Abstract
Background
β-alanine (βA) supplementation has been shown to increase intramuscular carnosine content and subsequent high-intensity performance in events lasting < 4 minutes (min), which may be dependent on total, as opposed to daily, dose. The ergogenic effect of βA has also been demonstrated for 2000-m rowing performance prompting interest in whether βA may be beneficial for sustained aerobic exercise. This study therefore investigated the effect of two βA dosing strategies on 30-min rowing and subsequent sprint performance.
Methods
Following University Ethics approval, twenty-seven healthy, male rowers (age: 24 ± 2 years; body-height: 1.81 ± 0.02 m; body-mass: 82.3 ± 2.5 kg; body-fat: 14.2 ± 1.0%) were randomised in a double-blind manner to 4 weeks of: i) βA (2.4 g·d− 1, βA1); ii) matched total βA (4.8 g on alternate days, βA2); or iii) cornflour placebo (2.4 g·d− 1, PL). Participants completed a laboratory 30-min rowing time-trial, followed by 3x30-seconds (s) maximal sprint efforts at days 0, 14 and 28 (T1-T3). Total distance (m), average power (W), relative average power (W·kg− 1), cardio-respiratory measures and perceived exertion were assessed for each 10-min split. Blood lactate ([La-]b mmol·L− 1) was monitored pre-post time-trial and following maximal sprint efforts. A 3-way repeated measures ANOVA was employed for main analyses, with Bonferonni post-hoc assessment (P ≤ 0.05).
Results
Total 30-min time-trial distance significantly increased from T1-T3 within βA1 only (7397 ± 195 m to 7580 ± 171 m, P = 0.002, ƞp2 = 0.196), including absolute average power (194.8 ± 18.3 W to 204.2 ± 15.5 W, P = 0.04, ƞp2 = 0.115) and relative average power output (2.28 ± 0.15 W·kg− 1 to 2.41 ± 0.12 W·kg− 1, P = 0.031, ƞp2 = 0.122). These findings were potentially explained by within-group significance for the same variables for the first 10 min split (P ≤ 0.01), and for distance covered (P = 0.01) in the second 10-min split. However, no condition x time interactions were observed. No significant effects were found for sprint variables (P > 0.05) with comparable values at T3 for mean distance (βA1: 163.9 ± 3.8 m; βA2: 161.2 ± 3.5 m; PL: 162.7 ± 3.6 m), average power (βA1: 352.7 ± 14.5 W; βA2: 342.2 ± 13.5 W; PL: 348.2 ± 13.9 W) and lactate (βA1: 10.0 ± 0.9 mmol·L− 1; βA2: 9.2 ± 1.1 mmol·L− 1; PL: 8.7 ± 0.9 mmol·L− 1).
Conclusions
Whilst daily βA may confer individual benefits, these results demonstrate limited impact of βA (irrespective of dosing strategy) on 30-min rowing or subsequent sprint performance. Further investigation of βA dosage > 2.4 g·d− 1 and/or chronic intervention periods (> 4–8 weeks) may be warranted based on within-group observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
β-alanine (βA) first gained popularity within the athletic population during the mid-2000’s following the inaugural work of Harris and colleagues [1]. Numerous research has since demonstrated that βA supplementation (1.6–6.4 g·day− 1 for ≥28 days) augments the naturally occurring histidine dipeptide, carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) within human muscle tissue [2,3,4,5]. As carnosine acts as a physico-chemical buffering agent (with an imidazole ring pKa of 6.83, and relative similarity to intracellular pH (6.5) [6,7,8]), βA supplementation was recently reported as producing small, yet significant performance improvements (effect size: 0.210; 95% CI: 0.057, 0.362) across a range of short (60–240 s) duration events [9] including cycling sprint performance [10], judo bouts [11], 800 m sprinting [12] and 1000 m rowing splits [13] in club-level through to well training men.
Beyond these short duration (60–240 s) bouts the magnitude of improvement appears to diminish. However, a recent meta-analysis based on 40 individual studies involving 1461 participants indicated that the predominant use of incremental tests in many studies may potentially bias this finding based on assessment of exercise capacity as opposed to aerobic performance [9]. Additionally, in a recent International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) Position Stand, Trexler et al [14] noted an apparent dearth of βA research investigating performance during endurance events (> 25-min), with inference that βA may ergogenically support training adaptations to sustained efforts typically employed in aerobically dominated events [15,16,17,18].
Specific to rowing, previous research has highlighted a significant correlation between muscle carnosine content and performances over multiple distances (100, 500, 2000 and 6000 m) [19]. It is therefore feasible that short-term βA supplementation could support prolonged training bouts or enhance > 2000 m performance, particularly in non-elite rowers or those with lower initial muscle carnosine levels [20,21,22]. With the high levels of acidity brought about as a bi-product of anaerobic glycolysis, and subsequent elevated blood lactate production observed in competitive rowers, the buffering potential of carnosine could facilitate higher power output throughout an endurance bout/race, or as part of a final sprint [19, 23]. However, such hypotheses rely on assumptions that perhaps over-simplify the mechanistic effects of βA, including improved calcium sensitivity [24], enhanced antioxidant capacity and reduced oxidative damage [25, 26].
