Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Flos Abelmoschus manihot (Malvaceae) on type 2 diabetic nephropathy (DN).
Methods
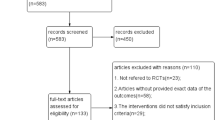
The Cochrane Library, PubMed/MEDLINE, Excerpta Medical Database, Chinese electronic literature databases, and the references of relevant articles were searched in March 2012 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that reported the effects of Flos A. manihot on type 2 DN patients with overt but subnephrotic-range proteinuria (500–3,500 mg/24 h). The quality of trials was evaluated using the Cochrane-recommended method. The results were summarized as risk ratios (RRs) for dichotomous outcomes or mean differences (MDs) for continuous outcomes.
Results
Seven trials (531 patients) were included. Flos A. manihot significantly decreased proteinuria [MD −317.32 mg/24 h, 95% confidence interval (CI) [−470.48, −164.17],P<0.01]. After excluding a trial that only included patients with well-preserved renal function, Flos A. manihot was associated with a significant decrease in serum creatinine (MD −11.99 μmol/L, 95% CI [−16.95, −7.04],P<0.01). Serious adverse events were not observed. The most common adverse event was mild to moderate gastrointestinal discomfort; however, patients receiving this herb did not have an increased risk for tolerated gastrointestinal discomfort (RR 1.48, 95% CI [0.39, 5.68],P=0.57).
Conclusions
Flos A. manihot may be considered as an important adjunctive therapy with the first-line and indispensable therapeutic strategies for type 2 DN. High-quality RCTs are urgently needed to confirm the effect of Flos A. manihot on definite endpoints such as end-stage renal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:580–591.
Gilbertson DT, Liu J, Xue JL, Louis TA, Solid CA, Ebben JP, et al. Projecting the number of patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States to the year 2015. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:3736–3741.
Parving HH, Lehnert H, Brochner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001;345:870–878.
Cravedi P, Ruggenenti P, Remuzzi G. Proteinuria should be used as a surrogate in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol 2012;8:301–306.
Holtkamp FA, de Zeeuw D, de Graeff PA, Laverman GD, Berl T, Remuzzi G, et al. Albuminuria and blood pressure, independent targets for cardioprotective therapy in patients with diabetes and nephropathy: a post hoc analysis of the combined RENAAL and IDNT trials. Eur Heart J 2011;32:1493–1499.
de Zeeuw D, Remuzzi G, Parving HH, Keane WF, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S, et al. Albuminuria, a therapeutic target for cardiovascular protection in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Circulation 2004;110:921–927.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001;345:861–869.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensinreceptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001;345:851–860.
Remuzzi G, Benigni A, Remuzzi A. Mechanisms of progression and regression of renal lesions of chronic nephropathies and diabetes. J Clin Invest 2006;116:288–296.
Ruggenenti P, Porrini EL, Gaspari F, Motterlini N, Cannata A, Carrara F, et al. Glomerular hyperfiltration and renal disease progression in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012;35:2061–2068.
Tu QN, Dong H, Lu FE. Effects of Panax notoginoside on the nephropathy in rats with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Chin J Integr Med 2011;17:612–615.
Wei FN, Chen ZL, Yang HF, Han L, Ding HM, Deng SG, et al. Effect of Sanqi Oral Liquid on the expressions of CD4+, CD8+ and CD68+ cells in 5/6 nephrectomized rats with chronic renal failure. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:589–595.
Zou C, Lu ZY, Wu YC, Yang LH, Su GB, Jie XN, et al. Colon may provide new therapeutic targets for treatment of chronic kidney disease with Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:86–91.
Li P, Zhang HJ, Zheng LT. The theory of homogeny of Liver and Kidney in the treatment of kidney and liver fibrosis. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:250–252.
Guo J, Shang EX, Duan JA, Tang Y, Qian D, Su S. Fast and automated characterization of major constituents in rat biofluid after oral administration of Abelmoschus manihot extract using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-offlight mass spectrometry and MetaboLynx. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2010;24:443–453.
Song GZ, Lian YG. Huangkui Capsule-based therapy in the treatment of 20 patients with IgA nephropathy. J New Chin Med (Chin) 2005;37:78.
