Abstract
Background
The filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei is widely utilized in industry for cellulase production, but its xylanase activity must be improved to enhance the accessibility of lignocellulose to cellulases. Several transcription factors play important roles in this progress; however, nearly all the reported transcription factors typically target both cellulase and hemi-cellulase genes. Specific xylanase transcription factor would be useful to regulate xylanase activity directly.
Results
In this study, a novel zinc binuclear cluster transcription factor (jgi|Trire2|123881) was found to repress xylanase activity, but not cellulase activity, and was designated as SxlR (specialized xylanase regulator). Further investigations using real-time PCR and an electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrated that SxlR might bind the promoters of GH11 xylanase genes (xyn1, xyn2, and xyn5), but not those of GH10 (xyn3) and GH30 (xyn4) xylanase genes, and thus regulate their transcription and expression directly. We also identified the binding consensus sequence of SxlR as 5′- CATCSGSWCWMSA-3′. The deletion of SxlR in T. reesei RUT-C30 to generate the mutant ∆sxlr strain resulted in higher xylanase activity as well as higher hydrolytic efficiency on pretreated rice straw.
Conclusions
Our study characterizes a novel specific transcriptional repressor of GH11 xylanase genes, which adds to our understanding of the regulatory system for the synthesis and secretion of cellulase and hemi-cellulase in T. reesei. The deletion of SxlR may also help to improve the hydrolytic efficiency of T. reesei for lignocellulose degradation by increasing the xylanase-to-cellulase ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Lignocellulosic biomass, consisting mostly of cellulose, hemi-cellulose, and lignin, is the most abundant and renewable energy source on earth [1]. Degradation of lignocellulosic biomass and continuation of the carbon cycle in nature is maintained mainly by microbial action, including different fungal species, such as Trichoderma, Aspergillus, and Penicillium. The biomass-degrading enzymes produced by these organisms also have applications in various fields of industry including food, fodder, paper, and textile industries. Trichoderma reesei is a well-known efficient producer of cellulase and hemi-cellulase, and is therefore widely employed by the enzyme industry for production of its own endogenous enzymes as well as production of heterogeneous proteins [2].
Cellulosic biofuel production continues to increase world-wide every year with a consequent rapidly increasing requirement for cellulase production from T. reesei. However, the production and optimization of enzyme formulations for lignocellulose degradation are still the major barriers to its extensive application. It is necessary to further enhance the hydrolytic efficiency of T. reesei enzyme preparations for lignocellulose and lower their relatively high cost. Due to the complex constitution and structure of native lignocellulose, the enzyme preparations produced by T. reesei must be supplemented with several types of exogenous enzymes to achieve effective degradation of natural complex lignocellulosic materials. For example, exogenous hemi-cellulase and other auxiliary enzymes are added to commercial cellulase complexes from Danisco or Novozymes [3]. This indicates that increasing the production of the most prominent hemi-cellulase (endo-β-1,4-xylanase), which catalyzes the hydrolysis of 1,4-β-d-xylosidic linkages in xylan to short xylooligosaccharides of varying length in T. reesei, is a good way to strengthen its hydrolysis activity [4].
Expression of genes encoding cellulase and hemi-cellulase in T. reesei is tightly controlled at the transcriptional level. Therefore, deleting and/or over-expressing transcription factors (TFs) that specifically regulate xylanase gene expression in T. reesei is a straightforward way to perform knowledge-based strain design. However, most known TFs regulate expression of both cellulase and xylanase genes in the same way. The most extensively studied TF is the negative TF CRE1 [5], which mediates carbon catabolite repression (CCR). In the cellulase hyperproduction strain T. reesei RUT-C30, CRE1 is truncated, which renders this strain carbon catabolite depressed [6]. The global transcriptional activator Xyr1 is obligatory for expression of most cellulase and hemi-cellulase genes [7, 8]. Other recognized TFs are the positively acting factor ACE2 [9, 10] and HAP2/3/5 complex [11], and the negatively acting factor ACE1 [12]. In addition, BglR [13] was identified as a new TF that upregulates expression of specific genes encoding β-glucosidases in T. reesei, and a putative methyltransferase, LAE1 [14, 15], was found to be essential for cellulase and hemi-cellulase production in T. reesei, although the mechanism is still unclear. ACE3 has been newly characterized to be indispensable for cellulase and xylanase activity in T. reesei [16]. All the above TFs have effects on the expression of both cellulase and hemi-cellulase genes.
Recently, a study found that some segmentally aneuploid (SAN) T. reesei strains exhibited enhanced growth in xylan-based media and produced higher levels of xylanase [17]. Further analysis confirmed that D segment duplication, not L segment deletion, in the genomes of these SAN strains, was responsible for the growth advantage in xylan-based media, but did not affect the cellulase activity. In fact, the Xpp1, TF, was identified by a pull-down assay based on the xyn2 promoter and was confirmed as a negative regulator of the xyn1 and xyn2 xylanase genes and the bxl2 β-xylosidase gene [18].
In this study, using bioinformatics analysis and gene deletion with the CRISPR/Cas9 system [19], we identified a gene encoding a protein designated as specialized xylanase regulator (SxlR). Deletion of the sxlr gene resulted in increased xylanase activity while not affecting cellulase activity. This indicated that SxlR might be a novel TF that regulates xylanase expression. According to the results of real-time PCR (qPCR) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) analyses, we demonstrated that SxlR plays a critical role in the inhibition of the expression of xylanases belonging to the glycoside hydrolase 11 family (GH11) in T. reesei through binding to the promoter regions of target genes directly. Finally, we identified the binding consensus sequence of SxlR as 5′-CATCSGSWCWMSA-3′.
Results
Screening the putative xylanase-specific TFs
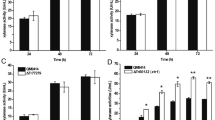
Based on bioinformatics analysis, we chose seven putative TFs as candidates (Additional file 1) for screening. All these genes were located in five different chromosomes [20, 21], and six of candidates were located in the D segment duplication resulting in higher xylanase activities as reported by Chen et al. [17]. We overexpressed these genes in T. reesei RUT-C30. After creating monoconidial cultures for genetic stability, we measured the xylanase and cellulase activities of the transformants. The xylanase activity, but not the cellulase activity, of the strain overexpressing the sxlr gene (jgi|TrireRUTC30_1|26638, Osxlr) decreased significantly (t test, P < 0.05) (Fig. 1a, b), and its extracellular protein concentration was decreased (Fig. 1c), which might indicate that this gene affects the xylanase activity alone. In contrast, no changes in xylanase activity, cellulase activity, or protein concentration were detected between RUT-C30 and the other six overexpression strains (Fig. 1).
