Abstract
Background
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is one of the most common primary glomerular diseases worldwide, but effective therapy remains limited and many patients progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Only angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I)/angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARB) show a high level of evidence (1B level) of being of value in the treatment for IgAN according to the 2012 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines. However, traditional Chinese medicine has raised attention in kidney disease research. Abelmoschus manihot, a single medicament of traditional Chinese medicine has shown therapeutic effects in primary glomerular disease according to the randomized controlled clinical trial that we have completed. Here, we conduct a new study to assess the efficacy and safety of Abelmoschus manihot in IgAN. Also, this study is currently the largest double-blind, randomized controlled registered clinical research for the treatment of IgAN.
Methods
We will conduct a multicenter, prospective, double-blind, double-dummy randomized controlled study. The study is designed as a noninferiority clinical trial. Approximately 1600 biopsy-proven IgAN patients will be enrolled at 100 centers in China and followed up for as long as 48 weeks. IgAN patients will be randomized assigned to the Abelmoschus manihot group (in the form of a huangkui capsule, 2.5 g, three times per day) and the losartan potassium group (losartan potassium, 100 mg/d). The primary outcome is the change in 24-h proteinuria from baseline after 48 weeks of treatment. Change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from baseline after 48 weeks of treatment, the incidence of endpoint events (proteinuria ≥3.5 g/24 h, the doubling of serum creatinine, or receiving blood purification treatment) are the secondary outcomes. Twenty-four-hour proteinuria and eGFR are measured at 0, 4, 12, 24, 36 and 48 weeks.
Discussion
This study will be of sufficient size and scope to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Abelmoschus manihot compared to losartan potassium in treating patients with IgAN. The results of this study may provide a new, effective and safe treatment strategy for IgAN.
Trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT02231125. Registered on 30 August 2014.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common primary glomerular disease worldwide, and it is an important cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [1, 2]. IgA nephropathy is also the most common primary glomerular disease and the leading cause of ESRD in China [3]. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Clinical Practice Guideline for Glomerulonephritis recommends angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I)/angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB), corticosteroids, and immunosuppressive agent treatment according to the level of the urinary protein and renal function of IgAN patients [4]. Since current therapy of IgAN is limited and most treatments have little evidence to recommend them, it is necessary to explore novel, effective and safe treatment for IgAN patients. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a long history in treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD), and a growing number of studies have confirmed that TCM has the curative effect of reducing urinary protein, protecting kidney function [5]. Abelmoschus manihot (AM) extracted from Flos Abelmoschus manihot, a single medicament of TCM has been widely used to treat chronic kidney diseases, such as IgAN, membranous nephropathy and diabetic nephropathy, and has shown the effects of reducing proteinuria and protecting kidney function [6–8]. ACE-I and ARB drugs are commonly used to treat proteinuria, and the range of reduction is reportedly 30–50% in adults [9, 10]. Thus, we use losartan as the positive control. We have finished a randomized controlled trial (RCT) to assess the efficacy and safety of AM in patients with primary glomerular disease. The clinical research enrolled a total of 417 patients from 26 hospitals who had been diagnosed with primary glomerular disease by renal biopsy. The results showed that AM can significantly reduce urinary protein in patients with primary kidney disease (CKD stages 1–2) and its effect is better than that of losartan potassium (50 mg/d) [11]. Since IgAN was the most common primary glomerular disease and the design of the former study had some limitations, such as not using a blind method, the low dose of losartan potassium (50 mg/d) used, and a short observation time (24 weeks), we conducted this prospective, double-blind, double-dummy randomized controlled study to evaluate efficacy and safety of AM in the treatment of IgAN.
Methods
Objectives
The objective of the trial is to assess the clinical effects and safety of AM in IgAN patients.