In terms of dosing strategies, βA intakes from 1.6 g·day− 1 to 12 g·day− 1 [2, 27] for ≥2-weeks have been shown to significantly increase muscle carnosine content (with typically recommended levels of 2–6 g·day− 1 [1, 4, 7, 10, 28]). However, research has also highlighted that muscle carnosine content correlates significantly with total dose (grams) of βA consumed [2, 29] irrespective of baseline carnosine levels or daily intake. This raises an important question as to whether βA needs to be consumed daily, or whether ergogenic benefits are based on total dose provided in a given timeframe [2]. This is particularly relevant considering a recent survey in which 61% of Australian team sport athletes used βA as part of their training, yet only 35% understood the mechanistic benefits, and 50% consumed less than half of the commercially recommended dose [30].
The aim of the current study was therefore to assess the efficacy of two βA strategies (daily versus alternate day intake for 4 weeks) on 30-min rowing time-trial performance and subsequent anaerobic sprint bouts in healthy, male rowers. It was hypothesised that βA would significantly enhance endurance performance irrespective of dosing strategy.
Materials/ methods
Study design and participants
A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled, parallel design was employed for this study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Faculty of Science and Technology Ethics Committee, Anglia Ruskin University (Project Number: FST/FREP/15/591). A priori sample size using G*power software (α = 0.05 and 1-β = 0.90) based on performance data from Ducker et al. [13] estimated a total sample population of 27 participants. Participants were required to be healthy, male rowers with > 6 months training experience (including familiarity with 30- min time-trial sessions), and actively training > 3 times per week at the point of inclusion.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants prior to study inclusion. All participants satisfactorily completed a health screen questionnaire, and had no known history of blood related disorders, cardiovascular or metabolic abnormalities; or recent viral infections or injuries, which would prevent them from maintaining habitual training sessions or taking part in laboratory time-trials. Individuals at risk of lowered baseline carnosine, as a result of dietary restriction of animal products (vegan/vegetarians), were excluded from participation [31]. All participants were required not to be taking any medication / supplementation in the previous 3 months which could interfere with the study parameters, and in particular, complete abstinence (> 6 months) from βA-containing supplements specifically due to the slow washout rate previously reported for muscle carnosine content [32, 33]. Thirty male individuals volunteered for study inclusion. However, 3 were excluded from final analyses due to non-compliance with protocol requirements. Participant characteristics are displayed in Table 1.
Procedures
All testing took place within the Cambridge Centre for Sport and Exercise Sciences, Human Physiology Laboratory, Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge under thermal neutral conditions (temperature:17.1–19.3 °C; humidity: 20–38%; barometric pressure: 993–1028 mbar). Following pre-familiarization with the laboratory equipment and test protocol, participants were required to attend the laboratory on 3 occasions across the intervention period (days 0, 14 and 28; T1-T3) at the same time of day for each participant to minimise diurnal variance. Participants were instructed to avoid strenuous exercise, and refrain from consuming caffeinated or alcohol containing products at least 24 hours prior to each laboratory visit. Participants were requested to arrive acutely fasted (i.e. no food within 3 hours of assessment and maintain habitual hydration patterns) with last consumption of fluid (~ 0.5 L water) 1 hour prior to assessment to standardise procedures.
Upon arrival, body mass (Seca 780, Hamburg, Germany), height (Seca 200 stadiometer, Hamburg, Germany) and estimated body composition (4-site skinfold measures in triplicate) were assessed by the same researcher. Following a 5-min seated period, 2-min baseline expired air samples were collected via the Douglas bag method [34] and analysed for percentage O2 and CO2, using a Servoflex MINIMP 5200 gas analyser (Servomex Group Ltd., Crowborough, UK). Total Douglas bag volume was measured using a dry gas meter (Harvard Apparatus, Holliston, USA), with sample temperature recorded during volume measurement. Heart rate (HR) was recorded via radio-telemetry (T-31, Polar Electro Ltd., Kempele, Finland), and 20 μl capillarised fingertip blood samples were collected for analysis of blood lactate [La−]b (Biosen C_Line, EKF Diagnostics, Cardiff, UK).
Rowing ergometer time trials (TT)
All time-trials were conducted on the same Concept 2 air braked rowing ergometer (Concept 2, Nottingham, UK) with resistance set at 5 for standardisation. Participants undertook a self-paced, continuous warm-up at 100 W for 5-min, after which the unit display was modified to display time remaining to minimise extraneous influences on pacing strategy [35]. Participants were instructed to row for maximal distance in 30- min at self-selected pace. To minimise effects of data collection on performance, expired air, rated perceived exertion (RPE [36]) and HR were assessed during the final minute of each 10-min split; along with split distance covered (m) and mean power output (W).Verbal encouragement was provided by the same tester at the end of each collection period in a standard manner. End-point [La−]b was assessed following the final collection period only.