Enzyme activities and proteins of supernatants from T. reesei RUT-C30 recombinant strains overexpressing candidate transcription factors. Xylanase activity (a), cellulase activity (b), and extracellular protein concentration (c) of 7-day culture supernatant with wheat bran and Avicel as carbon source. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates
To investigate how the sxlr gene is involved in regulation of xylanase activity in T. reesei, we deleted sxlr gene from the RUT-C30 strain to obtain Δsxlr transformants (Fig. 2a, b). In contrast to the Osxlr strain, the xylanase activity of the Δsxlr strains was increased significantly (Fig. 2c). However, the cellulase activity of the Δsxlr strains was almost the same as the parent RUT-C30 strain. We also deleted the homologous sxlr gene of T. reesei Qm6a (jgi|Trire2|123881, Δ6a-sxlr) using the CRISPR/Cas9 system to verify the common regulation of xylanase activity in T. reesei strains. As expected, the xylanase activity of Δ6a-sxlr transformants was also dramatically increased, similar to the Δsxlr strain (Fig. 2c), while its cellulase activity was not affected. Taken together, these results suggested that sxlr encoded a TF that negatively regulates xylanase activity.
Deletion of sxlr in T. reesei. a Schematic diagram of sxlr deletion in T. reesei 6a-u and RUT-C30. We used CRISPR/Cas9 system in the T. reesei QM6a background and the traditional method in the T. reesei RUT-C30 background. b PCR results for transformant identification. Three different transformants were chosen for verification. c The xylanase and cellulase activity of 7-day culture supernatant with wheat bran and Avicel as carbon sources. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates
The deletion of SxlR in T. reesei RUT-C30 results in higher xylanase activity and higher reducing sugar yield
We selected the cellulase hyperproduction strain RUT-C30 to explore the potential regulatory mechanism of SxlR in T. reesei. In addition to the sxlr deletion strain (Δsxlr, transformant 1) and the sxlr overexpression strain (Osxlr), we also constructed the in situ re-complementation strain (Rsxlr) based on the Δsxlr strain (Additional file 2). The xylanase activity of the Δsxlr strain increased relative to that of RUT-C30 by 0.7-fold and 1.4-fold after 3 and 7 days, respectively, of incubation in inducing medium containing wheat bran and Avicel (Fig. 3a). The xylanase activity was also examined when xylan or lactose was used as the inducer (the sole carbon source in the inducing medium). The xylanase activity of Δsxlr was 1.3-, 0.9-, and 0.7-fold higher than RUT-C30 after 1, 2, and 3 days, respectively, of cultivation with xylan as the inducer (Fig. 3b), and 14.2-, 4.7-, and 5.2-fold higher, respectively, with lactose as the inducer (Fig. 3c). The xylanase activity of the sxlr re-complementation control strain Rsxlr reverted to the same level as that of RUT-C30. In contrast, the sxlr overexpression strain Osxlr demonstrated weaker xylanase activity than RUT-C30 (Fig. 3a–c). However, no significant difference in cellulase activity was detected between the four strains (Fig. 3d).
Enzyme activities of sxlr transformants on various carbon sources. The xylanase activity of culture supernatants with wheat bran and Avicel (a), xylan (b), and lactose (c) as carbon sources. d The cellulase activity of 3-, 5-, and 7-day culture supernatants with wheat bran and Avicel as carbon source. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates
Degradation of lignocellulose is a growth-associated process. The growth rate affects the secretion of enzymes directly [22]. We observed the growth of RUT-C30 and its derivative strains on potato dextrose agar (PDA) and minimal medium (MM) containing 1% xylose, xylan, glucose, lactose, or Avicel as carbon sources, respectively (Fig. 4a). RUT-C30 and its derivative strains did not show significantly different growths and sporulations on PDA and MM containing 1% glucose, lactose or Avicel (Fig. 4a). However, the Δsxlr strain demonstrated rapid growth and the Osxlr strain demonstrated reduced growth on MM containing xylose or xylan when compared to RUT-C30. These results could be explained by differences in xylanase activities.
The phenotypes and extracellular protein of sxlr transformants. a RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr, and Rsxlr strains grown on PDA plates (3 days) and minimal medium plates containing various carbon sources (1%): xylose (4 days), xylan (4 days), glucose (4 days), lactose (6 days), and Avicel (6 days). Extracellular protein concentration (b) and SDS-PAGE analysis (c) of supernatants from RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr, and Rsxlr grown with wheat bran and Avicel as the carbon source. In c, lines 1 to 4 are the supernatants of RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr, and Rsxlr, respectively. Line M is a protein molecular weight marker. d The straw hydrolysis reaction was carried out for 3 days, as described in the "Methods" section. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates
Enzyme activities are also influenced by the concentration and composition of lignocellulose preparations. The extracellular protein concentrations of the Δsxlr, Osxlr, and RUT-C30 strains were 15.275 ± 0.096, 10.943 ± 0.399, and 13.378 ± 0.240 mg/mL, respectively. The Δsxlr strain had the highest extracellular protein concentration, and Osxlr had the lowest (Fig. 4b). According to sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), the band corresponding to ~20 kDa, which was identified as the xylanase protein XYN2 by MALDI-TOF/TOF, was enhanced dramatically in the Δsxlr strain but decreased in the Osxlr strain (Fig. 4c). This indicates that SxlR affects the amount of secreted XYN2 in the lignocellulose preparations produced by T. reesei.
