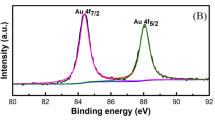
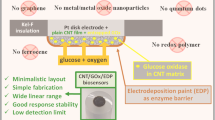
Abstract
Various types of carbon nanoparticles were directly mixed with microbial cells of Gluconobacter oxydans within a 3-D bionanocomposite in order to prepare a highly sensitive ethanol biosensor with a short response time. From all carbonaceous nanomaterials tested, single- or multi-walled carbon nanotubes provided the highest sensitivity of detection (117–121 µA cm−2 mM−1), but from a practical point of view, Ketjen black 300 and 600 provide very low detection limit (2–6 µM) and high sensitivity for the ethanol analysis (84–88 µA cm−2 mM−1)with a shortresponse time (14–33 s). Moreover, the price of Ketjen black is a few orders of magnitude lower compared to that of carbon nanotubes. Finally, the study showed that the morphology of nanoparticles rather than their surface modification is the key element in achieving high sensitivity of ethanol detection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertók, T., Katrlík, J., Gemeiner, P., & Tkac, J. (2013). Electrochemical lectin based biosensors as a label-free tool in glycomics. Microchimica Acta, 180, 1–13. DOI: 10.1007/s00604-012-0876-4.
Bertokova, A., Bertok, T., Filip, J., & Tkac, J. (2014). Gluconobacter sp. cells for manufacturing of efficient electrochemical biosensors and biofuel cells. Chemical Papers, in press.
Bucko, M., Mislovičová, D., Nahálka, J., Vikartovská, A., Šefčovičová, J., Katrlík, J., Tkáč, J., Gemeiner, P., Lacík, I., Štefuca, V., Polakovič, M., Rosenberg, M., Rebroš, M., Šmogrovičová, D., & Švitel, J. (2012). Immobilization in biotechnology and biorecognition: from macro- to nanoscale systems. Chemical Papers, 66, 983–998. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-012-0226-3.
Filip, J., Šefčovičová, J., Gemeiner, P., & Tkac, J. (2013). Electrochemistry of bilirubin oxidase and its use in preparation of a low cost enzymatic biofuel cell based on a renewable composite binder chitosan. Electrochimica Acta, 87, 366–374. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.09.054.
Ikeda, T., Kurosaki, T., Takayama, K., Kano, K., & Miki, K. (1996). Measurements of oxidoreductase-like activity of intact bacterial cells by an amperometric method using a membrane-coated electrode. Analytical Chemistry, 68, 192–198. DOI: 10.1021/ac950240a.
Kondo, T., & Ikeda, T. (1999). An electrochemical method for the measurements of substrate-oxidizing activity of acetic acid bacteria using a carbon-paste electrode modified with immobilized bacteria. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 51, 664–668. DOI: 10.1007/s002530051448.
Lei, Y., Chen, W., & Mulchandani, A. (2006). Microbial biosensors. Analytica Chimica Acta, 568, 200–210. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.11.065.
Logan, B. E., & Elimelech, M. (2012). Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature, 488, 313–319. DOI: 10.1038/nature11477.
Logan, B. E., & Rabaey, K. (2012). Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science, 337, 686–690. DOI: 10.1126/science.1217412.
Lovley, D. R. (2006). Bug juice: harvesting electricity with microorganisms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4, 497–508. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro1442.
Mahadevan, R., Palsson, B. Ø., & Lovley, D. R. (2011). In situ to in silico and back: elucidating the physiology and ecology of Geobacter spp. using genome-scale modelling. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 9, 39–50. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2456.
Mehdinia, A., Dejaloud, M., & Jabbari, A. (2013). Nanostructured polyaniline-coated anode for improving microbial fuel cell power output. Chemical Papers, 67, 1096–1102. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-013-0381-1.
Park, M., Tsai, S. L., & Chen, W. (2013). Microbial biosensors: Engineered microorganisms as the sensing machinery. Sensors, 13, 5777–5795. DOI: 10.3390/s130505777.
Šefčovičová, J., Filip, J., Gemeiner, P., Vikartovská, A., Pätoprstý, V., & Tkac, J. (2011). High performance microbial 3-D bionanocomposite as a bioanode for a mediated biosensor device. Electrochemistry Communications, 13, 966–968. DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2011.06.013.
Šefčovičová, J., Filip, J., Mastihuba, V., Gemeiner, P., & Tkac, J. (2012). Analysis of ethanol in fermentation samples by a robust nanocomposite-based microbial biosensor. Biotechnology Letters, 34, 1033–1039. DOI: 10.1007/s10529-012-0875-x.
Šefčovičová, J., & Tkac, J. (2014). Application of nanomaterials in microbial-cell biosensor constructions. Chemical Papers, in press.
Su, L., Jia, W., Hou, C., & Lei, Y. (2011). Microbial biosensors: A review. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 26, 1788–1799. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.09.005.
Švitel, J., Tkáč, J., Voštiar, I., Navrátil, M., Štefuca, V., Bučko, M., & Gemeiner, P. (2006). Gluconobacter in biosensors: applications of whole cells and enzymes isolated from gluconobacter and acetobacter to biosensor construction. Biotechnology Letters, 28, 2003–2010. DOI: 10.1007/s10529-006-9195-3.
Tans, S. J., Verschueren, A. R. M., & Dekker, C. (1998). Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature, 393, 49–52. DOI: 10.1038/29954.
Tkac, J., Vostiar, I., Gorton, L., Gemeiner, P., & Sturdik, E. (2003). Improved selectivity of microbial biosensor using membrane coating. Application to the analysis of ethanol during fermentation. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 18, 1125–1134. DOI: 10.1016/s0956-5663(02)00244-0.
Tkáč, J., Štefuca, V., & Gemeiner, P. (2005). Biosensors with immobilised microbial cells using amperometric and thermal detection principles. In V. Nedović, & R. Willaert (Eds.), Applications of cell immobilisation biotechnology (Series: Focus on biotechnology, Vol. 8B, pp. 549–566): Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/l-4020-3363-x_33.
Tkac, J., Svitel, J., Vostiar, I., Navratil, M., & Gemeiner, P. (2009). Membrane-bound dehydrogenases from Gluconobacter sp.: Interfacial electrochemistry and direct bioelectrocatalysis. Bioelectrochemistry, 76, 53–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2009.02.013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šefčovičová, J., Filip, J. & Tkac, J. Interfacing of microbial cells with nanoparticles: Simple and cost-effective preparation of a highly sensitive microbial ethanol biosensor. Chem. Pap. 69, 176–182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0012
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0012