Sprint efforts post-TT
Following a standardised 5-min inactive rest period, participants completed three 30-s maximal sprint efforts with 60-s inactive recovery in between. [La−]b, RPE and performance data (distance rowed (m), average power (W)) were recorded on completion of each sprint. At the mid-point of each sprint, standardised verbal encouragement was given to all participants to promote maximal engagement.
Supplemental treatments
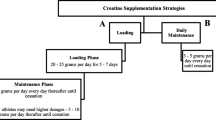
Participants were randomly assigned (using a random number generator – https://www.randomizer.org/) in a double-blind manner to 4 weeks of: i) crystalline βA (2.4 g·d− 1 Bulk Powders®, UK; βA1); ii) matched total βA (4.8 g on alternate days, βA2); or iii) cornflour placebo (2.4 g·d− 1, PL). These daily doses were selected to minimise the risk of paraesthesia and thus the potential to affect the double blinding process. Furthermore, the matched average daily dose of 2.4 g∙day− 1 was deemed appropriate given previous research demonstrating increased muscle carnosine concentrations at lower daily doses (1.6 g∙day− 1) [2]. All products were manually weighed under laboratory conditions for accuracy and capsulated in size 00 capsules (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose). Once weighed all capsules were placed in food safe containers before an independent researcher recorded and randomized all batches to ensure double blinding procedures. All participants received capsules on a 14-day basis, along with a daily adherence diary to monitor compliance. To limit both the occurrence and severity of potential paraesthesia symptoms, standard instructions were provided to participants to consume one (800 mg) capsule daily with breakfast before repeatedly consuming (800 mg) capsules every 3 hours until required dosage was met, in accordance with previous research [37, 38]. Upon completion of each 14-day period participants were instructed to return any remaining capsules as a secondary measure of compliance.
Dietary intake
Prior to baseline measures, and throughout the intervention, participants were requested to maintain habitual dietary intake and exercise patterns, and record using standard food/activity diaries (following individual guidance in diary collation, with emphasis on meal content, portion size and weight and fluid intake). In particular, participants were requested to refrain from introducing atypical foods during the intervention period. Diaries were comprehensively checked by the research team at each visit, with dietary analyses undertaken using Nutritics software (version 3.74 professional edition, Nutritics Ltd., Co. Dublin, Ireland). No differences were reported between groups for macronutrients and/or energy intake (Table 2), demonstrating general dietary compliance prior to testing sessions.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS (v24, Chicago, USA). Normal distribution of data was assessed via a Shapiro-Wilks test [39]. A 3-way repeated measures ANOVA was employed for main analyses (including effect size (partial eta squared; ηp2)), with Bonferonni post-hoc assessment where applicable. Where pertinent, a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc assessment was utilised to evaluate within treatment effects (e.g. baseline variables and resting measures). An alpha level of ≤0.05 was employed for statistical significance. Data are reported as means ± SE.
Results
Baseline characteristics and resting measures
Intervention groups were matched for age (yrs), rowing experience (yrs), body-height (m), body-mass (kg) and body-fat (%) at baseline (Table 1). Non significant differences (P > 0.05) were reported between groups for baseline resting HR (b·min− 1) (βA1: 66 ± 3, βA2: 62 ± 3, PL: 60 ± 2), [La−]b (mmol·L− 1) (βA1: 1.4 ± 0.1, βA2: 1.4 ± 0.1, PL: 1.3 ± 0.1), absolute VO2 (L·min− 1) (βA1: 0.34 ± 0.04, βA2: 0.34 ± 0.02, PL: 0.37 ± 0.03) or relative VO2 (ml·kg− 1·min− 1) (βA1: 4.08 ± 0.40, βA2: 4.11 ± 0.24, PL: 4.28 ± 0.28).
Time-trial performance measures
Overall distance
Data for distance rowed (m) during the 30-min time trial are shown as absolute a) and relative b) values in Fig. 1. No group x time interactions were shown for overall 30-min time trial performance (F = 1.50, P = 0.22, ηp2 = 0.11). A significant effect was shown for time only (F = 5.87, P = 0.005 ηp2 = 0.20), with βA1 distance increasing from 7397 ± 195 m at T1 to 7580 ± 171 m by T3 only (P = 0.002, Fig. 1). This represented a 2.45% absolute improvement in performance within-group only. When expressed relatively (T1-T3), despite a 2.60% increase in distance covered (183 ± 52 m) with βA1, and a 1.50% increase in distance covered (107 ± 48 m) with βA2, no significant between group differences were noted (F = 1.91, P = 0.17).