To determine whether the deletion of SxlR in T. reesei RUT-C30 could improve the strain’s efficiency to hydrolyze pretreated lignocellulose, steam-exploded rice straw and steam-exploded rice straw mixed with corn straw were used as saccharification substrates. The crude enzyme complex of the mutant Δsxlr strain produced more reducing sugar than that of RUT-C30 (Fig. 4d). The straw hydrolysis increased to 21% by the supernatant of the Δsxlr strain, while 14.1% by the supernatant of RUT-C30 strain after 3 days of hydrolysis from the pretreated rice and corn straw. Similarly, the straw hydrolysis increased to 11.9% by the supernatant of the Δsxlr strain, while 7.6% by the supernatant of RUT-C30 strain after 3 days of hydrolysis from the pretreated rice straw.
SxlR regulates the GH11 xylanase genes
To further identify the regulation mechanism of SxlR on xylanase activity, we examined the expression levels of five xylanase-encoding genes using qPCR; the xylanases encoded by these genes included three members of GH11 family (XYN1, XYN2, and newly discovered XYN5), a GH10 family member XYN3 and a GH30 family member XYN4 [23]. The transcription levels of the genes encoding the three GH11 members showed significant differences in the Δsxlr strain (upregulated) and the Osxlr strain (downregulated) at all sampling time points using wheat bran and Avicel were used as inducers (Fig. 5a).
Quantitative PCR analysis of gene expression levels. The expression levels of xyn1 (GH11), xyn2 (GH11), xyn5 (GH11), xyn3 (GH10), and xyn4 (GH30) in RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr, and Rsxlr when wheat bran and Avicel (a) and xylan (b) were used as carbon sources, expression levels were normalized to the signal of rpl6e. RNA was extracted after 4, 8, and 12 h. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. c Expression levels of sxlr in RUT-C30, the xyr1 deletion mutant (Δxyr1), and the xyr1-overexpression strain (Oxyr1); and xyr1 expression levels in RUT-C30, Δsxlr, and Osxlr when wheat bran and Avicel were used as the carbon source. Expression levels were normalized to the signal of β-actin. RNA was extracted after 4, 8, and 12 h. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates
The transcription level of the genes encoding XYN3 and XYN4 were also downregulated in the Osxlr strain at all sampling time points (Fig. 5a). However, their transcription levels in the Δsxlr strain changed differently (Fig. 5a).
In the Δsxlr strain, the relative expression level of xyn3 was upregulated compared to the wild-type stain in the first 8 h of incubation in the inducing medium. The relative expression level of xyn4 was upregulated after 4 h of induction, but downregulated after 8 and 12 h of induction (Fig. 5a). When using xylan as the inducer, the transcription level variation tendency of the encoding genes of XYN1, XYN2, XYN5, and XYN3 was similar to that using wheat bran and Avicel as the inducer (Fig. 5b). In contrast, the relative expression level of xyn4 was upregulated in the Osxlr strain after 4 h of induction (Fig. 5b).
To further confirm the qRT-PCR results, qRT-PCR experiments were re-carried out using rpl6e (a ribosomal protein encoding gene) [24] and sar1 (a small GTPase encoding gene) [25] as the reference gene. The transcription level variation tendency of the five xylanase-encoding genes was similar to that using β-actin gene as the reference gene (Additional file 3).
Additionally, we examined the relative expression levels of other genes coding (hemi-) cellulases or their regulators, including three major cellulase genes (cbh1, cbh2, egl1), the key transcriptional activator (xyr1), and two hemi-cellulase genes (β-mannanase, man1 and α-l-arabinofuranosidase, abf1). There were no significant differences in the relative expression levels of these genes between RUT-C30 strain and Δsxlr strain (Additional file 3). These results provide the first experimental evidence that SxlR is a negative and specific regulator of GH11 family xylanases.
Xyr1, a major transcription activator in T. reesei, regulates expression of most cellulase and hemi-cellulase genes directly, including xylanases [26, 27]. To investigate the relationship between Xyr1 and SxlR, we determined the relative expression levels of sxlr in the Δxyr1 strain (an xyr1-deletion strain derived from RUT-C30) and in the Oxyr1 strain (an xyr1-overexpression strain derived from RUT-C30) as well as the relative expression levels of xyr1 in Δsxlr strain and Osxlr strain (Fig. 5c). Comparing with xyr1, the transcription level of sxlr was quite low in RUT-C30. The xyr1 transcription level decreased significantly in the Osxlr strain at all the sampling time points. In contrast, its transcription level in the Δsxlr strain significantly increased at 4-h induction, and then decreased from 8-h induction. It seemed that SxlR might repress xyr1 expression somehow. The transcription level of sxlr in the Oxyr1 strain was nearly the same as that in RUT-C30 strain, and its transcription level in the Δxyr1 strain was lower or similar to that in RUT-C30 strain. The variation tendency of the sxlr transcription level was quite different from that of the downstream genes of Xyr1, of which the transcription were sharply repressed after the deletion of Xyr1 [27].
SxlR binds the promoters of GH11 xylanase genes
According to functional domain analysis, SxlR contains two distinct conserved domains, one GAL4-like Zn2Cys6 binuclear cluster DNA binding domain at the N-terminus (cd00067: residues 282–317) and one fungal transcription factor regulatory middle homology region at the C-terminus (cd12148: residues 436–853). To verify the regulation of the GH11 xylanase genes by SxlR, the GAL4-like Zn2Cys6 binuclear cluster DNA binding domain was expressed in vitro for EMSAs. The nearly 1500-bp upstream regions (nucleotide position −1500 to −1) assumed to be the promoter regions of the xylanase-encoding genes were divided into six parts (for example, xyn2-P1, 268 bp, nucleotide position −268 to −1; xyn2-P2, 268 bp, position −516 to −249; xyn2-P3, 268 bp, position −764 to −497; xyn2-P4, 268 bp, position –1012 to −745; xyn2-P5, 268 bp, position −1260 to −993; xyn2-P6, 268 bp, position −1508 to −1241). Based on the EMSA gel shifts, SxlR could bind the xyn1-P5, xyn2-P4, xyn2-P5, and xyn5-P5 promoter regions of the three GH11 xylanases (Fig. 6a). No specific gel shift was observed for the xyn3 and xyn4 promoters, which belonged to the GH10 and GH30 families, respectively (Fig. 5b; Additional file 4). It means that SxlR plays a critical role in the inhibition of GH11 family genes through binding to their promoter regions directly.