Zhang QD, Qu ZS. The effect of Huangkui Capsule on serum SOD, MDA, ET, NO, and urinary protein in patients with chronic kidney disease. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:544–545.
Zhu KY, Bi CY. Observation of effects of Huangkui Capsule in the treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis with proteinuria. China Pract Med (Chin) 2010;5:122–123.
Peng T, Yang XD, Li DR, Guo L, Xia Q, Hu Z. Observation of effect of Huangkui Capsule combined with valsartan in the treatment of IgA nephropathy. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:723–724.
Zhang N, Xia T. Clinical observation and analysis of Huangkui Capsule associated with losartan in 102 patients with IgA nephropathy. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:1108.
Han YR, Qiu ZY. Clinical study of Huangkui Capsule combined with benazepril in the treatment of primary IgA nephropathy. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:998–999.
Chen P, Wan Y, Wang C, Zhao Q, Wei Q, Tu Y, et al. Mechanisms and effects of Abelmoschus manihot preparations in treating chronic kidney disease. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2012;37:2252–2256.
Liu KH, Wang L, Zhang Y. The clinical research of Abelmoschus manihot in treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Jilin Med J (Chin) 2005;26:1022–1023.
Zhou BX, Bai XM. Observation of effects of Huangkui Capsule combined with telmisartan for the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy. Chin Commun Doct (Chin) 2008;10:75.
Chang LL, Yang SL, Zhao XL, Zhang XS, Wu WB. The effect of Huangkui Capsule on renal tubular function in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Shandong Med J (Chin) 2009;49:56–57.
Li XH, Lu YM, Liang YP. Clinical research of combination therapy with Abelmosehus moschatus and losartan for diabetic nephropathy. Clin Med Engin (Chin) 2009;16:3–4.
Su JP, Xu J, Zhai XL, Zhang X, Cheng BZ, Lu X. The effects of Huangkui Capsule on the serum indicators of renal fibrosis in patients with clinical diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Clinic (Chin) 2009;37:48–50.
Yang S, Liu XH. Clinical observation of Huangkui Capsule combination therapy in the treatment of 32 patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Hebei J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;31:600–602.
Cai XY, Huang BY, Wang YF, Chen ZP, Lin M. Clinical observation of effects of Huangkui Capsule combined with valsartan for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Contemp Med (Chin) 2010;16:153–154.
Chen Y. Clinical research of effect of Huangkui Capsule combined with telmisartan in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy (a report of 52 cases). J Xianning Univ (Med Sci, Chin) 2010;24:411–412.
He YN. Clinical observation of the effect of Huangkui Capsule combined with valsartan in the treatment of 40 patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Yunnan J Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (Chin) 2010;31:24–25.
Li QH, He JL. Clinical observation of the effect of Huangkui Capsule combined with valsartan for the treatment of early proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:142–143.
Liu H, Zhong LY, Li RH. Observation of the effect of Huangkui Capsule on diabetic nephropathy and the underlining mechanism. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:633–634.
Shan JP, Ye YX. Clinical observation of Abelmoschus manihot combined with glutathione for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Gerontol (Chin) 2010;30:2374–2375.
Shen LL, Shen Y, Fang XX, Qiu ZL. Observation of effect of Huangkui Capsule on early and mid-stage diabetic nephropathy. Shandong Med J (Chin) 2010;50:59–60.
Su Y, Zhang DC, Zhong S. The efficacy of combination of Huangkui Capsule and Salvia miltiorrhiza and Ligustrazine on diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol (Chin) 2010;11:1112.
Wang XC, Gao F. Observation of effect of Huangkui Capsule combined with valsartan in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. J Hebei Med Univ (Chin) 2010;31:733–734.
Xiao ZZ, Sun HJ. Effects of Okra Capsule combined with valsartan in treatment of early diabetic nephropathy with microalbuminuria. Modern J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 2010;19:263–264.
Shen XH, Wang H, Xu SX, Tao J. Clinical observation of Huangkui Capsule combined with telmisartan in the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy. Med Inform (Chin) 2011;15:228–229.