Power: Weight
Similarly, mean power significantly increased for time only (F = 3.11, P = 0.05, ηp2 = 0.12) with βA1 from 194.8 ± 18.3 W (T1) to 204.2 ± 15.5 (T3) (P = 0.04). No differences were reported within group for βA2 (200.3 ± 9.8 W (T1) to 208.8 ± 8.0 W (T3); P > 0.05) or PL (173.0 ± 13.8 W (T1) to 174.8 ± 13.7 W (T3); P > 0.05). When adjusted for body-mass, average power output expressed as a) absolute and b) relative change is shown in Fig. 2. A significant time effect was observed for changes in average power to weight (W·kg− 1) between T1 and T3 (F = 3.35, P = 0.04, ηp2 = 0.12) for βA1 only (2.28 ± 0.15 W·kg− 1 to 2.41 ± 0.12; P = 0.03). A significant between group main effect was reported (F = 3.53, P = 0.04, ηp2 = 0.12), with post-hoc analysis indicating an overall difference between βA2 and PL only (P = 0.04). However, no group x time interactions were shown for absolute changes in average power to weight ratio (F = 1.12, P = 0.36, ηp2 = 0.09). When data was expressed as relative change in average power, no significant between group differences were observed (F = 1.31, P = 0.29); despite small improvements of 0.13 ± 0.06 W·kg− 1 for βA1 and 0.11 ± 0.05 W·kg− 1 for βA2, in contrast to negligible changes of 0.01 ± 0.06 W·kg− 1 for PL.
demonstrates effect of beta-alanine (βA) interventions on a) absolute and b) relative power to weight during the 30-min rowing time trial. Abbreviations: βA1 – daily intervention; βA2 – alternate day; PL – placebo. * represents significant difference, from T1, within group only. # represents overall group difference to PL (P = 0.04)
30-min time trial- average physiological variables and perceived effort
Average HR significantly increased by T3 (F = 4.22, P = 0.02, ηp2 = 0.15) for βA1 only (175 ± 3 to 180 ± 2 b·min− 1; P = 0.01), however RPE was maintained throughout the intervention (average RPE: 7.7 ± 0.2 (T1), 7.8 ± 0.2 (T2), 7.8 ± 0.3 (T3) P > 0.05). In contrast, average RPE significantly increased by T3 (F = 5.12, P = 0.01, ηp2 = 0.18) for both βA2 (7.1 ± 0.5 (T1) to 7.7 ± 0.4 (T3); P = 0.04) and PL (6.5 ± 0.4 (T1) to 7.3 ± 0.03 (T3); P = 0.01). Average VO2 was maintained across all trials with no group x time interactions reported (βA1: 3.12 ± 0.12 L·min− 1 (T1) to 3.14 ± 0.10 (T3); βA2: 3.17 ± 0.10 L·min− 1 (T1) to 3.24 ± 0.14 (T3); PL: 2.93 ± 0.13 L·min− 1 (T1) to 2.86 ± 0.14 (T3); P > 0.05).
30-min time trial- Split data (0–10 min)
No group x time interactions were shown for overall 0-10 min time trial performance (F = 1.17, P = 0.34, ηp2 = 0.089; Table 3). A significant effect was shown for time only (F = 8.27, P = 0.001, ηp2 = 0.256), with βA1 significantly increasing between T1-T2 (P = 0.03), T1-T3 (P = 0.004) representing a 3.65% (T1-T2) and 4.52% (T1-T3) distance increase, respectively. Likewise, βA2 also increased distance covered significantly by 2.55% from T2-T3 (P = 0.01). Accompanying these effects for distance, time effects (F = 4.77, P = 0.01, ηp2 = 0.166) for absolute power was observed in βA1 only between T1-T2 (P = 0.03) and T1-T3 (P = 0.01). These represented a 14.04 and 14.61% increase in watts, respectively. Time effects (F = 5.37, P = 0.01, ηp2 = 0.166) for power to weight was observed in βA1 only, between T1-T2 (P = 0.02) and T1-T3 (P = 0.01). These represented a 6.20 and 6.75% increase in W·kg− 1, respectively.
A significant effect was observed for changes in HR (b·min− 1) between T1 and T3 (F = 4.992, P = 0.01, ηp2 = 0.17) for βA1 (164 ± 4 to 172 ± 3 b·min− 1; P = 0.02) and βA2 (159 ± 5 b·min− 1 to 166 ± 4; P = 0.05), but not PL (P > 0.05). In contrast, average RPE (F = 1.607, P = 0.19, ηp2 = 0.118), VE (F = 0.410, P = 0.41, ηp2 = 0.036), VO2 (F = 1.398, P = 0.25, ηp2 = 0.104), VCO2 (F = 0.384, P = 0.82, ηp2 = 0.031) and RER (F = 2.234, P = 0.08, ηp2 = 0.157) were maintained across all trials with no significant interactions reported.