EMSAs of SxlR binding to the promoter regions of xylanase genes. a DNA binding of SxlR to the promoter regions of xyn1, xyn2, and xyn5. The amounts of purified SxlR binding domain (SxlR-B, μM) used were as indicated; ~10 ng of Cy5-labeled probe was added to each reaction. The shifts were verified to be specific by adding 100-fold excess of unlabeled specific (S) and non-specific (NS) competitor DNA. The SxlR-DNA complex is indicated by the arrow. b DNA binding of SxlR to the xyn3 and xyn4 promoter regions. We used three concentrations of SxlR-B: 0, 0.5, and 1 μM; ~10 ng of Cy5-labeled probe was added to each reaction
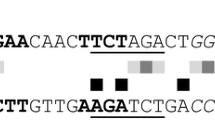
To identify the binding motif of SxlR, three promoter fragments (xyn2-P4, xyn1-P5, and xyn5-P5) were each divided into two 144-bp segments (Additional file 5A). SxlR bound to xyn2-P4-1, xyn1-P5-2, and xyn5-P5-2 (Additional file 5B). Based on MEME Suite (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) analysis, three candidate consensus motifs were predicted (Additional file 5C, D). However, the deletion of these three motifs did not affect the binding of SxlR to these DNA fragments (Additional file 5E). The 144 -bp fragments were further shortened for identification of a consensus motif, and two motifs were predicted (Fig. 7a). Based on the disappearance of the SxlR-DNA complex with the deletion of motif 5 (Fig. 7b), the consensus motif of SxlR was determined as 5′-CATCSGSWCWMSA-3′ (Fig. 7c, d). In this motif, one guanine and one cytosine are present in the core region and the consistent nucleotides are located in the flanks. The potential SxlR binding motif were not detected in the promoter regions of Xyr1 and xylanases XYN3 and XYN4. It suggested that SxlR might not regulate the transcription of Xyr1 and the GH10 family member XYN3 as well as the GH30 family member XYN4 directly.
Identification of the SxlR binding consensus sequence. a Sequence motifs of a putative SxlR binding consensus sequence derived by MEME from Dxyn2-P4-1, Dxyn1-P5-2 and Dxyn5-P5-2. Two putative SxlR binding consensus sequences were obtained. b EMSA results of SxlR binding to Dxyn2 P4-1, D4 (Motif 4 deletion), and D5 (Motif 5 deletion); the SxlR-DNA complex is indicated by the arrow. The amounts of purified SxlR binding domain (SxlR-B, μM) used were as indicated; ~10 ng of Cy5-labeled probe was added to each reaction. c Alignment of SxlR binding consensus sequence on sense (+) or antisense (−) strand in the upstream regions of xyn1, xyn2, and xyn5. The numbers following the gene name indicated the point of the 5′ starting nucleotide relative to the translation start point and the same nucleotide was indicated by asterisk. d The location of motif 4 and motif 5 in Dxyn2 P4-1 probe. Motif 4 was indicated by underline while motif 5 was indicated by pane
Discussion
The aim of this study was to gain a comprehensive understanding of how viable SAN progeny produces higher levels of xylanases [17]. We focused on candidate TFs exhibiting differential expression levels between SAN and euploid progeny (six TF-encoding genes: ID in jgi|Trire2: 106677, 65854, 111446, 68930, 111515, 36913), as well as another candidate TF, SxlR. We confirmed that SxlR is a negative regulator of GH11 family xylanases. However, overexpression of the other six tested TFs had no effect on the xylanase activity. It seems that the segmental aneuploidy did not result in a change in sxlr gene copy number; however, it is still unknown whether segmental aneuploidy affects the expression of sxlr in SAN progeny.
Recently, another negative regulator of hemi-cellulase, xylanase promoter-binding protein 1 (Xpp1) was reported in T. reesei [18]. Xpp1 regulates transcription of hemi-cellulase genes only at later stages of cultivation. There was no significant difference in xylanase activity between an xpp1-disrupted strain and its parent strain before 72 h [18]. In this study, SxlR regulated expression of GH11 xylanase genes during the entire induction period, and the xylanase activity of the deletion strain was significantly higher than that of the parent strain (Fig. 3a). It has been suggested that SxlR may play an important role in regulating xylanase expression in T. reesei. Xpp1 repressed the expression of xyn1, xyn2, and bxl2 (encoding a putative β-xylosidase) but like SxlR, did not affect cellulase genes [18]. SxlR bound the xyn1, xyn2, and xyn5 promoter regions in vitro (Fig. 6a) and was demonstrated to be a GH11-specific TF. This indicated that the regulation mechanisms of SxlR and Xpp1 are not identical. Additionally, in inducing medium containing xylan, the xpp1-disrupted strain showed nearly 2.2-fold increases in transcription levels of xyn2 at 72 h, while the Δsxlr strain showed 9.9-, 2.1-, and 4.6-fold increases in transcription levels of xyn2 at 4, 8, and 12 h, respectively. Both the intensity and timing of these two TFs differed.
The binding consensus sequence of SxlR (5′-CATCSGSWCWMSA-3′) differs from that of the hemi-cellulase regulator Xpp1 (a hexameric palindrome 5′-WCTAGW-3′ together with an inverted AGAA-repeat [18]). In the xyn1 promoter region, the binding consensus sequence of Xpp1 is located in the xyn1-P3 fragment, while SxlR binds to xyn1-P5. In the xyn2 promoter region, the binding consensus sequence of Xpp1 is located in xyn2-P1 fragment, while SxlR binds to xyn2-P4 and xyn2-P5. In the xyn5 promoter region, only the SxlR binding consensus sequence was found. Meanwhile, in the bxl2 promoter region, only the Xpp1 binding consensus sequence was found. Therefore, SxlR has a regulon that differs from that of Xpp1.
Most xylanases (endo-β-1, 4-xylanase, EC 3. 2. 1. 8) belong to the GH10 and GH11 families. Compared to GH10, the GH11 family is much more xylan-specific [28]. In T. reesei, XYN2 belonging to GH11 family was the dominant extracellular xylanase. The Δsxlr strain grew more vigorously than the wild-type on MM with xylan or xylose as the sole carbon source. This indicates that the deletion of sxlr results in the high ability to utilize xylan or xylose. According to our hypothesis, the role of SxlR is the downregulation of the main xylanases to save energy when cellulose or glucose is present in the habitat of T. reesei. Hexose is, after all, the preferred carbon resource of these organisms [29]. The novel TF SxlR is indicative of the sophisticated regulatory network evolved by T. reesei to adapt to complex environments.