Trial design
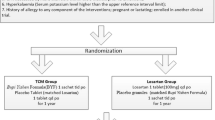
This study is a multicenter, prospective, double-blind, double-dummy RCT. The study is designed as a noninferiority clinical trial. The hypothesis is that AM significantly reduces the urinary protein levels of IgAN patients and that its curative effect is not inferior to that of losartan potassium (100 mg/d) after 48 weeks of treatment. We have followed the Standardised Protocol Interventions: Recommendations for Interventional Trials (SPIRIT) 2013 Statement which defines standard protocol items for clinical trials [12]. See the items in Fig. 1 and Additional file 1 for the Checklist. The study protocol was designed by members of the Executive Committee (composed of the Department of Kidney Disease of Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Peking University Clinical Research Institute). The protocol is being implemented by the study group comprising 100 clinical centers across China. The network database was designed by the Executive Committee. Venturepharm CRO Service Group which provides the clinical research associate service.
Setting and participants
Approximately 1600 biopsy-proven IgAN patients will be enrolled at 100 centers in China and followed up for as long as 48 weeks.
Eligibility, exclusion and exit criteria
The inclusion criteria are: (1) diagnosis of IgAN by kidney biopsy, (2) age 18 to 65 years, (3) blood pressure of ≤140/90 mmHg, (4) estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥45 ml/min/1.73 m2 (calculated with the use of the CKD-EPI Creatinine Equation 2009) [13], (5) 24-h proteinuria range of between 0.5 and 3.0 g, (6) agreement to participate and provision of signed informed consent. Additional file 2 shows the Informed Consent Form in more detail. The exclusion criteria are: (1) secondary IgAN, (2) allergy to AM or losartan potassium, (3) history of AM and ACE-I and/or ARB use within the last 6 months, (4) history of glucocorticoid, immunosuppressant, or Tripterygium drug use within the previous 1 year, (5) blood pressure of <90/60 mmHg, (6) serum potassium >5.5 mmol/L, (7) serum albumin <30 g/L, (8) unilateral or bilateral renal artery stenosis, (9) pregnant or lactating women, (10) severe heart, brain, liver, or hematopoietic system disease, or other serious illnesses that may affect survival, (11) participation in another clinical investigation. The exit criteria are: (1) endpoint event: proteinuria ≥3.5 g/24 h, doubling of serum creatinine, or receiving blood purification treatment, (2) blood pressure of >160/90 mmHg after antihypertensive drug combination therapy (convinced by measuring blood pressure three times within 2 weeks), (3) blood pressure of <90/60 mmHg after stopping using other antihypertensive agents, (4) serum potassium >5.5 mmol/L after antihyperkalemia drug treatment, (5) serum creatinine rapidly rising to >50% of the baseline within 4 weeks after treatment, (6) serious adverse events (SAEs): hospitalization (initial or prolonged), disability or permanent damage, life-threatening, death, congenital anomaly/birth defect and other serious events (important medical events) [14], (7) serious breach of protocol: participants failing to take medications according to protocol or taking some drugs that have a significant impact on the primary and secondary outcomes during the 48-week observation period, (8) loss to follow-up or withdrawal from the trial, (9) pregnancy during the trial.
Interventions
Abelmoschus manihot (AM) group: a huangkui capsule given orally, 2.5 g three times per day after meals, and a losartan potassium tablet dummy 100 mg/day in the morning.
Losartan group: a losartan potassium tablet given orally, 100 mg/day in the morning and a huangkui capsule dummy at 2.5 g three times per day after meals.
Abelmoschus manihot (AM): huanghui capsule (Jiangsu Suzhong Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.), 0.5 g × 30 capsules/box. A huangkui capsule is a single, plant drug extract of Flos Abelmoschus manihot. The main composition is of flavonoids. Content: dry extract (powder), 80%; magnesium stearate, 3%; and calcium hydrogen phosphate, 17%. The medicinal parts are the corolla with the stamens and the style. The plant is picked in early August to late October (flowering period), undergoes alcohol extraction into ambrette fluid extract, and is then vacuum-dried and crushed into a dry-extract powder. Pharmaceutical preparation does not involve boiling. The huanghui capsule was approved by the China Food and Drug Administration in 1999 (Z19990040, approval date: 13 August 1999).
