Abstract
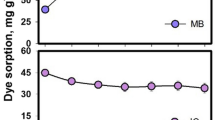
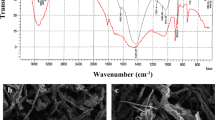
The sorption of thioflavine T (TT) and malachite green (MG) cationic synthetic dyes on dried biomass of green microalga (Chlorella pyrenoidosa) immobilised in polyurethane foam under continuous column systems conditions using spectrophotometric methods of detection was investigated. Data characterising the sorption of TT and MG on microalgal biomass immobilised in polyurethane foam in a column system from single (C 0 = 25 μmol dm−3) or binary equimolar (C 0 = 25 μmol dm−3) dye solutions in the form of breakthrough curves were well described by the Thomas (R 2 = 0.994–0.912), Yoon-Nelson (R 2 = 0.994–0.911), and Clark (R 2 = 0.993–0.911) models. Useful parameters characterising the sorption column system were obtained from these mathematical models. The Thomas model, in particular, provided the Q max (maximal sorption capacity in μmol g−1) parameter for characterisation of biosorbent and also for evaluation of competitive effects in the TT and MG dyes sorption. For the purposes of biomass regeneration, a one-step desorption of the dyes studied from the microalgal biomass in batch and continuous column systems was performed. Efficiency of TT desorption from microalgal biomass increased in the order: deionised H2O (50.7 %), 99.5 vol. % 1,4-dioxane (67 %), 20 mmol dm−3 NiCl2 (83 %), 96 vol. % ethanol (85 %), 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl (89 %), 1 mol dm−3 acetic acid (89 %). In the case of MG, the desorption efficiency increased in the order: deionised H2O (13 %), 20 mmol dm−3 NiCl2 (50 %), 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl (91 %), 99.5 vol. % 1,4-dioxane (94 %), 1 mol dm−3 acetic acid (99 %), 96 vol. % ethanol (> 99 %). The presence of carboxyl, phosphoryl, amino, and hydroxyl groups, the important functional groups for sorption of cationic xenobiotics, was also confirmed on the algae biomass surface by potentiometric titration and ProtoFit modelling software. The data obtained showed that the dried immobilised algae biomass could be used as a sorbent for removing toxic xenobiotics from liquid wastewaters or contaminated waters and also presenting the possibilities of mathematical modelling of sorption processes in continuous column systems in order to obtain important parameters for use in practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu, Z. (2005). Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: a review. Process Biochemistry, 40, 997–1026. DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2004.04.008.
Ansari, R., & Mosayebzadeh, Z. (2011). Application of polyaniline as an efficient and novel adsorbent for azo dyes removal from textile wastewaters. Chemical Papers, 65, 1–8. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-010-0083-x.
Bohart, G., & Adams, E. Q. (1920). Some aspects of the behavior of charcoal with respect to chlorine. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 42, 523–544. DOI: 10.1021/ja01448a018.
Bradbury, M. H., & Baeyens, B. (2009). Sorption modelling on illite Part I: Titration measurements and the sorption of Ni, Co, Eu and Sn. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73, 990–1003. DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.11.017.
Branquinho, C., & Brown, D. H. (1994). A method for studying the cellular location of lead in lichens. The Lichenologist, 26, 83–90. DOI: 10.1006/lich.1994.1007.
Charumathi, D., & Das, N. (2012). Packed bed column studies for the removal of synthetic dyes from textile wastewater using immobilised dead C. tropicalis. Desalination, 285, 22–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.09.023.
Chen, G. Q., Zeng, G. M., Tang, L., Du, C. Y., Jiang, X. Y, Huang, G. H., Liu, H. L., & Shen, G. L. (2008). Cadmium removal from simulated wastewater to biomass byproduct of Lentinus edodes. Bioresources Technology, 99, 7034–7040. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.020.
Clark, R. M. (1987). Evaluating the cost and performance of field-scale granular activated carbon systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 21, 573–580. DOI: 10.1021/es00160a008.
Febrianto, J., Kosasih, A. N., Sunarso, J., Ju, I. H., Indraswati, N., & Ismadji, S. (2009). Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: A summary of recent studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162, 616–645. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.042.
Fernandez, M. E., Nunell, G. V., Bonelli, P. R., & Cukierman, A. L. (2010). Effectiveness of Cupressus sempervirens cones as biosorbent for the removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions in batch and dynamic modes. Bioresource Technology, 101, 9500–9507. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.102.
Fernandez, M. E., Nunell, G. V., Bonelli, P. R., & Cukierman, A. L. (2012). Batch and dynamic biosorption of basic dyes from binary solutions by alkaline-treated cypress cone chips. Bioresource Technology, 106, 55–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.003.
Gad, H. M. H., & El-Sayed, A. A. (2009). Activated carbon from agricultural by-products for the removal of Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 1070–1081. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.155.
Gao, J. F., Zhang, Q., Su, K., & Wang, J. H. (2010). Competitive biosorption of Yellow 2G and Reactive Brilliant Red K-2G onto inactive aerobic granules: Simultaneous determination of two dyes by first-order derivative spectrophotometry and isotherm studies. Bioresource Technology, 101, 5793–5801. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.091.