Unlike the previously reported global regulators of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes), SxlR, as a specific regulator of GH11 family xylanases, might provide new leads for strain engineering to enhance hemi-cellulase activity in T. reesei. In the straw hydrolysis assay, more reducing sugar was produced by the Δsxlr culture supernatant than by the parent strain. Compared with steam-exploded rice straw, higher straw hydrolysis was achieved by steam-exploded rice and corn straw mixture (Fig. 4d). This was probably because the hemi-cellulose content of corn straw was much higher than that of rice straw (41% vs 22%) [30, 31]. It has been suggested that the utilization of hemi-cellulose-rich substrate was significantly improved by the modified enzyme preparation. Because most TFs regulate cellulase and hemi-cellulase genes concurrently [32], the ratio of cellulase and hemi-cellulase is difficult to optimize by genetic manipulation of TFs. Our results shown that the appropriate proportion of the enzyme preparation can be conveniently optimized via engineering of sxlr. The derived strain would have a higher xylanase activity, while the cellulase activity would not be affected.
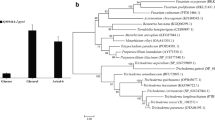
Through phylogenetic analysis of SxlR, we found its homologous genes in other cellulase producer including Trichoderma virens (XP_013961599.1), T. atroviride (XP_013948752.1), Neurospora crassa (XP_960943.2), Penicillium oxalicum (EPS34484.1), Aspergillus nidulans (XP_681446.1), A. oryzae (KOC12472.1), and A. niger (CAK40371.1), which indicates that its function may be conserved (Additional file 6).
Conclusions
SxlR appears to be a major xylanase regulator in T. reesei that represses the expression of xylanases belonging to the GH11 family and does not affect cellulase activity. Deletion of sxlr dramatically increases xylanase activity. SxlR is a good target candidate for T. reesei strain modification, especially for hydrolyzing substrates rich in hemi-cellulose.
Methods
Strains and culture conditions
Trichoderma reesei strains including QM6a (ATCC 13631) and RUT-C30 (ATCC 56765) were maintained on potato dextrose agar plate (PDA) at 28 °C for 7 days for spore collection. Escherichia coli DH5α used as cloning host was culture at 37 °C in Luria–Bertani (LB) medium. Agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1 was used to transform the gene to T. reesei strains. To induce enzyme production, the conidial suspension (0.5 mL, 1 × 107 conidia/mL) was inoculated into a 50-mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 10 mL of Sabouraud Dextrose Broth (SDB) and incubated for 40 h on an orbital shaker at 200 rpm at 28 °C. The culture was then transferred into a flask containing 10 mL of inducing fermentation medium at 10% inoculum ratio (v/v). The flasks were incubated on an orbital shaker at 200 rpm at 28 °C for 1 week. The wheat bran and Avicel medium were prepared as follows: 0.4% KH2PO4, 0.28% (NH4)2SO4, 0.06% MgSO4·7H2O, 0.05% CaCl2, 0.06% urea, 0.3% tryptone, 0.1% Tween-80, 0.5% CaCO3, 0.001% FeSO4·7H2O, 0.00032% MnSO4·H2O, 0.00028% ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.0004% CoCl2, 2% wheat bran, 3% microcrystalline cellulose. We also used minimal medium (MM) containing 0.5% (NH4)2SO4, 1.5% KH2PO4, 0.06% MgSO4, 0.06% CaCl2, 0.0005% FeSO4·7H2O, 0.00016% MnSO4·H2O, 0.00014% ZnSO4·7H2O, and 0.0002% CoCl2 with 1% lactose or 1% xylan used as carbon source for 3 days of fermentation.
Construction of Δsxlr in T. reesei QM6a strain using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
T. reesei 6a-u (a uridine-dependent strain derived from 6a-pc) [19] was used as host. The guide RNA (gRNA) cassette including the synthetic gRNA sequence and target DNA of the sxlr gene (5′-GGGCAAGCCTCGCAAGCGGTtgg-3′, PAM is shown in italics) was driven by T7 promoter and transcribed into RNA in vitro with the MEGAscript T7 Kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). Donor DNA-sxlr (dDNA-sxlr) containing the 5′- and 3′ flanking sequences of sxlr (jgi|Trire2|123881) and the selectable marker cassette (the ura5 gene from P. oxalicum controlled by the Pgpda promoter and Ttrpc terminator, Pgpda-poura5-Ttrpc) was ligated into the pMD-18T vector (Takara, Dalian, China). The gRNA and dDNA-sxlr were co-transformed using a modified polyethylene glycol-mediated protoplast transformation procedure [33]. The transformants were selected using MM plates with 1% glucose as the carbon source.
Deletion, overexpression, and re-complementation of sxlr in T. reesei RUT-C30
To delete the sxlr gene (jgi|TrireRUTC30_1|26638) of T. reesei, the 2.8-kb sxlr coding region was replaced by the hph (hygromycin phosphotransferase) gene. This was performed by amplifying 1.5 kb from upstream and 1.7 kb from downstream of sxlr from genomic DNA of T. reesei using the primer pairs listed in Additional file 7. Then, the two resulting PCR fragments were ligated into the HindIII (upstream) and XhoI (downstream) sites of the linearized pXBthg vector [30] using the ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China).
For overexpression of sxlr under a strong constitutive promoter in T. reesei, we fused the T. reesei translation-elongation factor 1α (tef1) promoter, the sxlr coding region and the Ttrpc terminator from A. nidulans and inserted this fragment into the HindIII and XbaI sites of pXBthg using the ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit. Besides, we overexpressed 76601, 83920, 89588, 133726, 26508, and 43491 (gene ID in jgi|TrireRUTC30_1) with the same method.