Losartan potassium (Hangzhou MSD Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), 100 mg × 7 capsules/box.
The Huanghui capsule dummy and the losartan potassium dummy are produced by Jiangsu Suzhong Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.
Treatment continues for 48 weeks. Patients whose blood pressures are >140/90 mmHg after treatment will be given calcium channel blockers. Appropriate treatment is also given when patients develop hyperlipidemia, infection, or a hypercoagulable state. Glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents are prohibited. To improve adherence to intervention protocols, patients will be asked to take back the drug kit at every visit to exchange the new drug and whether the drug has been taken will be recorded.
Study outcomes
Primary and secondary outcome measure
The primary outcome is the change in 24-h proteinuria from baseline after 48 weeks of treatment. For this measurement, patients are instructed to collect urine over 24 h (from 07:00 to 07:00 the next day). Urine output and the total amount are measured and recorded. Twenty-four-hour urinary protein excretion is calculated based on the concentration and 24-h urine volume. The secondary outcome measures are the change in eGFR from baseline after 48 weeks treatment and the incidents of endpoint events (proteinuria ≥3.5 g/24 h, doubling of serum creatinine, or receiving blood purification treatment). All the urine and blood samples are delivered to the central laboratory within 4 weeks for testing.
Other measurements
The patients’ general condition, demographic data, clinical history, physical examination, blood pressure and renal biopsy report are recorded. Laboratory assessments include routine urine test, routine blood test, blood biochemical tests (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglyceride, cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein level, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, total protein, albumin, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, uric acid, blood glucose and potassium). Enrolled patients also undergo electrocardiogram and chest X-ray examinations. Central laboratory tests include 24-h urinary proteinuria, urine routine test, serum cystatin C and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. The urine and blood samples are both stored in a −80 °C refrigerator at central laboratory and participating centers.
Safety
Safety evaluation includes the patients’ general condition, the incidence of adverse events, and laboratory assessments. Adverse events and SAEs are defined according to the definitions of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) by the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) [14].
Participant follow-up
The enrollment process includes a screening visit to assess eligibility and obtain the informed consent and collection of clinical and demographic information. After enrollment, participants are evaluated at visit 1 (baseline visit), visit 2 (4 weeks), visit 3 (12 weeks), visit 4 (24 weeks) and visit 5 (36 weeks) and visit 6 (48 weeks) with similar data collection as performed in the baseline visit (Table 1).
Sample size
The sample size determination is based on the primary outcome 24-h proteinuria. The alpha level is set to a one-sided value of 0.025%. We assume that the expected decline of 24-h proteinuria is 1600 ± 500 mg. The noninferiority margin (0.5 of the estimated standard deviation) is 250 mg. With a 15% dropout rate, to enroll 124 patients per arm will offer 95% power to demonstrate noninferiority of AM compared to losartan with a 250-mg noninferiority margin. At the same time, based on the observation of safety, sample size expanded to 800 patients per arm will offer 80% power to detect the rare adverse reactions (incidence <0.5%) at least in one patient.
Recruitment
The process of recruiting participants will be based on medical record review. All the hospitalized patients undergoing a kidney biopsy from September 2014 and the outpatients with a documented history of IgAN by kidney biopsy within 1 year will be screened according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. There are 100 participating clinical centers and every center will need to enroll at least 12 patients.
Randomization procedure, allocation concealment, implementation of blind method
Consecutive numbers are assigned to each participating center according to a center-stratified random order generated by SAS 9.4 Proc Plan. Peking University Clinical Research Institute takes the responsibility of generating the allocation sequence and an interactive voice-response or web-response system will be used to assign each patient a number and group. The centers then randomly assign patients to the AM or losartan potassium treatment group. The allocation ratio is 1:1. The test uses a double-dummy drug; therefore, in the whole course of the trial, the patients, the doctors and the statistical analysts of the trial are unaware of the treatments. In patients with SAEs, an emergency unblinding procedure will be initiated.