30-min time trial- Split data (11–20 min)
No group x time interactions were shown during the second 10-min split (F = 0.694, P = 0.60, ηp2 = 0.055; Table 4). Within group however a significant time effect was demonstrated (F = 3.987, P = 0.03, ηp2 = 0.257), with βA1 increasing distance rowed by 54 ± 14 m between T1-T3 (P = 0.01). Other performance variables such as absolute power (F = 1.283, P = 0.29, ηp2 = 0.051) and power to weight (F = 1.177, P = 0.32, ηp2 = 0.073) failed to reach significance overall. Average HR (F = 1.893, P = 0.16, ηp2 = 0.073), VE (F = 0.959, P = 0.39, ηp2 = 0.038), VO2 (F = 0.780, P = 0.46, ηp2 = 0.031), VCO2 (F = 1.115, P = 0.34, ηp2 = 0.044), RPE (F = 2.971, P = 0.07, ηp2 = 0.205), and RER (F = 0.079, P = 0.93, ηp2 = 0.003) were maintained across all trials with no significant interactions reported.
30-min time trial- Split data (21–30 min)
No group x time interactions were shown for overall 21–30 min time trial distance covered (F = 2.027, P = 0.21, ηp2 = 0.144; Table 5). Likewise, no effects were shown for time (F = 1.594, P = 0.12, ηp2 = 0.062) in distance covered or other performance variables (P > 0.05). Average HR (F = 0.841, P = 0.41, ηp2 = 0.034), VE (F = 0.959, P = 0.39, ηp2 = 0.038), VO2 (F = 1.649, P = 0.20, ηp2 = 0.064), VCO2 (F = 1.850, P = 0.18, ηp2 = 0.070) RPE (F = 2.882, P = 0.66, ηp2 = 0.107) and RER (F = 0.803, P = 0.0.76, ηp2 = 0.032) were maintained across trials with no significant group x time interactions reported.
Overall sprint performance
No significant between-group effects existed at T1 with all groups rowing 166.0 ± 2.5 m (F = 2.325, P = 0.07, ηp2 = 0.162; Table 6). Following treatment with their respective intervention, no significant group x time (F = 2.325, P = 0.07, ηp2 = 0.162), or time (F = 1.936, P = 0.16, ηp2 = 0.075) effects were observed at any time-point for distance covered. Likewise, power (F = 1.961, P = 0.15, ηp2 = 0.076), power to weight (F = 1.251, P = 0.30, ηp2 = 0.050), HR (F = 1.241, P = 0.30, ηp2 = 0.049), RPE (F = 3.920, P = 0.26, ηp2 = 0.140) and [La-]b (F = 0.759, P = 0.46, ηp2 = 0.032) failed to reach significance.
Discussion
The aim of the current randomised controlled trial was to observe the effects of two separate, 28-day, βA dosing strategies (matched for total overall dose), on 30-min rowing time trial and subsequent anaerobic sprint performance. A recent 2018 ISSN Position Stand [40] stated there is ‘strong evidence’ to support the efficacy of βA as an ergogenic aid, with research demonstrating positive influences over short duration performance [11,12,13] and capacity [3] measures alike. However, the primary finding of this study indicates that βA does not appear to offer significant benefits to sustained endurance performance, as assessed via a 30-min time trial when compared to placebo. These findings concur with an earlier 2015 ISSN Position Stand [14] indicating that βA consumption “does not demonstrate a consistent positive effect” on events lasting beyond a 25-min timeframe. It is, however, noteworthy that within-group improvements were observed for mean distance covered, average power and average power to weight ratio when participants consumed βA daily, increasing by 2.6, 14.6 and 14.9%, respectively over the intervention period. This may likely be the result of improved effort (distance covered and power output (including relative to mass)) in the first 10-min split. In the second 10-min split, whilst a within group increase was observed for distance covered (T1-T3) for βA1, power output did not significantly change, potentially indicating a diminishing effect with time trial duration.
The findings from the current study support previous research on 10-km running performance [41], whereby a mean reduction in time taken to complete 10-km (Pre = 3441 ± 327, Post = 3209 ± 271 s) was observed within the βA group only. However, it should be noted that the participants mean baseline 10-km time was a conservative 57.35 min, suggesting that results may have been confounded by the experience of the runners. Nonetheless, beyond this study there exists a lack of results during comparable (≥30- min) protocols. More specifically, the current split data support Saunders and colleague’s meta-analysis in suggesting that the strength of evidence supporting βA’s efficacy does not extend to longer duration (> 10-min) events [9] (despite the fact that many athletes use βA for endurance-based events). This same review noted that findings were potentially confounded by an absence of research investigating longer duration events [14] and the predominant use of incremental tests [9], two issues the current study attempted to circumvent. Therefore, whilst these data could be interpreted as providing preliminary support for βA’s potential to facilitate small scale improvements, when compared to a placebo there appears to be no significant benefit of consuming βA in the short term for longer duration aerobic exercise.
