Abstract
Background
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is an inherited immunodeficiency disease caused by the defect of NADPH oxidase. Mutations in CYBB or CYBA gene may result in membrane subunits, gp91phox or p22phox, expression failure respectively and NADPH oxidase deficiency. Previous study showed that three variants, c.214 T > C (rs4673), c.521 T > C (rs1049254) and c.*24G > A (rs1049255), in CYBA gene form a haplotype, which are associated with decreased reactive oxygen species generation. The study aims to confirm the three above mentioned variants are benign and report a novel mutation in CYBB gene.
Methods
A patient with CGD and his family members were enrolled in the study. NADPH oxidase activity and gp91phox protein expression of neutrophils were analyzed by flow cytometry. Direct sequencing was used to detect CYBB and CYBA gene mutations.
Results
The patient was diagnosed with CGD according to clinical and immune phenotype. The case has a novel homozygous mutation in CYBB gene and the above mentioned three variants in CYBA gene. The mutation in CYBB gene was confirmed to be pathogenic, and the three variants in CYBA gene to be benign.
Conclusions
The study not only reported a novel mutation in CYBB, which results in CGD, but also confirmed the above mentioned three variants in CYBA are benign.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is an inherited immunodeficiency disease caused by the defect of NADPH oxidase [1]. There are seven NADPH oxidase isoforms, NADPH oxidase 1-5, DUOX1 and DUOX2, encoded by NCF4, NCF1, NCF2, CYBB and CYBA respectively [2, 3]. Mutations in CYBB gene, encoding the gp91phox subunit, result in X-linked CGD that affects the majority of CGD patients (~70%) [4]. As expected from the genetics, the overwhelming majority of CGD patients are males. Protein p22phox was discovered as the membrane subunit associated with NADPH oxidase 2, encoded by CYBA [5, 6] and more than 240 polymorphisms in the CYBA gene have been reported in dbSNP [7]. Some polymorphisms of the CYBA gene cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation failure and susceptibility to infection and autoinflammation, referred to autosomal CGD [8, 9].
Bedard et al. used Epstein-Barr virus transformed B lymphocytes from 50 healthy unrelated individuals to analyze their CYBA mRNA sequence and NADPH oxidase 2 dependent ROS generation [10]. Seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified, yielding 11 distinct haplotypes which were grouped into seven haplogroups. In the study, a haplogroup containing all three major SNPs (c.214 T > C (rs4673), c.521 T > C (rs1049254), c.*24G > A (rs1049255)) in the CYBA gene showed a significant p22phox deficiency and markedly reduced ROS generation compared to other haplogroups [10].
In our study, we found a CGD patient with a novel homozygous mutation in CYBB gene and the above mentioned three variants in CYBA gene. The other family members of the patient, who have no CGD, also have the same three variants in CYBA gene.
Methods
Patient
The patient, a boy from a nonconsanguineous marriage, was referred to our hospital at 3 months of age. He had pneumonia and diarrhea when he was 20 days old, and then perianal abscess occurred. He received antibiotics and supportive therapy for 22 days, and discharged after condition improved. Shortly after discharge, he had fever again. His condition had no improvement after treatment in local hospital. Then, he was transferred to our hospital. Physical examination showed cervical and inguinal lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and perianal abscess. His father, mother, sister and other relatives all have no recurrent infection history. The family tree is showed in Fig. 1. All of the family members were detected.
Neutrophil respiratory burst functional assays
The respiratory burst of neutrophils was assessed by hydrogen peroxide production using dihydrorhodamine oxidation (DHR) assay [11]. After stimulation with Phorbol-12-myrismte-14-acetate (PMA), neutrophils were immediately analyzed by using a FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer (Becton Dickinson, USA). The comparison was based on a stimulation index (SI), which was defined as mean channel fluorescence intensity of PMA-stimulated neutrophils over mean channel fluorescence intensity of unstimulated neutrophils [12].
