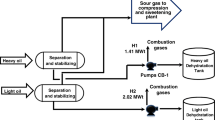
Abstract
Sustainability in design and operation of industrial processes has become a global issue in process engineering. Of late, there has been keen interest in operationalizing sustainability particularly in the oil and gas processing industries. One way of operationalizing sustainability is to combine ‘process integration’ and ‘process optimization’ in a framework that allows engineers to significantly improve operating efficiencies. In this study, methods, mechanisms and perspectives for integrating waste minimization and process parameter optimization in order to improve operating efficiencies in natural-gas-liquids (NGL) process systems are discussed. The aim of the analysis is to provide a basis for; reducing wastes, increasing the efficiency of materials processing, as well as optimize the consumption of natural gas in NGL operations and processing facilities. The solution trajectory for operationalizing sustainability was developed by creating an innovative cleaner-production-based framework that addresses sustainability concepts through process system optimization and implementation of optimal production operation strategies. To this end, opportunities for cleaner production assessments in NGL operations and processing systems were investigated. Cleaner production alternatives were examined and evaluated with respect to in-place environmental management systems. An adapted cleaner production model that dynamically incorporates; (a) process integration, (b) process optimization, (c) optimal production operation strategies, and (d) operational excellence in a bid to deploy sustainability concepts in NGL plants was developed. The applicability of the proposed model was illustrated through a case study of an existing NGL plant in Qatar. It was concluded that innovative cleaner production models that take cognizance of existing environmental management systems can quickly reveal sustainability initiatives in NGL process systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klemes J, Friedler F, Bulatov I, Varbanov P (2011) Sustainability in the process industry, integration and optimization. McGraw Hill, New York
Dennis P, Shobirin M (2009) Reducing environmental risks to as low as reasonably practicable in South East Asia, Doi: 10.2118/122724-MS
Linnhoff B, Vredeveld DR (1984) Pinch technology has come of age. Chem Eng Progr 80(7):33–40
Tan R, Foo DCY (2007) Pinch analysis approach to carbon-constrained energy sector planning. Energy 32(8):1422–1429
Gundersen T (2000) A process integration primer-implementing agreement on process integration Trondheim. International Energy Agency, SINTEF Energy Research, Norway
Rivera A, Gonzalez J, Carrillo R, Martinez J (2009) Operational change as a profitable cleaner production tool for a brewery. J Cleaner Prod 17:137–142
Berkel RV (2000) Overview of the cleaner production concept and relation with other environmental management strategies, cleaner production for process industries, pp 1–14, www.p2pays.org/ref/13/12031.pdf
Kjaerheim G (2005) Cleaner production and sustainability. J Cleaner Prod 13:329–339
Himmelblau M (1967) Basic principles and calculations in chemical engineering, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Morris, A. E., Geiger, G. and Fine, H. A. (2011) Fundamentals of Material Balances with Applications to Non-Reacting Systems, in Handbook on Material and Energy Balance Calculations in Material Processing, Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA
Musharavati F (2012) Cleaner Production Opportunities for Natural-Gas-Liquids Operations That Implement BATs Within an Environmental Management Framework, In Abdelwahab Aroussi and Farid Benyahia (eds) Proceedings of the 3rd Gas Processing Symposium, Volume 3 in Advances in Gas Processing Pages 50–57
Acknowledgement
This research was made possible by a UREP award [UREP 09-078-2-021] from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of The Qatar Foundation). The statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Nomenclature
Nomenclature
- Hg:
-
Mercury
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- H2S:
-
Hydrogen sulphide
- RSH:
-
Mercaptan compounds
- COS:
-
Carbonyl sulphide
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxide
- CH4 :
-
Methane
- VOC:
-
Volatile organic compounds
- SO2 :
-
Sulphur dioxide
- Cl2 :
-
Residual chlorine
- SOx :
-
Sulphur oxides
- NOx :
-
Nitrogen oxides
- NGL:
-
Natural gas liquids
- BATs:
-
Best available technologies
- EMS:
-
Environmental management systems
- CP:
-
Cleaner production
- AGRU:
-
Acid gas removal unit
- SRU:
-
Sulphur recovery unit
- GDU:
-
Glycol dehydration unit
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Fahd, R., Musharavati, F. (2014). Perspectives on Sustainability in Natural-Gas-Liquids Operations Through a Cleaner Production Framework. In: Dincer, I., Midilli, A., Kucuk, H. (eds) Progress in Sustainable Energy Technologies Vol II. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07977-6_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07977-6_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-07976-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-07977-6
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)