Abstract
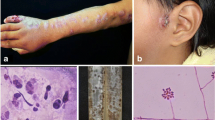
Definitive diagnosis of sporotrichosis is based on fungal detection in culture. Microscopic methods for the detection of Sporothrix yeast cells in clinical samples have low sensitivity. Although culture methods have high sensitivity, they also have some limitations, such as the time required to conclude the diagnosis, usually from 10 to 15 days, and the difficulty of obtaining an adequate clinical specimen for the test in cases of extracutaneous sporotrichosis. Serological methods are useful tools for a presumptive diagnosis of this infection. The most-used antigenic Sporothrix molecules are the peptide-rhamnomannan and secreted exoantigens. The enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) technique using the peptide-rhamnomannan has high efficiency, and it is useful in the serological follow-up of infection. Exoantigens were first used in immunoprecipitation and agglutination tests, but they have been used more recently in immunoenzymatic tests, with high sensitivity and specificity for both human and feline disease. A glycoprotein of 70 kDa was purified from Sporothrix exoantigens, presenting high immunogenicity, which allows its use in the development of more sensitive and specific methods for sporotrichosis serodiagnosis. Molecular methods of diagnosis can lower the time for diagnosis conclusion, but described methodologies in this field are scarce. In conclusion, the diagnosis of sporotrichosis is a challenging field, and the development of new serological and molecular diagnostic methods is mandatory.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albornoz MB, Villanueva E et al (1984) Application of immunoprecipitation techniques to the diagnosis of cutaneous and extracutaneous forms of sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 85:177–183
Almeida-Paes R, Pimenta MA, Pizzini CV et al (2007a) Use of mycelial-phase Sporothrix schenckii exoantigens in an Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay for diagnosis of sporotrichosis by antibody detection. Clin Vac Immunol 14:244–249
Almeida-Paes R, Pimenta MA, Monteiro PC et al (2007b) Immunoglobulins G, M, and A against Sporothrix schenckii exoantigens in patients with sporotrichosis before and during treatment with itraconazole. Clin Vac Immunol 14:1149–1157
Almeida-Paes R, Bailão AM, Pizzini CV et al (2012) Cell-free antigens of Sporothrix brasiliensis: antigenic diversity and application in an immunoblot assay. Mycoses 55:467–475
Arenas G, Toriello C (1986) Actividad inmunológica de antígenos miceliales y levaduriformes de diferentes fases de crecimiento de Sporothrix schenckii. Rev Mex Mic 2:131–144
Barros MB, Schubach AO, Valle AC et al (2004) Cat-transmitted sporotrichosis epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: description of a series of cases. Clin Infect Dis 38:529–535
Barros MBL, Almeida-Paes R, Schubach AO (2011) Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 24:633–654
Berbee ML, Taylor JW (1992) 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequence characters place the human pathogen Sporothrix schenckii in the genus Ophiostoma. Exp Mycol 16:87–91
Bernardes-Engemann AR, Costa RC, Miguens BR et al (2005) Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the serodiagnosis of several clinical forms of sporotrichosis. Med Mycol 43:487–493
Bernardes-Engemann AR, Loureiro y Penha CV, Benvenuto F et al (2009) A comparative serological study of the SsCBF antigenic fraction isolated from three Sporothrix schenckii strains. Med Mycol 47:874–878
Blumer SO, Kaufman L, Kaplan W et al (1973) Comparative evaluation of five serological methods for the diagnosis of sporotrichosis. Appl Microbiol 26:4–8
Bonifaz A, Vázquez-González D (2010) Diagnostic methods: an update. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 145:659–673
Bonifaz A, Vázquez-González D (2013) Diagnosis and treatment of lymphocutaneous Diagnostic methods: what are the options? Curr Fungal Infect Rep 7:252–259
Bonifaz A, Araiza J, Perez-Mejía A et al (2013) Prueba intradérmica con esporotricina en una comunidad de la Sierra Norte de Puebla. Dermatol Rev Mex 57:428–432
Casserone S, Conti-Diaz IA, Zanetta E et al (1983) Serologia de laesporotricosis cutânea. Sabouraudia 21:317–321
Costa RO, de Mesquita KC, Damasco PS et al (2008) Infectious arthritis as the single manifestation of Diagnostic methods: serology from serum and synovial fluid samples as an aid to diagnosis. Rev Iberoam Micol 25:54–56