Data collection and management
Table 1 gives an overview of assessment tests and the time of data collection. For each patient who is randomly assigned to a group, regardless of their final completion of the experiment, the baseline data and follow-up data will be saved. Patients enrolled in the trial will be treated preferentially and checked for free. The clinical investigators from each center collect the data and fill in the Case Report Forms. For keeping intact, first-hand data, we also design specified medical records for the clinical trial. Researchers write the medical records at the same time as making follow-up observations on the patients and ensure that the data records are timely, complete, accurate and true. The inspectors of the Venturepharm CRO Service Group will review the data. The inspectors are responsible for checking the consistency of all data sources, paper Case Report Forms and electronic databases. Original medical records and informed consents are archived in the participating centers and saved for at least 5 years after the clinical trials finish. The General Hospital of PLA is responsible for the establishment of network data registration platform, and investigators are responsible for the paper case report table entry to the platform. All data will be transferred to the data statistical units for data entry and management with the EpiData3.1 database.
Statistical methods
The statistical analysis plan will be decided before database lock and unblinding of the trial. Statistical analysis for the trial will be performed by the Peking University Clinical Research Institute. Statistics software SAS 9.4 will be used for the data analysis. Data analysis follows the principles of intention-to-treat analysis (ITT). The full analysis set is defined as all randomly assigned patients with both a baseline and a post-baseline assessment. Last observation carried forward (LOCF) will be used to handle the missing data. Categorical variables are presented as counts with percentages and compared by the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables are presented as mean with standard deviation and compared by t test if the variables are normal distribution or Mann-Whitney U test if the variables are non-normally distributed. A t test (two independent samples) will be conducted to compare the primary and secondary outcomes. An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model for the primary outcome will be conducted considering baseline proteinuria and study center effect. The LS-means and 95% LS confidence intervals will be generated.
Monitoring
Data monitoring
The Data Monitoring Committee (DMC) is composed of The Implement and Management Office of the Significant New Drug Creation of the National Science and Technology Major Projects and the Clinical Research Management Center of PLA General Hospital.
Harms
Potential adverse events include dizziness, gastrointestinal discomfort, rash, itching, amenorrhea and cough. In the process of the clinical trial, any SAEs must be immediately reported to the principal investigator, the Medical Ethics Committee of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, and to Safety Supervision of CFDA within 24 h. At the same time, the researchers must fill in the record of SAEs including the time that the SAEs occur, their severity and duration and the measures and outcome. Adverse events are recorded every 4 weeks from the baseline visit until the final visit. SAEs are recorded up to 30 days after the final visit.
Auditing
The Implement and Management Office of the Significant New Drug Creation of the National Science and Technology Major Projects will audit this trial every 6 months and it is independent from the investigators and the sponsor.
Dissemination
During its implementation in clinical trials, if the plan need to be revised, the principle investigator is responsible for the revision of the plan and for re-submitting it to the Ethics Committee for approval after consultation and discussion with the Executive Committee. Clinicians in each study center are responsible for the patient’s consent or assent. The enrolled patients have also signed the consent for blood and urine sample collection. All patient data will be saved according to the assigned serial number and the private information will be protected. The principal investigator declares that there are no competing interests for the overall trial and each study site. After all patients complete follow-up data records, the database will be locked by Peking University Clinical Research Institute. No person will obtain the data before analysis has finished. We plan to report the trial results for publication in an appropriate journal and to communicate the results at an academic conference. The Executive Committee will write the report and our final report will follow Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) guidelines [15].
