Abstract
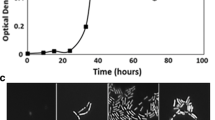
In order to measure the substrate-oxidizing activity of intact cells of Acetobacter pasteurianus no. 2, a given amount of the bacterial cells was immobilized on a carbon-paste electrode, and the current at the electrode was measured in a buffer solution. When Fe(CN)3− 6 was added to the buffer solution, an anodic current was observed at 0.5 V (against Ag/AgCl). Further, when ethanol was added to the solution, the current started to increase to reach a steady-state within 3 min. The electrode had a good response to acetaldehyde and lactic acid as well as ethanol. Culture conditions affected the current response to various substances; the response of the electrode modified with the cells grown in static culture was much higher than that of the electrode with the cells grown in shaking culture, and the electrode with ethanol-grown cells had a high response to ethanol and acetaldehyde compared with that of the electrode with glucose-grown cells. The increase in the amount of the current after the addition of ethanol (ΔI EtOH) was linearly proportional to the total number of immobilized cells per electrode in the range 1.0 × 104–1.0 × 108 cells. The ΔI EtOH values were measured with the electrode prepared with a fixed volume of the cell suspensions taken from the culture at 6-h intervals; the dependence of the ΔI EtOH value on time agreed well with the cell growth measured by colony counting and turbidity in the lag and logarithmic phase. After the logarithmic phase, the value of ΔI EtOH sharply decreased, resembling to the growth measured by colony counting, rather than by turbidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 October 1998 / Received revision: 2 February 1999 / Accepted: 5 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, T., Ikeda, T. An electrochemical method for the measurements of substrate-oxidizing activity of acetic acid bacteria using a carbon-paste electrode modified with immobilized bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51, 664–668 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051448
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051448