Regarding the anaerobic sprint data, no significant interaction effects were observed for any variables. This was unexpected as previously Suzuki et al. [42] noted a strong positive correlation between muscle carnosine concentration and Wingate performance. Likewise, rowers have exhibited greater muscle carnosine concentration and buffering capacity when compared with both marathoners and non-trained controls [43] . Therefore, it had been hypothesised that facilitating elevated muscle carnosine via βA consumption could have a significant effect on rowing sprint performance. One explanation for the lack of effect in the current study may have been the different exercise modality (rower vs cycle) employed. When cycling, the smaller muscle mass engaged may be more susceptible to localised muscular acidosis [44], providing a more optimal environment for βA’s effects to augment. This theory could help support previous research whereby mean power was significantly increased during a 30-s sprint following an endurance cycling event [10], proposing that βA may only facilitate ergogenic effects when there is an increased requirement to protect the ‘milieu interieur’ from homeostatic perturbations caused by supra-maximal levels of intracellular acidosis. However, whilst the current cohorts [La−]b were clearly elevated following each sprint bout, the mean [La−]b post time trial and during associated sprint efforts for βA1 were not significantly affected by βA consumption compared to PL, possibly suggesting an absence of meaningful carnosine facilitated buffering at the current dosage.
A novel aspect of this study was the inclusion of an alternate day dosing strategy (at a matched total dose). Previous research has suggested that the primary facilitator of muscle carnosine concentration is the total dose consumed, not factors such as baseline content or daily dose [29]. The current data does not support this hypothesis given the lack of significant findings in overall power, power to weight and distance covered at all time-points for βA2. Likewise, despite an isolated increase from T2-T3 in distance rowed during the first 10-min of the time trial, all other split data recorded support a lack of effectiveness when βA is not consumed daily. It is noteworthy, however, that although body composition (including fat-free mass) was not significantly different between groups, two individuals within βA2 reported body-fat percentages below 10% in contrast to other participants. Furthermore, fat-free mass ranged from 63.3–77.0 kg within βA2 (in contrast to 62.6–85.3 kg for βA1 and 60.3–85.0 kg for PL). Although unlikely, based on individual performance differences and average power (W and W·kg− 1), it is feasible that one explanation for a lack of significant findings with βA2 may have been influenced as a result of variances in lean muscle mass.
Other reasons for variation caused by dosing may reside in the pharmacokinetics of βA, with previous research [45] exhibiting a large variation between participants when given an equimolar amount (1400 mg) of the supplement. Alternatively, the consistency of daily consumption could potentially produce a more favourable environment for the bio-availability and subsequent augmentation of carnosine. Future research is required to investigate both the pharmacokinetics of βA beyond a single bolus and the potential mechanistic pathways that facilitate more optimal carnosine augmentation.
Limitations of this study include a lack of baseline and/or temporal measures of skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations. However, the dosing strategy utilised was equal to or greater than preceding work that has quantified muscle carnosine content [2, 46]. Furthermore, whilst [La−]b, RPE and HR were recorded throughout the test, blood pH was not. Subsequently, it must be conceded that the capacity to assess or infer whether effects were associated with carnosine directed (pH) buffering are limited. Additionally, due to a commonly reported side effect of βA (paraesthesia [1]), participants within either experimental arm of this trial may have become aware they were consuming the supplement. However, instructions to consume small (800 mg) individual doses, with food and regular verbal questioning at each visit indicated this was highly unlikely, with no cases of paraesthesia being reported. Future research should adopt dosing protocols that deliver βA in a sustained-release (SR) formula which may negate this issue [47, 48].
Beyond the delivery method of βA, previous research demonstrated that at an average daily dose of 5.2 g·day− 1 for four-weeks is not sufficient to maximise muscle carnosine content [3]. More recently this claim has been supported by research that supplied participants with 6.4 g·day− 1 of βA each day for 24 weeks, observing gene expression, muscle carnosine content and cycling capacity (CCT110%) [49]. Interestingly, this study’s primary observations was that muscle carnosine increased in the experimental group at all time-points with no change in PL, thus, investigations into the effects of higher dose (> 4 g·day− 1 [14]) or duration (24+ weeks) interventions with βA during endurance events are merited. Finally, whilst βA may provide some ergogenic influence in young, well-trained athletes, its effects within individuals who have reduced carnosine content (untrained, vegan/vegetarian or master’s athletes) [31] may be worthwhile, due to potentially amplified effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regardless of dose strategy, when compared to placebo, βA does not enhance sustained aerobic performance or subsequent high intensity efforts. However, the within-group finding that daily βA use increased 30-min rowing time trial performance warrants further investigation. The inclusion of higher dosing strategies (> 2.4 g·day− 1) for longer periods (> 28 days) should also be considered.
Abbreviations
- [La−]b :
-
Blood lactate
- P:W:
-
power to weight ratio
- SR:
-
Sustained release
- βA:
-
Beta-alanine
- βA1:
-
Beta-alanine daily intervention strategy
- βA2:
-
Beta-alanine alternate day strategy
References
Harris RC, Tallon M, Dunnett M, Boobis L, Coakley J, Kim HJ, et al. The absorption of orally supplied β-alanine and its effect on muscle carnosine synthesis in human vastus lateralis. Amino Acids. 2006;30:279–89.