Discussion
Due to the low quality of guideline evidence, the efficacy of drug treatment is still lack in IgAN patients. Since the 2012 KDIGO guidelines were released, the results of two multicenter, large-sample RCTs are worth looking at. The STOP-IgAN trial has not yet confirmed that glucocorticoid and other immunosuppressive agents can significantly improve the long-term prognosis of patients with IgN [16]. Another clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of glucocorticoids (TESTING test) is still ongoing, and our center also participated in this study [17]. Therefore, it is imperative to find new nonimmune suppressive drugs for IgAN. The efficacy of TCM has been confirmed in some randomized controlled studies in recent years [18] and great progress has been made recently in the field of TCM, but large and well-designed RCTs are still lacking.
The flowers of Abelmoschus manihot (Linn.) Medicus (family Malvaceae) have been used as a traditional treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis in China for centuries and the flowers are widely distributed in China. The major biologically active constituents are flavonoids [19]. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC)/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QTOF MS) can be both used to determine the content of the main chemical constituents of AM. Therefore, they can be used for standardization of AM production [20, 21]. Recent studies have indicated that flavonoids can be converted to a combination of acid sulfates in animals, which may be the main active metabolic ingredient for kidney protection [22]. For the mechanistic studies, AM has shown to improve kidney inflammation and glomerular injury in rats with doxorubicin-induced nephropathy through inhibition of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and TGF-β1 protein expression [23]. The results of our previous study have shown that AM significantly reduced proteinuria and maintained kidney function in patients with primary glomerular disease, non-nephrotic-range proteinuria and normal kidney function [11]. AM even showed a better therapeutic effect on reducing proteinuria than losartan (50 mg/d) after 24 weeks of treatment [24]. In addition, the combination of AM and losartan showed better efficacy than losartan monotherapy. Studies have suggested that high doses of ARBs could retard the progression of kidney disease in hypertensive and/or diabetic patients [25, 26]. This study was based on losartan at 100 mg/day as a positive control, and one of the inclusion criteria was effective control of hypertension (blood pressure of ≤140/90 mmHg); thus, we do not suggest changing the dosage of losartan. Other studies have shown that AM has good efficacy in patients with nephrotic syndrome and diabetic nephropathy [27–30]. Our team has carried out meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of the Huangkui capsule in the treatment of chronic kidney disease. The analysis included all RCTs and non-randomized controlled trials published between January 1995 and July 2011. The results showed that AM can reduce urinary protein in both nephrotic syndrome and nephritis syndrome [31]. Our team also conducted the meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of the Huangkui capsule in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy (urinary protein of 0.5–3.5 g/24 h). AM showed the effect of reducing urinary protein in diabetic nephropathy. According to the previous studies, AM is well tolerated with minimal adverse events [32].
To further evaluate the efficacy and safety of AM in the treatment of IgAN, we are conducting this study comparing AM and losartan (100 mg/d) which will enroll 1600 IgAN patients. In conclusion, the results of this trial will provide clinical evidence for the efficacy and safety of AM in the treatment of patients with stages 1 to 3 CKD with IgAN.
Trial status
This trial began recruiting participants in October 2015. We have recruited 912 patients in 87 hospitals as of 13 June 2016. We estimate to have collected post-treatment and follow-up data by the winter of 2017.
Abbreviations
- ACE-I:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibit
- AM:
-
Abelmoschus manihot
- ARB:
-
Angiotensin-receptor blocker
- CFDA:
-
China Food and Drug Administration
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- GCP:
-
Good Clinical Practice
- IgAN:
-
IgA nephropathy
- ITT:
-
Intention-to-treat analysis
- KDIGO:
-
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes
- SAEs:
-
Serious adverse events
- TCM:
-
Traditional Chinese medicine
References
Magistroni R, D’Agati VD, Appel GB, Kiryluk K. New developments in the genetics, pathogenesis, and therapy of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2015;88:974–89.
Wyatt RJ, Julian BA. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2402–14.
Xie Y, Chen X. Epidemiology, major outcomes, risk factors, prevention and management of chronic kidney disease in China. Am J Nephrol. 2008;28:1–7.
Beck L, Bomback AS, Choi MJ, Holzman LB, Langford C, Mariani LH, Somers MJ, Trachtman H, Waldman M. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62:403–41.