Detection of Cytochrome b558 protein
The presence of flavocytochrome b558 in neutrophils membrane was detected by Flow Cytometry using the monoclonal antibody (mAb) 7D5 (murine IgG1), provided by Toshio Miyawaki (Japan). In brief, neutrophils were stained with mAb 7D5 followed by fluorescent isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-mouse antibody. The stained neutrophils were run on a FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer (Becton Dickinson, USA) [11].
CYBB and CYBA gene sequencing
Genomic DNA was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells using the RelaxGene Blood DNA System (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of CYBB, CYBA was performed using synthetic oligonucleotide primers for each exon. After an initial denaturation for 5 min at 95 °C, 35 cycles of amplification were performed as follows: 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 40 s. Final extension was performed at 72 °C for 7 min. PCR products were purified by Performa DTR Gel Filtration Cartridges and directly sequenced by ABI Prism BigDye terminators. Both strands were sequenced.
Results
Clinical characteristics
After hospitalization, the boy received antibiotics therapy. The chest CT scan showed pneumonia and pulmonary consolidation (Fig. 2). According to his clinical characteristics, we considered the boy might have CGD. So we did some laboratory test to check it. Finally, the diagnosis of CGD was confirmed by laboratory test. And then, we treated the boy with interferon-gamma, in addition to antibiotics. Diarrhea and pneumonia were controlled well. Until now, the boy is 2 years old and in good clinical condition.
DHR analysis
The patient’s neutrophils were unable to produce superoxide after PMA stimulation. His mother’s and sister’s neutrophils showed a bimodal response pattern to PMA stimulation, superoxide production was higher than that in the patient, but lower than normal. His father and other relatives had normal neutrophil respiratory burst function (Fig. 3), consistent with healthy control. The results indicated that the patient has CGD and the mother and sister are carriers. To further confirm it, we did associated protein detection and gene analysis.
Respiratory burst of neutrophils. Hydrogen peroxide generation in neutrophils measured by dihydrorhodamine oxidation (DHR) analysis with Flow Cytometry. a the patient. b the patient’s sister. c the patient’s mother. d the patient’s father. e the patient’s paternal aunt. f the patient’s maternal uncle. g the patient’s paternal grandmother. h the patient’s maternal grandfather
Cytochrome b558 expressions
Protein expressions closely resembled the DHR assay pattern. The patient’s flavocytochrome b558 was not expressed, suggesting a complete or near complete absence of gp91phox or p22phox. His mother and sister showed a bimodal curve, indicating partial protein expression. His father and other relatives, who have normal SI, showed normal expression of flavocytochrome b558 (Fig. 4).
Gene sequencing
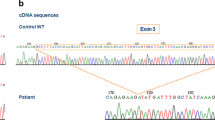
Analysis of CYBB and CYBA genes was done. With respect to the reference sequence, the patient’s CYBA gene contains the above mentioned three variants, c.214 T > C, c.521 T > C, and c.*24G > A, and all the three variants are homozygous, as well as his father and sister. His mother has two homozygous SNPs, c.214 T > C and c.521 T > C, and one heterozygous mutation, c.*24G > A. Other relatives, including his maternal grandfather, his paternal aunt and grandmother all have two homozygous mutations and one heterozygous mutation. Besides, his maternal uncle has homozygous c.214 T > C mutation and heterozygous c.521 T > C mutation, no c.*24G > A mutation (Fig. 5). As to the CYBB gene, the patient has a novel homozygous mutation, c.141 + 5G > C, his mother and sister have heterozygous mutations at the same site and his father as well as all other relatives have normal CYBB gene (Fig. 6).