For re-complementation of sxlr in the Δsxlr strain, the promoter, coding region, and terminator of sxlr were inserted into the HindIII and XbaI sites of the pXBt vector [the sequence is similar to pXBthg, except the hph marker gene was replaced by the bleomycin resistance (ble) gene] and the sequence downstream of sxlr was inserted into the XhoI site by the same method mentioned above.
All vectors constructed were verified by sequencing. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation was conducted as described previously by Ma et al. [34].
Biochemical assays
FPAase activities were determined using cellulose filter paper as described previously [35]. Xylanase activities were tested using 2% xylan from beechwood (Sigma, St. Louis, USA) as described previously [36]. Protein concentrations in the culture supernatant were determined by RC-DC protein assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) (1976). Biomass was tested by the diphenylamine colorimetric method [37].
For straw hydrolysis, different pretreated biomasses such as rice straw and a corn stover plus rice straw mixture (3:7 ratio) [38] were used as substrates. The standard hydrolysis assay was carried out in a volume of 1 mL of 50 mM sodium acetate, pH 4.8, and 5% (w/v) pretreated straw as substrate in a 2-mL FastPrep tube (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA). The enzyme dosage was 20 U of cellulase activity/g substrate. Incubation was typically at 50 °C with shaking at 200 rpm for 3 days, followed by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min to obtain the supernatant to determine the reducing sugar with DNS. Each sample was examined in triplicate.
Growth of sxlr transformants on plates
Spores of T. reesei RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr, and Rsxlr were first prepared by growth on PDA plates at 28 °C and harvesting spores after 7 days. Spores were counted using a hemocytometer and 105 spores of each strain were inoculated onto PDA plates and MM plates containing 1% xylose, xylan, glucose, lactose, or Avicel. Double-layer Avicel plates were prepared by first casting an MM agarose bottom layer containing no carbon source, followed by an MM agarose top layer containing 1% Avicel; each strain was grown in triplicates. These plates were incubated at 28 °C before phenotypic examination.
Protein identification with MALDI-TOF/TOF analysis
After 7 days’ culture with wheat bran and Avicel medium, the supernatant of RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr, and Rsxlr strain was collected. The samples were loaded into 12.5% PAGE gel, 70 min at 120 V were preferred for proteins separation. Coomassie brilliant blue R250 (Sangon, Shanghai, China) was used to color the gel for 1 h. Destainer (distilled water: ethanol: acetic acid, 5:4:1, v/v) was added for another 2–4 h. Finally, the protein band was excised from the gel and send to Shanghai Applied Protein Technology Co. Ltd, protein analysis was conducted with a MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometer 5800 Proteomics Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Framingham, MA, USA), NCBI Trichoderma (59929 protein sequence) was selected as database.
RNA extraction and real-time PCR
Mycelia were harvested after induction by wheat bran and Avicel for 4, 8, and 12 h, then transferred into TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA) with standard protocol. Three biological replicates were prepared in the process. Real-time PCR was performed with primers listed in Additional file 7 with standard method using β-actin gene, rpl6e (a ribosomal protein encoding gene) and sar1 (a gene encoding a small GTPase) as the reference genes, respectively.
Expression and purification of the DNA binding domain of SxlR
The DNA binding domain (residues 252–347) of SxlR (SxlR-B) was expressed by the pGEX system according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. First-strand cDNA was used as a template to amplify the fragment encompassing the DNA binding domain of SxlR using the primers indicated in Additional file 7. The fragment was then ligated into plasmid pGEX-4T-1 via BamHI and XhoI double digestion to produce pGEX-4T-SxlR-B, then subsequently introduced into E. coli BL21 (DE3) for protein production. The recombinant protein was purified using a GST-Bind resin column (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the supplier’s recommendations. SDS-PAGE was used to verify the purified protein.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assays
For EMSA, the labeling of probes containing the promoter regions of specific genes was performed via PCR using the primers listed in Additional file 7. The nearly 1500-bp upstream regions (nucleotide position −1500 to −1) assumed to be the promoter regions of the xylanase-encoding genes from T. reesei RUT-C30 were divided into six parts and each part was about 268 bp (Additional file 4A). The genomic DNA of T. reesei RUT-C30 was used as the template and the PCR products were purified by gel electrophoresis and quantified using a BioPhotometer plus (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). The experiment was then performed as described previously by Chen et al. [39]. Motif 1 (5′-AMTGSAGAG-3′) was located in −1034 to −1026 position of xyn1 promoter, −890 to −882 position of xyn2 promoter and −1091 to −1083 position of xyn5 promoter. Motif 2 (5′-TGAWGAG-3′) was located in −1022 to −1016 position of xyn1 promoter, −957 to −951 position of xyn2 promoter and −1021 to −1015 position of xyn5 promoter. Motif 3 (5′-WTATAT-3′) was located in −998 to −993 position of xyn2 promoter and −1117 to −1112 position of xyn5 promoter. Motif 4 (5′-AATGSASAG-3′) was located in −1119 to −1111 position of xyn1 promoter, −890 to −882 position of xyn2 promoter and −1091 to −1083 position of xyn5 promoter. Motif 5 (5′-CATCSGSWCWMSA-3′) was located in −1110 to −1098 position of xyn1 promoter, −905 to −893 position of xyn2 promoter and −1053 to −1041 position of xyn5 promoter.
Abbreviations
- SxlR:
-
specialized xylanase regulator
- EMSA:
-
electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- TFs:
-
transcriptional factors
- CCR:
-
carbon catabolite repression
- SAN:
-
segmentally aneuploid
- Xpp1:
-
xylanase promoter‑binding protein 1
- CRISPR:
-
clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- GH11:
-
glycoside hydrolase family 11
- CAZymes:
-
carbohydrate-active enzymes
References
Rubin EM. Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature. 2008;454:841–5.
Singh A, Taylor LE, Vander Wall TA, Linger J, Himmel ME, Podkaminer K, Adney WS, Decker SR. Heterologous protein expression in Hypocrea jecorina: a historical perspective and new developments. Biotechnol Adv. 2015;33:142–54.
Harris PV, Welner D, McFarland KC, Re E, Navarro Poulsen JC, Brown K, Salbo R, Ding H, Vlasenko E, Merino S, et al. Stimulation of lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis by proteins of glycoside hydrolase family 61: structure and function of a large, enigmatic family. Biochemistry. 2010;49:3305–16.