Hornik, M., Pipiška, M., Augustin, J., Lesny, J., & Baratova, Z. (2007a). Distribution of 137Cs and 60Co in fresh water plants. Cereal Research Communications, 35, 477–480. DOI: 10.1556/crc.35.2007.2.78.
Hornik, M., Pipiška, M., Augustin, J., Lesny, J., & Kočiova, M. (2007b). Distribution of 137Cs and 60Co in components of fresh water system. Cereal Research Communications, 35, 473–476. DOI: 10.1556/crc.35.2007.2.77.
Khataee, A. R. Zarei, M., Dehghan, G., Ebadi, E., & Pourhassan, M. (2011). Biotreatment of a triphenylmethane dye solution using a Xanthophyta alga: Modeling of key factors by neural network. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42, 380–386. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtice.2010.08.006.
Koprivanac, N., & Kusic, H. (2008). Hazardous organic pollutants in colored wastewaters (pp. 81). New York, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers.
Lim, S. L., Chu, W. L., & Phang, S. M. (2010). Use of Chlorella vulgaris for bioremediation of textile wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 101, 7314–7322. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.092.
Malik, R., Ramteke, D. S., & Wate, S. R. (2007). Adsorption of malachite green on groundnut shell waste based powdered activated carbon. Waste Management, 27, 1129–1138. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.06.009.
Mehta, S. K., & Gaur, J. P. (2005). Use of algae for removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: Progress and prospects. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 25, 113–152. DOI: 10.1080/07388550500248571.
Muhamad, H., Doan, H., & Lohi, A. (2010). Batch and continuous fixed-bed column biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+. Chemical Engineering Journal, 158, 369–377. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.042.
Naja, G., & Volesky, B. (2006). Multi-metal biosorption in a fixed-bed flow-through column. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 281, 194–201. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.02.040.
Park, D. H., Yun, Y. S., & Park, J. M. (2010). The past, present, and future trends of biosorption. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 15, 86–102. DOI: 10.1007/s12257-009-0199-4.
Rao, K. S., Anand, S., & Venkateswarlu, P. (2011). Modeling the kinetics of Cd(II) adsorption on Syzygium cumini L. leaf powder in a fixed bed mini column. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 17, 174–181. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2011.02.003.
Rathinam, A., Maharshi, B., Janardhanan, S. K., Jonnalagadda, R. R., & Nair, B. U. (2010). Biosorption of cadmium metal ion from simulated wastewaters using Hypnea valentiae biomass: A kinetic and thermodynamic study. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1466–1470. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009. 08.008.
Robinson, T., McMullan, G., Marchant, R., & Nigam, P. (2001). Remediation of dyes in textiles effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresource Technology, 77, 247–255. DOI: 10.1016/s0960-8524(00)00080-8.
Salleh, M. A. M., Mahmoud, D. K., Karim, W. A. W. A., & Idris, A. (2011). Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination, 280, 1–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.07.019.
Tang, L., Zeng, G. M., Shen, G. L., Li, Y. P., Zhang, Y., & Huang, D. L. (2008). Rapid detection of picloram in agricultural field samples using a disposable immunomembranebased electrochemical sensor. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 1207–1212. DOI: 10.1021/es7024593.
Thomas, H. C. (1944). Heterogeneous ion exchange in a flowing system. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 66, 1664–1666. DOI: 10.1021/ja01238a017.
Turner, B. F., & Fein, J. B. (2006). Protofit: A program for determining surface protonation constants from titration data. Computers & Geosciences, 32, 1344–1356. DOI: 10.1016/j.cageo.2005.12.005.
Verma, A. K., Dash, R. R., & Bhunia, P. (2012). A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour from textile wastewaters. Journal of Environmental Management, 93, 154–168. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.09.012.
Vijayaraghavan, K., & Yun, Y. S. (2008). Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnology Advances, 26, 266–291. DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.02.002.
Volesky, B. (2003). Sorption and biosorption (pp. 316). Quebec, Canada: BV Sorbex.
Wang, J. L., & Chen, C. (2009). Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 195–226. DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.11.002.
Yan, G. G., Viraraghavan, T., & Chen, M. (1999). A new model for heavy metal removal in a biosorption column. Adsorption Science & Technology, 19, 25–43. DOI: 10.1260/0263617011493953.
Yoon, Y. H., & Nelson, J. H. (1984). Application of gas adsorption kinetics. I. A theoretical model for respirator cartridge service time. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 45, 509–516. DOI: 10.1080/15298668491400197.
Zhang, Y. S., Liu, W. G., Xu, M., Zheng, F., & Zhao, M. J. (2010). Study of the mechanisms of Cu2+ biosorption by ethanol/caustic-pretreated baker’s yeast biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178, 1085–1093. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.051.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horník, M., Šuňovská, A., Partelová, D. et al. Continuous sorption of synthetic dyes on dried biomass of microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa . Chem. Pap. 67, 254–264 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0235-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0235-2