Gene sequencing of CYBB. The patient and his sister and mother have c. 141 + 5G > C mutation in CYBB gene. The other relatives are normal. Arrows indicate the mutation points. a the patient. b the patient’s sister. c the patient’s mother. d the patient’s father. e the patient’s paternal aunt. f the patient’s maternal uncle. g the patient’s paternal grandmother. h the patient’s maternal grandfather
Discussion
CGD is an uncommon inherited immunodeficiency occurring approximately between 1 in 200,000 and 1 in 250,000 live births [4]. CGD patients always suffer from recurrent bacterial and fungal infections including involvement of lung, lymph nodes, skin and gastrointestinal tract [13]. The X-linked forms are generally more prevalent in the world; about two-thirds of CGD patients show an X-linked inheritance, which is caused by mutations in the CYBB gene [14].
In this study, we suspected that the patient suffered CGD according to his clinical characteristics. The diagnosis of CGD was confirmed by defective neutrophil respiratory burst function and complete absence of flavocytochrome b558 expression. CYBB and CYBA gene sequencing was performed. We found a homozygous mutation, c.141 + 5G > C, in CYBB gene in the patient, and the same heterozygous mutation in his mother and sister. The CYBB gene of patient’s father and other relatives were normal. Two mutations at the same site were reported previously [15, 16]. They are c.141 + 5G > A and c.141 + 5G > T, respectively. They are not the same mutation as the mutation in our patient. The mutation we found is novel.
Interestingly, we found three variants (c.214 T > C (rs4673), c.521 T > C (rs1049254), c.*24G > A (rs1049255)) in CYBA gene in the patient. All the three variants are homozygous. His father and sister have exactly the same variants as the patient. Other relatives we detected all have these three SNPs, two sites are homozygous and the other one is heterozygous with the exception of his maternal uncle with one normal site. Because the patient’s father has the normal respiratory burst of neutrophils, the three variants should be benign. Previous study showed that there is a significant defect in ROS generation when these three SNPs form a haplotype [10]. Since lymphocytes are not the natural site for the respiratory burst, EBV transformed lymphocytes model with the three variants maybe have limitations and cannot reflect real state. Overall, the mutation in CYBB (c.141 + 5G > C) should be pathogenic from a combined analysis of DHR, protein expression and gene results.
Conclusions
In summary, our study not only reported a novel mutation in CYBB, which cause CGD, but also confirmed the above mentioned three variants in CYBA are benign.
Abbreviations
- CGD:
-
Chronic granulomatous disease
- DHR:
-
Dihydrorhodamine oxidation
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SI:
-
Stimulation index
- SNPs:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
References
Segal BH, Leto TL, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM. Genetic, biochemical, and clinical features of chronic granulomatous disease. Medcine (Baltimore). 2000;79:170–200.
Matute JD, Arias AA, Wright NA, Wrobel I, Waterhouse CC, Li XJ, Marchal CC, Stull ND, Lewis DB, Steele M, Kellner JD, Yu W, Meroueh SO, Nauseef WM, Dinauer MC. A new genetic subgroup of chronic granulomatous disease with autosomal recessive mutations in p40 phox and selective defects in neutrophil NADPH oxidase activity. Blood. 2009;114:3309–15.
Tarazona-Santos E, Machado M, Magalhães WC, Chen R, Lyon F, Burdett L, Crenshaw A, Fabbri C, Pereira L, Pinto L, Redondo RA, Sestanovich B, Yeager M, Chanock SJ. Evolutionary dynamics of the human NADPH Oxidase genes CYBB, CYBA, NCF2, and NCF4: functional implications. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2157–67.
Van den Berg JM, van Koppen E, Ahlin A, Belohradsky BH, Bernatowska E, Corbeel L, Español T, Fischer A, Kurenko-Deptuch M, Mouy R, Petropoulou T, Roesler J, Seger R, Stasia MJ, Valerius NH, Weening RS, Wolach B, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Chronic granulomatous disease: the European experience. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5234.
Dinauer MC, Orkin SH, Brown R, Jesaitis AJ, Parkos CA. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic Granulomatous-disease locus is a component of the Neutrophil Cytochrome-B complex. Nature. 1987;327:717–20.