Hu JG, Arantes V, Saddler JN. The enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates by the addition of accessory enzymes such as xylanase: is it an additive or synergistic effect? Biotechnol Biofuels. 2011;4:36–48.
Portnoy T, Margeot A, Linke R, Atanasova L, Fekete E, Sandor E, Hartl L, Karaffa L, Druzhinina IS, Seiboth B, et al. The CRE1 carbon catabolite repressor of the fungus Trichoderma reesei: a master regulator of carbon assimilation. Bmc Genom. 2011;12:269–80.
Ilmén M, Thrane C, Penttilä M. The glucose repressor gene cre1 of Trichoderma: isolation and expression of a full-length and a truncated mutant form. Mol Gen Genet. 1996;251:451–60.
Stricker AR, Grosstessner-Hain K, Wurleitner E, Mach RL. Xyr1 (xylanase regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and d-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina. Eukaryot Cell. 2006;5:2128–37.
Derntl C, Gudynaite-Savitch L, Calixte S, White T, Mach RL, Mach-Aigner AR. Mutation of the Xylanase regulator 1 causes a glucose blind hydrolase expressing phenotype in industrially used Trichoderma strains. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013;6:62–72.
Aro N, Saloheimo A, Ilmén M, Penttilä M. ACEII, a novel transcriptional activator involved in regulation of cellulase and xylanase genes of Trichoderma reesei. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:24309–14.
Stricker AR, Trefflinger P, Aro N, Penttilä M, Mach RL. Role of Ace2 (activator of cellulases 2) within the xyn2 transcriptosome of Hypocrea jecorina. Fungal Genet Biol. 2008;45:436–45.
Zeilinger S, Ebner A, Marosits T, Mach R, Kubicek CP. The Hypocrea jecorina HAP 2/3/5 protein complex binds to the inverted CCAAT-box (ATTGG) within the cbh2 (cellobiohydrolase II-gene) activating element. Mol Genet Genom. 2001;266:56–63.
Aro N, Ilmén M, Saloheimo A, Penttilä M. ACEI of Trichoderma reesei is a repressor of cellulase and xylanase expression. Appl Environ Microb. 2003;69:56–65.
Nitta M, Furukawa T, Shida Y, Mori K, Kuhara S, Morikawa Y, Ogasawara W. A new Zn(II)2Cys6-type transcription factor BglR regulates beta-glucosidase expression in Trichoderma reesei. Fungal Genet Biol. 2012;49:388–97.
Seiboth B, Karimi RA, Phatale PA, Linke R, Hartl L, Sauer DG, Smith KM, Baker SE, Freitag M, Kubicek CP. The putative protein methyltransferase LAE1 controls cellulase gene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Mol Microbiol. 2012;84:1150–64.
Fekete E, Karaffa L, Karimi Aghcheh R, Németh Z, Fekete É, Orosz A, Paholcsek M, Stágel A, Kubicek CP. The transcriptome of lae1 mutants of Trichoderma reesei cultivated at constant growth rates reveals new targets of LAE1 function. Bmc Genom. 2014;15:447–56.
Häkkinen M, Valkonen MJ, Westerholm-Parvinen A, Aro N, Arvas M, Vitikainen M, Penttilä M, Saloheimo M, Pakula TM. Screening of candidate regulators for cellulase and hemicellulase production in Trichoderma reesei and identification of a factor essential for cellulase production. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014;7:14–34.
Chuang YC, Li WC, Chen CL, Hsu PW, Tung SY, Kuo HC, Schmoll M, Wang TF. Trichoderma reesei meiosis generates segmentally aneuploid progeny with higher xylanase-producing capability. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8:30–44.
Derntl C, Rassinger A, Srebotnik E, Mach RL, Mach-Aigner AR. Xpp1 regulates the expression of xylanases, but not of cellulases in Trichoderma reesei. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8:12–22.
Liu R, Chen L, Jiang Y, Zhou Z, Zou G. Efficient genome editing in filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Cell Discov. 2015;1:15007–17.
Marie-Nelly H, Marbouty M, Cournac A, Flot JF, Liti G, Parodi DP, Syan S, Guillen N, Margeot A, Zimmer C, Koszul R. High-quality genome (re) assembly using chromosomal contact data. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5695–704.
Druzhinina IS, Kopchinskiy AG, Kubicek EM, Kubicek CP. A complete annotation of the chromosomes of the cellulase producer Trichoderma reesei provides insights in gene clusters, their expression and reveals genes required for fitness. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016;9:75–90.
Arvas M, Pakula T, Smit B, Rautio J, Koivistoinen H, Jouhten P, Lindfors E, Wiebe M, Penttilä M, Saloheimo M. Correlation of gene expression and protein production rate—a system wide study. Bmc Genom. 2011;12:616–40.
Herold S, Bischof R, Metz B, Seiboth B, Kubicek CP. Xylanase gene transcription in Trichoderma reesei is triggered by different inducers representing different hemicellulosic pentose polymers. Eukaryot Cell. 2013;12:390–8.
Tisch D, Kubicek CP, Schmoll M. New insights into the mechanism of light modulated signaling by heterotrimeric G-proteins: ENVOY acts on gna1 and gna3 and adjusts cAMP levels in Trichoderma reesei (Hypocrea jecorina). Fungal Genet Biol. 2011;48:631–40.
Steiger MG, Mach RL, Mach-Aigner AR. An accurate normalization strategy for RT-qPCR in Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei). J Biotechnol. 2010;145:30–7.
Portnoy T, Margeot A, Seidl-Seiboth V, Le Crom S, Ben Chaabane F, Linke R, Seiboth B, Kubicek CP. Differential regulation of the cellulase transcription factors XYR1, ACE2, and ACE1 in Trichoderma reesei strains producing high and low levels of cellulase. Eukaryot Cell. 2011;10:262–71.
Castro LD, de Paula RG, Antonieto ACC, Persinoti GF, Silva-Rocha R, Silva RN. Understanding the role of the master regulator XYR1 in Trichoderma reesei by global transcriptional analysis. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:175–90.
Paës G, Berrin JG, Beaugrand J. GH11 xylanases: structure/function/properties relationships and applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30:564–92.
