, Oturan MA (2003) Degradation of azo dyes in water by electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 1:39–44
Haidar M, Dirany A, Sirés I, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2013) Electrochemical degradation of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine by hydroxyl radicals generated at a BDD anode. Chemosphere 91:1304–1309
Hammami S, Oturan N, Bellakhal N, Dachraoui M, Oturan MA (2007) Oxidative degradation of direct orange 61 by electro-Fenton process using a carbon felt electrode: application of the experimental design methodology. J Electroanal Chem 610:75–84
Khan R, Bhawana P, Fulekar MH (2013) Microbial decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 12:75–97
Kobylewski S, Jacobson MF (2012) Toxicology of food dyes. Int J Occup Environ Health 18:220–246
Lahkimi A, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Chaouch M (2007) Removal of textile dyes from water by the electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 5:35–39
Oturan N, Brillas E, Oturan MA (2012) Unprecedented total mineralization of atrazine and cyanuric acid by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton with a boron-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 10:65–170
Oturan N, Wu J, Zhang H, Sharma VK, Oturan MA (2013) Electrocatalytic destruction of the antibiotic tetracycline in aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: effect of electrode materials. Appl Catal B Environ 140–141:92–97
Özcan A, Şahin Y, Savaş Koparal A, Oturan MA (2008) Carbon sponge as a new cathode material for the electro-Fenton process: comparison with carbon felt cathode and application to degradation of synthetic dye basic blue 3 in aqueous medium. J Electroanal Chem 616:71–78
Ramírez C, Saldaña A, Hernández B, Acero R, Guerra R, Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E, Peralta-Hernández JM (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of methyl orange azo dye at pilot flow plant using BDD technology. J Indus Eng Chem 19:571–579
Singh K, Arora S (2011) Removal of synthetic textile dyes from wastewaters: a critical review on present treatment technologies. Cri Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:807–878
Sirés I, Brillas E (2012) Remediation of water pollution caused by pharmaceutical residues based on electrochemical separation and degradation technologies: a review. Environ Int 40:212–229
Sirés I, Guivarch E, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2008) Efficient removal of triphenylmethane dyes from aqueous medium by in situ electrogenerated Fenton’s reagent at carbon-felt cathode. Chemosphere 72:592–600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diagne, M., Sharma, V.K., Oturan, N. et al. Depollution of indigo dye by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton using B-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 12, 219–224 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0437-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0437-z