Zhong Y, Menon MC, Deng Y, Chen Y, He JC. Recent advances in Traditional Chinese Medicine for kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66:513–22.
Peng T, Yang XD, Li DR, Guo L, Xia Q, Hu Z. Observation of effect of Huang Kui capsule combined with valsartan in the treatment of IgA nephropathy. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol. 2010;11:723–4.
Wang XC, Gao F. Observation of effect of Huang Kui capsule combined with valsartan in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. J Hebei Medical University. 2010;31:733–4.
Zhu KY, Bi CY. Observation of effects of Huang Kui capsule in the treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis with proteinuria. Chin Pract Med. 2010;05:122–3.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1456–62.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
Zhang L, Li P, Xing CY, Zhao JY, He YN, Wang JQ, Wu XF, Liu ZS, Zhang AP, Lin HL, Ding XQ, Yin AP, Yuan FH, Fu P, Hao L, Miao LN, Xie RJ, Wang R, Zhou CH, Guan GJ, Hu Z, Lin S, Chang M, Zhang M, He LQ, Mei CL, Wang L, Chen X. Efficacy and safety of Abelmoschus manihot for primary glomerular disease: a prospective, multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64:57–65.
Chan AW, Tetzlaff JM, Gotzsche PC, Altman DG, Mann H, Berlin JA, Dickersin K, Hrobjartsson A, Schulz KF, Parulekar WR, Krleza-Jeric K, Laupacis A, Moher D. SPIRIT 2013 explanation and elaboration: guidance for protocols of clinical trials. BMJ. 2013;346:e7586.
Levey AS, Stevens LA. Estimating GFR using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) creatinine equation: more accurate GFR estimates, lower CKD prevalence estimates, and better risk predictions. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;55:622–7.
Administration CFaD. “Good Clinical Practice” (Order No. 3). 2003. http://www.sda.gov.cn/. Accessed May 2011.
Piaggio G, Elbourne DR, Pocock SJ, Evans SJ, Altman DG, Group C. Reporting of noninferiority and equivalence randomized trials: extension of the CONSORT 2010 statement. JAMA. 2012;308:2594–604.
Rauen T, Eitner F, Fitzner C, Sommerer C, Zeier M, Otte B, Panzer U, Peters H, Benck U, Mertens PR, Kuhlmann U, Witzke O, Gross O, Vielhauer V, Mann JF, Hilgers RD, Floege J, Investigators ST-I. Intensive supportive care plus immunosuppression in IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2225–36.
Lv J, Xu D, Perkovic V, Ma X, Johnson DW, Woodward M, Levin A, Zhang H, Wang H, Group TS. Corticosteroid therapy in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1108–16.
Chen Y, Deng Y, Ni Z, Chen N, Chen X, Shi W, Zhan Y, Yuan F, Deng W, Zhong Y. Efficacy and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Shenqi particle) for patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(6):1068-76.
Lai X, Liang H, Zhao Y, Wang B. Simultaneous determination of seven active flavonols in the flowers of Abelmoschus manihot by HPLC. J Chromatogr Sci. 2009;47:206–10.
Guo JM, Lu YW, Shang EX, Li T, Liu Y, Duan JA, Qian DW, Tang YP. Metabolite identification strategy of non-targeted metabolomics and its application for the identification of components in Chinese multicomponent medicine Abelmoschus manihot L. Phytomedicine. 2015;22:579–87.
Xue C, Jiang S, Guo J, Qian D, Duan JA, Shang E. Screening for in vitro metabolites of Abelmoschus manihot extract in intestinal bacteria by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011;879:3901–8.
Guo J, Du L, Shang E, Li T, Liu Y, Qian D, Tang Y, Duan J. Conjugated metabolites represent the major circulating forms of Abelmoschus manihot in vivo and show an altered pharmacokinetic profile in renal pathology. Pharm Biol. 2016;54:595–603.