Stellingwerff T, Anwander H, Egger A, Buehler T, Kreis R, Decombaz J, et al. Effect of two β-alanine dosing protocols on muscle carnosine synthesis and washout. Amino Acids. 2012;42(6):2461–72.
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, et al. Influence of β-alanine supplementation on skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations and high intensity cycling capacity. Amino Acids. 2007;32(2):225–33.
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, et al. β-Alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinters. J Appl Physiol. 2007;103(5):1736–43.
Sale C, Saunders B, Harris RC. Effect of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine concentrations and exercise performance. Amino Acids. 2010;39(2):321–33.
Smith EB. The buffering of muscle in rigor; protein, phosphate and carnosine. J Physiol. 1938;92(3):336–43.
Tallon MJ, Harris RC, Boobis LH, Fallowfield JL, Wise JA. The carnosine content of vastus lateralis is elevated in resistance-trained bodybuilders. J Strength Cond Res. 2005;19(4):725–9.
Quinn PJ, Boldyrev AA, Formazuyk VE. Carnosine: its properties, functions and potential therapeutic applications. Mol Asp Med. 1992;13(5):379–444.
Saunders B, Elliott-Sale K, Artioli GG, Swinton PA, Dolan E, Roschel H, et al. β-Alanine supplementation to improve exercise capacity and performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2016;51(8):658.
Van Thienen R, Van Proeyen K, Vanden Eynde B, Puype J, Lefere T, Hespel P. Beta-alanine improves sprint performance in endurance cycling. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(4):898–903.
de Andrade Kratz C, de Salles Painelli V, de Andrade Nemezio KM, da Silva RP, Franchini E, Zagatto AM, et al. Beta-alanine supplementation enhances judo-related performance in highly-trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;20(4):403–8.
Ducker KJ, Dawson B, Wallman KE. Effect of beta-alanine supplementation on 800-m running performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2013;23(6):554–61.
Ducker KJ, Dawson B, Wallman KE. Effect of Beta-alanine supplementation on 2,000-m rowing-ergometer performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2013;23(4):336–43.
Trexler ET, Smith-Ryan AE, Stout JR, Hoffman JR, Wilborn CD, Sale C, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Beta-alanine. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015;12(1):1–14.
Seiler S. What is best practice for training intensity and duration distribution in endurance athletes? Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2010;5(3):276–91.
Steinacker JM, Lormes W, Lehmann M, Altenburg D. Training of rowers before world championships. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30(7):1158–63.
Fiskerstrand Å, Seiler KS. Training and performance characteristics among Norwegian international rowers 1970–2001. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2004;14(5):303–10.
Arne G, Stephen S, Eike E. Training methods and intensity distribution of young world-class rowers. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2009;4(4):448–60.
Baguet A, Bourgois J, Vanhee L, Achten E, Derave W. Important role of muscle carnosine in rowing performance. J Appl Physiol. 2010;109(4):1096–101.
Abe H. Role of histidine-related compounds as intracellular proton buffering constituents in vertebrate muscle. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2000;65(7):757–65.
Hobson RM, Harris RC, Martin D, Smith P, Macklin B, Gualano B, et al. Effect of beta-alanine with and without sodium bicarbonate on 2,000-m rowing performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2013;23(5):480–7.
Shephard RJ. Science and medicine of rowing: a review. J Sports Sci. 1998;16(7):603–20.
Stellingwerff T, Maughan RJ, Burke LM. Nutrition for power sports: middle-distance running, track cycling, rowing, canoeing/kayaking, and swimming. J Sports Sci. 2011;29(sup1):S79–89.
Dutka TL, Lamboley CR, McKenna MJ, Murphy RM, Lamb GD. Effects of carnosine on contractile apparatus Ca2+ sensitivity and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release in human skeletal muscle fibers. J Appl Physiol. 2011;112(5):728–36.
Boldyrev AA, Aldini G, Derave W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(4):1803–45.
Kohen R, Yamamoto Y, Cundy KC, Ames BN. Antioxidant activity of carnosine, homocarnosine, and anserine present in muscle and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(9):3175–9.
Church DD, Hoffman JR, Varanoske AN, Wang R, Baker KM, La Monica MB, et al. Comparison of two β-alanine dosing protocols on muscle carnosine elevations. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017;36(8):608–16.
Currell K. Ergogenic aids. In: Hopker J, Jobson S, editors. Performance cycling: the science of success. London: A&C Black; 2012. p. 180–1.
Stellingwerff T, Decombaz J, Harris RC, Boesch C. Optimizing human in vivo dosing and delivery of β-alanine supplements for muscle carnosine synthesis. Amino Acids. 2012;43(1):57–65.