Dominguez-Soto L, Hojyo-Tomoka MT (1983) The intradermal sporotrichin test and the diagnosis of sporotrichosis. Int J Dermatol 22:520
Fernandes GF, Amaral CC, Sasaki A et al (2009) Heterogeneity of proteins expressed by Sporothrix schenckii isolates. Med Mycol 47:855–861
Fernandes GF, Lopes-Bezerra LM, Bernardes-Engemann AR et al (2011) Serodiagnosis of sporotrichosis infection in cats by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a specific antigen, SsCBF, and crude exoantigens. Vet Microbiol 147:445–449
Fernandes GF, Santos PO, Rodrigues AM et al (2013) Characterization of virulence profile, protein secretion and immunogenicity of different Sporothrix schenckii sensu stricto isolates compared with S. globosa and S. brasiliensis species. Virulence 4:241–249
Freitas DFS, Valle ACF, Almeida-Paes R et al (2010) Zoonotic sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: a protracted epidemic yet to be curbed. Clin Infect Dis 50:453
González-Ochoa A, Figueroa ES (1947) Polisacaridos del Sporotrichum schenckii. Datos immunologicos: intradermoreaccion en el diagnostic de la esporotrichosis. Rev Inst Salubr Enferm Trop 8:143–153
González-Ochoa A, Ricoy E (1970) Valoración comparativa de los antígenos polisacáridos y celular de Sporothrix schenckii. Rev Invest Salud Publica 30:303–315
Hu S, Chung WH, Hung SI et al (2003) Detection of Sporothrix schenckii in clinical samples by a nested PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol 41:1414–1418
Kano R, Nakamura Y, Watanabe S et al (2001) Identification of Sporothrix schenckii based on sequences of the chitin synthase 1 gene. Mycoses 44:261–265
Kano R, Matsuoka A, Kashima M et al (2003) Detection of Sporothrix schenckii chitin synthase 1 (CHS1) gene in biopsy specimens from human patients with sporotrichosis. J Dermatol Sci 33:73–74
Karlin JV, Nielsen HS (1970) Serologic aspects of sporotrichosis. J Infect Dis 121:316–327
Kashima T, Honma R, Kishi S et al (2010) Bulbar conjunctival sporotrichosis presenting as a salmon-pink tumor. Cornea 29:573–576
Kwon-Chung KJ, Bennett JE (eds) (1992) Medical mycology. Lea & Febiger, London
Liu X, Zhang Z, Hou B et al (2013) Rapid identification of Sporothrix schenckii in biopsy tissue by PCR. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27:1491–1497
Lloyd KO, Bitoon MA (1971) Isolation and purification of a peptido-rhamnomannan from the yeast form of Sporothrix schenckii. Structural and immunochemical studies. J Immunol 107:663–671
Lopes-Bezerra LM, Lima OC (1997) Identification of a concavalin A-binding antigen of the cell surface of Sporothrix schenckii. J Med Vet Mycol 35:167–172
Lopes-Bezerra LM, Schubach A, Costa RO (2006) Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. Ann Acad Bras Ciencias 78:293–308
Marimon R, Cano J, Gené J et al (2007) Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest. J Clin Microbiol 45:198–3206
Marimon R, Gené J, Cano J et al (2008) Sporothrix luriei: rare fungus from clinical origin. Med Mycol 46:621–625
Mayorga R, Cáceres A, Toriello C et al (1978) Etude d’une zone d’endemie sporotrichosique au Guatemala. Sabouraudia l6:l85–l98
Mendez-Tovar LJ, Lemini-López A, Hernández-Hernández F et al (2003) Frecuencia de micosis en tres comunidades de la sierra norte de Puebla. Gac Med Mex 139:1–6
Mendoza M, Diaz AM, Hung MB et al (2002) Production of culture filtrates of Sporothrix schenckii in diverse culture media. Med Mycol 40:447–454
Mendoza M, Brito A, Schaper DA et al (2012) Evaluación de la técnica PCR anidada para el diagnóstico de la esporotricosis experimental. Rev Iberoam Micol 29:120–125
Morris-Jones R (2002) Sporotrichosis. Clin Exp Dermatol 27:427–431
Nascimento RC, Almeida SR (2005) Humoral immune response against soluble and fractionate antigens in experimental sporotrichosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 43:241–247
Nascimento RC, Espíndola NM, Castro RA et al (2008) Passive immunization with monoclonal antibody against a 70-Kda putative adhesin of Sporothrix schenckii induces protection in murine sporotrichosis. Eur J Immunol 38:3080–3089
Oliveira MME, Almeida-Paes R, Muniz MM et al (2011) Phenotypic and molecular identification of Sporothrix isolates from an epidemic area of sporotrichosis in Brazil. Mycopathologia 172:257–267
Oliveira MME, Almeida-Paes R, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC et al (2014) Molecular identification of the Sporothrix schenckii complex. Rev Iberoam Micol 31:2–6