Tu Y, Sun W, Wan YG, Che XY, Pu HP, Yin XJ, Chen HL, Meng XJ, Huang YR, Shi XM. Huangkui capsule, an extract from Abelmoschus manihot (L.) medic, ameliorates adriamycin-induced renal inflammation and glomerular injury via inhibiting p38MAPK signaling pathway activity in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;147:311–20.
Carney EF. Antiproteinuric efficacy of A. manihot superior to losartan. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:300.
Iino Y, Hayashi M, Kawamura T, Shiigai T, Tomino Y, Yamada K, Kitajima T, Ideura T, Koyama A, Sugisaki T, Suzuki H, Umemura S, Kawaguchii Y, Uchida S, Kuwahara M, Yamazaki T. Renoprotective effect of losartan in comparison to amlodipine in patients with chronic kidney disease and hypertension—a report of the Japanese Losartan Therapy Intended for the Global Renal Protection in Hypertensive Patients (JLIGHT) study. Hypertens Res. 2004;27:21–30.
Yasuda G, Ando D, Hirawa N, Umemura S, Tochikubo O. Effects of losartan and amlodipine on urinary albumin excretion and ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1862–8.
Chang LL, Yang SL, Zhao XL, Zhang XS, Wu WB. The effect of Huang Kui capsule on renal tubular function in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Shandong Med J. 2009;49:56–7.
Su JP, Xu J, Zhai XL, Zhang X, Cheng BZ, Lu X. The effects of Huang Kui capsule on the serum indicators of renal fibrosis in patients with clinical diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Clinicians. 2009;37:48–50.
Shan JP, Ye YX. Clinical observation of Huang Kui combined with glutathione for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Gerontol. 2010;30:2374–5.
Shen LL, Shen Y, Fang XX, Qiu ZL. Observation of effect of Huang Kui capsule on early and mid-stage diabetic nephropathy. Shandong Med J. 2010;50:59–60.
Chen Y, Gong Z, Chen X, Wei R, Tang L, Zhou J, Cao X. The efficacy and safety of Abelmoschus manihot (a traditional Chinese medicine) for chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies (FP-373). 49th European Renal Association—European Dialysis and Transplant Association Congress. 24–27 May 2012, Paris, France: http://www.postersessiononline.com/173580348_eu/congresos/49era/aula/-FP_373_49era.pdf, 49th European Renal Association—European Dialysis and Transplant Association Congress.
Chen YZ, Gong ZX, Cai GY, Gao Q, Chen XM, Tang L, Wei RB, Zhou JH. Efficacy and safety of Flos Abelmoschus manihot (Malvaceae) on type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review. Chin J Integr Med. 2015;21:464–72.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Yang Wang, PhD and Xiao-yan Yan, PhD for their support with statistical analysis planning.
Funding
This study is funded by a National Science and Technology Major Project (Significant New Drugs Creation) (No. 2013ZX09104003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81270794) and the Beijing Science and Technology Project (No. D13110700473003).
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during the current study are not publicly available due to the clinical data collecting and analysis being unfinished but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributions
PL, HL, ZN, YZ, RW, HY, JF, NW, WL, XS and XC discussed and designed the trial. PL and YC drafted the manuscript. XS planned the statistical analyses. XS and XC are the principal investigators. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study has been approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital on 28 April 2014 (journal number: S2014-039-01). Patients who agree to participate and sign the informed consent will be involved.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional files
Additional file 1:
SPIRIT 2013 Checklist: recommended items to address in a clinical trial protocol and related documents. (DOC 123 kb)
Additional file 2:
Informed Consent Form. A Multi-center, Double-blind, Double-simulation and Randomized Control Study of Huangkui Capsule for the Treatment of IgA Nephropathy: Informed Consent. (PDF 85 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Chen, Yz., Lin, Hl. et al. Abelmoschus manihot – a traditional Chinese medicine versus losartan potassium for treating IgA nephropathy: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 18, 170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-016-1774-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-016-1774-6