Kelly VG, Leveritt MD, Brennan CT, Slater GJ, Jenkins DG. Prevalence, knowledge and attitudes relating to β-alanine use among professional footballers. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(1):12–6.
Everaert I, Mooyaart A, Baguet A, Zutinic A, Baelde H, Achten E, et al. Vegetarianism, female gender and increasing age, but not CNDP1 genotype, are associated with reduced muscle carnosine levels in humans. Amino Acids. 2011;40(4):1221–9.
Baguet A, Reyngoudt H, Pottier A, Everaert I, Callens S, Achten E, et al. Carnosine loading and washout in human skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol. 2009;106(3):837–42.
Derave W, Everaert I, Beeckman S, Baguet A. Muscle carnosine metabolism and β-alanine supplementation in relation to exercise and training. Sports Med. 2010;40(3):247–63.
Bassett DR, Howley ET, Thompson DL, King GA, Strath SJ, McLaughlin JE, et al. Validity of inspiratory and expiratory methods of measuring gas exchange with a computerized system. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91(1):218–24.
K C, Jeukendrup AE. Validity, reliability and sensitivity of measures of sporting performance. Sports Med. 2008;38(4):297–316.
Borg G. Ratings of perceived exertion and heart rates during short term cycle exercise and their use in a new strength test. Int J Sports Med. 1982;3(3):153–8.
Kendrick IP, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Kim CK, Dang VH, Lam TQ, et al. The effects of 10 weeks of resistance training combined with β-alanine supplementation on whole body strength, force production, muscular endurance and body composition. Amino Acids. 2008;34(4):547–54.
Kendrick IP, Kim HJ, Harris RC, Kim CK, Dang VH, Lam TQ, et al. The effect of 4 weeks β-alanine supplementation and isokinetic training on carnosine concentrations in type I and II human skeletal muscle fibres. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009;106(1):131–8.
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika. 1965;52(3/4):591–611.
Kerksick CM, Wilborn CD, Roberts MD, Smith-Ryan A, Kleiner SM, Jäger R, et al. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: research & recommendations. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018;15(1):38.
Santana JO, Freitas MC, dos Santos DM, Rossi FE, Lira FS, Neto R, et al. Beta-alanine supplementation improved 10-km running time trial in physically active adults. Frontiers Physiol. 2018;9:1105.
Suzuki Y, Ito O, Mukai N, Takahashi H, Takamatsu K. High level of skeletal muscle carnosine contributes to the latter half of exercise performance during 30-s maximal cycle ergometer sprinting. Jpn J Physiol. 2002;52(2):199–205.
Parkhouse WS, McKenzie DC, Hochachka PW, Ovalle WK. Buffering capacity of deproteinized human vastus lateralis muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1985;58(1):14–7.
Robertson RJ, Falkel JE, Drash AL, Swank AM, Metz KF, Spungen SA, et al. Effect of induced alkalosis on physical work capacity during arm and leg exercise. Ergonomics. 1987;30(1):19–31.
Stautemas J, Everaert I, Lefevere FB, Derave W. Pharmacokinetics of β-alanine using different dosing strategies. Frontiers Nutr. 2018;5:70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6107792/.
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, et al. The effect of beta-alanine supplementation on neuromuscular fatigue in elderly (55–92 years): a double-blind randomized study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(1):21.
Décombaz J, Beaumont M, Vuichoud J, Bouisset F. Stellingwerff. Effect of slow-release β-alanine tablets on absorption kinetics and paresthesia. Amino Acids. 2012;43(1):67–76.
Varanoske AN, Hoffman JR, Church DD, Coker NA, Baker KM, Dodd SJ, et al. Comparison of sustained-release and rapid-release β-alanine formulations on changes in skeletal muscle carnosine and histidine content and isometric performance following a muscle-damaging protocol. Amino Acids. 2018:1–2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30003336. Epub ahead of print.
Saunders B, de Salles Painelli V, De Oliveira LF, da Eira Silva V, Da Silva RP, Riani L, et al. Twenty-four weeks of β-alanine supplementation on carnosine content, related genes, and exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(5):896–906.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge support from Bulk Powders Ltd. for independent provision of beta-alanine for this study.
Funding
There was no external funding for this study. However, local funding support was provided by the Open Access Publishing Fund, Anglia Ruskin University.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in the study. J.R and L.B conceived and designed the study; L.B. was centrally involved with data collection; data were analysed by L.B and J.R with support from L.S; J.R and L.B. constructed the manuscript. All authors reviewed the paper and approved the final version prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Faculty of Science and Technology Ethics Committee, Anglia Ruskin University (FST/FREP/15/591).Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
As part of the written informed consent procedure, all participants were duly made aware (as part of both the study briefing and information sheet) that the study results may be published. As such, consent for publication was included as part of this process.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Beasley, L., Smith, L., Antonio, J. et al. The effect of two β-alanine dosing strategies on 30-minute rowing performance: a randomized, controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 15, 59 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3