Aristidou A, Penttilä M. Metabolic engineering applications to renewable resource utilization. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2000;11:187–98.
Shawky BT, Mahmoud MG, Ghazy EA, Asker MMS, Ibrahim GS. Enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw and corn stalks for monosugars production. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2011;9:59–63.
Sumphanwanich J, Leepipatpiboon N, Srinorakutara T, Akaracharanya A. Evaluation of dilute-acid pretreated bagasse, corn cob and rice straw for ethanol fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Ann Microbiol. 2008;58:219–25.
Wang SW, Liu G, Wang J, Yu JT, Huang BQ, Xing M. Enhancing cellulase production in Trichoderma reesei RUT C30 through combined manipulation of activating and repressing genes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;40:633–41.
Liu T, Wang T, Li X, Liu X. Improved heterologous gene expression in Trichoderma reesei by cellobiohydrolase I gene (cbh1) promoter optimization. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008;40:158–65.
Ma L, Zhang J, Zou G, Wang CS, Zhou ZH. Improvement of cellulase activity in Trichoderma reesei by heterologous expression of a beta-glucosidase gene from Penicillium decumbens. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2011;49:366–71.
Xiao Z, Storms R, Tsang A. Microplate-based filter paper assay to measure total cellulase activity. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2004;88:832–7.
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K. Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol. 1992;23:257–70.
Zhao Y, Xiang S, Dai X, Yang K. A simplified diphenylamine colorimetric method for growth quantification. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97:5069–77.
Jin SY, Chen HZ. Fractionation of fibrous fraction from steam-exploded rice straw. Process Biochem. 2007;42:188–92.
Chen L, Zou G, Zhang L, de Vries RP, Yan X, Zhang J, Liu R, Wang C, Qu Y, Zhou Z. The distinctive regulatory roles of PrtT in the cell metabolism of Penicillium oxalicum. Fungal Genet Biol. 2014;63:42–54.
Authors’ contributions
GZ and ZHZ designed the study. RL, LC, and YPJ performed the experiments. RL and GZ analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. GZ and ZHZ revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor TingFang Wang (Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica) for research discussion and providing gene information of 106677, 65854, 111446, 68930, 111515, 36913 for test.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
This work was financially supported by High-tech Research and Development Program of China (863:2013AA102806) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470201, 31300073).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional files
13068_2017_878_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Additional file 2. sxlr transformants verification. (A) PCR result for Rsxlr transformants identification. Three different transformants were chosen to verify. (B) Verification of random insertion in Rsxlr transformants. During the Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, the T-DNA will randomly insert into genome with LB and RB, so we can verify it with PCR. The expected PCR product length of 5′ and 3′ verification was 6.1 kb and 2.6 kb. The sxlr re-complementation vector was used as positive control. Three different transformants were chosen to verify. The sxlr transcription levels in sxlr transformants were normalized to the signal of β-actin (C) or rpl6e (D), a gene encoding a ribosomal protein. RNA was extracted after 12 h induction by wheat bran and Avicel. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates.
13068_2017_878_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Additional file 3. Quantitative PCR analysis of cellulase and hemi-cellulase gene expression levels. The expression level of five xylanase genes in RUT-C30, Δsxlr, Osxlr and Rsxlr when wheat bran and Avicel were used as carbon sources. Expression levels were normalized to the signal of rpl6e, (A) or sar1 (B), a gene encoding a small GTPase. (C) The expression levels of cbh1, cbh2, egl1, xyr1, man1 and abf1 in RUT-C30 and Δsxlr. Expression levels were normalized to the signal of β-actin. RNA was extracted after 24, 48, and 72 h after induction by wheat bran and Avicel. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates.
13068_2017_878_MOESM4_ESM.docx
Additional file 4. The description of xylanase genes promoter and EMSAs of SxlR binding to xyn3 and xyn4. (A) The nearly 1500-bp upstream regions (nucleotide position –1500 to –1) assumed to be the promoter regions of the xylanase-encoding genes from T. reesei RUT-C30 were divided into six parts and each part was about 268 bp. (B) DNA binding of SxlR to the xyn3 and xyn4 promoter regions. We used three concentrations of SxlR-B: 0, 0.5, and 1 μM; ~ 10 ng of Cy5-labeled probe was added to each reaction. For specific (S) and non-specific (NS) control experiment, 100-fold excess of unlabeled S and NS competitor DNA were added.
13068_2017_878_MOESM5_ESM.docx
Additional file 5. Truncation prmoter sequence of GH11 xylanase genes. (A) The description of DNA sequence truncation. Each sequence was divided into two parts. (B) EMSAs of SxlR binding to xyn2-P4, xyn1-P5 and xyn5-P5 truncation sequence, respectively. (C) Three putative SxlR binding consensus sequences derived by MEME. (D)The location of three putative SxlR binding consensus sequences in xyn2-P4-1, xyn1-P5-2 and xyn5-P5-2. Motif 1, 2 and 3 was labeled as red, blue and green, respectively. Dxyn2-P4-1, Dxyn1-P5-2 and Dxyn5-P5-2 was the sequence after truncation. (E) EMSAs of SxlR binding to Dxyn2-P4-1, Dxyn1-P5-2 and Dxyn5-P5-2, the SxlR-DNA complex was indicated by arrow. The amounts of purified SxlR binding domain (SxlR-B, μM) used were as indicated; ~ 10 ng of Cy5-labeled probe was added to each reaction.
13068_2017_878_MOESM6_ESM.docx
Additional file 6. Phylogenetic relationship between SxlR and putative orthologs. The phylogenetic tree was inferred using the neighbor-joining method. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA 5. The gene ID in NCBI is ETR97987.1 (T. reesei), XP_013961599.1 (T. virens), XP_013948752.1 (T. atroviride), XP_960943.2 (Neurospora crassa), EPS34484.1 (Penicillium oxalicum), XP_681446.1 (Aspergillus nidulans), CAK40371.1 (A. niger) and KOC12472.1 (A. oryzae).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Chen, L., Jiang, Y. et al. A novel transcription factor specifically regulates GH11 xylanase genes in Trichoderma reesei . Biotechnol Biofuels 10, 194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0878-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0878-x