Zhu YZ. The clinical research of Okra in treatment of diabetic nephropathy. World Health Digest (Chin) 2009;6:74–75.
Yu ZW, Wang JZ, Zhang LP, Sheng XY, Zhang W, Qiu ZY, et al. Clinical observation of Huangkui Capsule combined with candesartan in the treatment of type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Pract Diabetol (Chin) 2011;7:41–42.
Ding LP, Li XM, Xu C, Zhuo L, Ding M. Observation of effect of Abelmoschus manihot combined with alprostadil in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy stage IV. Chin J Misdiagnost (Chin) 2011;11:6370–6371.
Li ZF, Qiu GP, Peng R. Observation of effect of Huangkui Capsule combination therapy in 31 patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Jiujiang Med J (Chin) 2009;24:17–19.
Li HY, Xiang F, Wang Q, Li SF. Clinical observation of effect of Huangkui Capsule combined with fosinopril for the treatment of IV stage diabetic nephropathy. Pract J Card Cerebr Pneum Vascul Dis (Chin) 2009;17:691–692.
Guan ZX, Zhang WH. Clinical observation of the effects of Abelmoschus manihot combined with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. J Pract Med Techniq (Chin) 2008;15:4670–4671.
Li YL. Huangkui Capsule combined with lotensin in the treatment of 30 patients with diabetic nephropathy. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2007;28:562–563.
Yu JY, Xiong NN, Guo HF, Deng Y. Clinical observation on diabetic nephropathy treated with alcohol of Abelmoschus manihot. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 1995;15:263–265.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011.
Chen Y, Gong Z, Chen X, Wei R, Tang L, Zhou J, et al. The efficacy and saftey of Abelmoschus manihot (a traditional Chinese medicine) for chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies (FP-373). Poster presented at: 49th European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association Congress, 24–27 May 2012, Paris, France. Available at: http://www.postersessiononline.com/173580348_eu/congresos/49era/aula/-FP_373_49era.pdf.
Lai X, Liang H, Zhao Y, Wang B. Simultaneous determination of seven active flavonols in the flowers of Abelmoschus manihot by HPLC. J Chromatogr Sci 2009;47:206–210.
Lai X, Zhao Y, Liang H, Bai Y, Wang B, Guo D. SPE-HPLC method for the determination of four flavonols in rat plasma and urine after oral administration of Abelmoschus manihot extract. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2007;852:108–114.
Xu TT, Yang XW, Wang B, Xu W, Zhao YY, Zhang QY. Metabolism of hibifolin by human intestinal bacteria. Planta Med 2009;75:483–487.
Xue C, Jiang S, Guo J, Qian D, Duan JA, Shang E. Screening for in vitro metabolites of Abelmoschus manihot extract in intestinal bacteria by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2011;879:3901–3908.
Xue C, Guo J, Qian D, Duan JA, Shang E, Shu Y, et al. Identification of the potential active components of Abelmoschus manihot in rat blood and kidney tissue by microdialysis combined with ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2011;879:317–325.
Zhou L, An XF, Teng SC, Liu JS, Shang WB, Zhang AH, et al. Pretreatment with the total flavone glycosides of Flos Abelmoschus manihot and hyperoside prevents glomerular podocyte apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. J Med Food 2012;55:461–468.
Zhao Q, Wan YG, Sun W, Wang CJ, Wei QX, Chen HL, et al. Effects of Huangkui Capsule on renal inflammatory injury by intervening p38MAPK signaling pathway in rats with adriamycin-induced nephropathy. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2012;37:2926–2934.
Harbord RM, Egger M, Sterne JA. A modified test for smallstudy effects in meta-analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Stat Med 2006;25:3443–3457.
Harbord RM, Harris RJ, Sterne JAC. Updated tests for smallstudy effects in meta-analyses. Stata J 2009;9:197–210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Major New Drug Creation Plan of China (No. 2013ZX09104003) and Key Science and Technology Planning of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Beijing, China (No. D131100004713000)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yz., Gong, Zx., Cai, Gy. et al. Efficacy and safety of Flos Abelmoschus manihot (Malvaceae) on type 2 diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 464–472 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1891-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1891-6