Orofino-Costa R, Bóia MN, Magalhães GAP et al (2009) Arthritis as a hypersensitivity reaction in a case of sporotrichosis transmitted by a cat: clinical and serological follow up of 13 months. Mycoses 53:81–83
Penha CV, Lopes-Bezerra LM (2000) Concanavalin A-binding cell wall antigens of Sporothrix schenckii: a serological study. Med Mycol 38:1–7
Quintella LP, Passos SRL, Valle ACF et al (2011) Histopathology of cutaneous sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro: a series of 119 consecutive cases. J Cutan Pathol 38:25–32
Rippon JW (1988) Sporotrichosis. Medical mycology: the pathogenic fungi and pathogenic actinomycetes. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Rocha-Posada H (1968) Pruebacutánea con esporotricina. Mycopathologia 36:42–54
Ruiz-Baca E, Toriello C, Pérez-Torres A et al (2009) Isolation and some properties of a glycoprotein of 70 kDa (Gp70) from the cell wall of Sporothrix schenckii involved in fungal adherence to dermal extracellular matrix. Med Mycol 47:185–196
Ruiz-Baca E, Cuéllar-Cruz M, López-Romero E, Reyes Montes MR, Toriello C (2013) Fungal cell wall antigens for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections. Fungal cell wall. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., New York, pp 207–208
Ruiz-Baca E, Hérnandez-Mendoza G, Cuéllar-Cruz M et al (2014) Detection of 2 immunoreactive antigens in the cell wall of Sporothrix brasiliensis and Sporothrix globosa. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 79:328–330
Sánchez-Aleman MA, Araiza J, Bonifaz A (2004) Aislamiento y caracterización de cepas silvestres de Sporothrix schenckii e investigación de reactores a la esporotricina. Gac Med Mex 140:507–513
Sandhu GS, Kline BC, Stockman L et al (1995) Molecular probes for diagnosis of fungal infections. J Clin Microbiol 33:2913–2919
Schubach TMP, Schubach AO, Okamoto T et al (2004) Evaluation of an epidemic of sporotrichosis in cats: 347 cases (1998-2001). J Am Vet Med Assoc 224:1623–1629
Schubach TMP, Schubach AO, Okamoto T et al (2006) Canine sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: clinical presentation, laboratory diagnosis and therapeutic response in 44 cases (1998-2003). Med Mycol 44:87–92
Scott EN, Muchmore HG (1989) Immunoblot analysis of antibody responses to Sporothrix schenckii. J Clin Microbiol 27:300–304
Sharma S, Choudhary R, Juneja M et al (2005) Cutaneous tuberculosis mimicking sporotrichosis. Indian J Pediatr 72:86
Silva MB, Costa MM, Torres CC et al (2012) Urban Diagnostic methods: a neglected epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Cad Saude Publica 28:1867–1880
Takata M, Ishizaki H (1983) Correlations among culture times, sugar composition and biological activities of Sporothrix schenckii antigens. Mycopathologia 84:31–39
Teixeira PAC, Castro RA, Nascimento RC et al (2009) Cell spots surface expression of adhesins for fibronectin correlates with virulence of Sporothrix schenckii. Microbiology 155:3730–3738
Toriello C, ArjonaRosado L, Taylor ML (1991) Efficiency of crude and purified fungal antigens in serodiagnosis to discriminate mycotic from other respiratory diseases. Mycoses 34:133–140
Widal F, Abrami P, Joltrain E et al (1910) Sero diagnostic mycosique. Applications audiagnostic de la sporotrichose et de l’ctinomycose. Les coagglutination set cofixations mycosiques. Ann Inst Pasteur 24:1–33
Xu TH, Lin JP, Gao XH et al (2010) Identification of Sporothix schenckii of various mtDNA types by nested PCR assay. Med Mycol 48:161–165
Zancope-Oliveira RM, Almeida-Paes R, Oliveira MME et al (2011) New diagnostic applications in sporotrichosis. In: Khopkar U (ed) Skin biopsy perspectives, 1st edn. InTech, Croatia
Zhang Z, Liu X, Lv X et al (2011) Variation in genotype and higher virulence of a strain of Sporothrix schenckii causing disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 172:439–446
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zancope-Oliveira, R.M., Almeida-Paes, R., Ruiz-Baca, E., Toriello, C. (2015). Diagnosis of Sporotrichosis: Current Status and Perspectives. In: Zeppone Carlos, I. (eds) Sporotrichosis. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11912-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11912-0_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-11911-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-11912-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)