Dinauer MC, Pierce EA, Bruns GA, Curnutte JT, Orkin SH. Human Neutrophil Cytochrome-B light chain (p22-phox) - gene structure, chromosomal location, and mutations in Cytochrome-negative Autosomal recessive chronic Granulomatous-disease. J Clin Invest. 1990;86:1729–37.
Lepetsos P, Pampanos A, Lallos S, Kanavakis E, Korres D, Papavassiliou AG, Efstathopoulos N. Association of NADPH oxidase p22phox gene C242T, A640G and-930A/G polymorphisms with primary knee osteoarthritis in the Greek population. Mol Biol Reports. 2013;40:5491–9.
Berendes H, Bridges RA, Good RA. A fatal granulomatosus of childhood: the clinical study of a new syndrome. Minn Med. 1957;40:309–12.
Amulic B, Cazalet C, Hayes GL, Metzler KD, Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil function: from mechanisms to disease. Ann Rev of Immunol. 2012;30:459–89.
Bedard K, Attar H, Bonnefont J, Jaquet V, Borel C, Plastre O, Stasia MJ, Antonarakis SE, Krause KH. Three common polymorphisms in the CYBA gene form a haplotype associated with decreased ROS generation. Hum Mutat. 2009;30:1123–33.
Sun J, Wang Y, Liu D, Yu Y, Wang J, Ying W, Wang X. Prenatal diagnosis of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by percutaneous umbilical blood sampling. Scand J Immunol. 2012;76:512–8.
Vowells SJ, Sekhsaria S, Malech HL, Shalit M, Fleisher TA. Flow cytometric analysis of the granulocyte respiratory burst - a comparison study of fluorescent-probes. J Immunol Methods. 1995;178:89–97.
Mahdaviani SA, Mohajerani SA, Rezaei N, Casanova JL, Mansouri SD, Velayati AA. Pulmonary manifestations of chronic granulomatous disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:153–60.
Fattahi F, Badalzadeh M, Sedighipour L, Movahedi M, Fazlollahi MR, Mansouri SD, Khotaei GT, Bemanian MH, Behmanesh F, Hamidieh AA, Bazargan N, Mamishi S, Zandieh F, Chavoshzadeh Z, Mohammadzadeh I, Mahdaviani SA, Tabatabaei SA, Kalantari N, Tajik S, Maddah M, Pourpak Z, Moin M. Inheritance pattern and clinical aspects of 93 Iranian patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31:792–801.
Roesler J, Heyden S, Burdelski M, Schäfer H, Kreth HW, Lehmann R, Paul D, Marzahn J, Gahr M, Rösen-Wolff A. Uncommon missense and splice mutations and resulting biochemical phenotypes in German patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Exp Hematol. 1999;27:505–11.
Di Matteo G, Giordani L, Finocchi A, Ventura A, Chiriaco M, Blancato J, Sinibaldi C, Plebani A, Soresina A, Pignata C, Dellepiane RM, Trizzino A, Cossu F, Rondelli R, Rossi P, De Mattia D, Martire B, IPINET (Italian Network for Primary Immunodeficiencies). Molecular characterization of a large cohort of patients with chronic Granulomatous disease and identification of novel CYBB mutations: an Italian multicenter study. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:1935–41.
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to the patient and their relatives.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471482, 81373221), and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14411965400).
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author’s contributions
JS and MW carried out the molecular genetic studies, data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. YW, DL and WY participated in the sample collection, data analysis and manuscript revision. JS and XW designed the study and performed the manuscript writing. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Children’s Hospital of Fudan University. The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. The patient’s parents gave written informed consent for this study, who on behalf of themselves, their children and their relatives.
Consent for publication
I confirm that I have obtained consent to publish from the participant (or legal parent or guardian for children) to report individual patient data.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Wen, M., Wang, Y. et al. The three CYBA variants (rs4673, rs1049254 and rs1049255) are benign: new evidence from a patient with CGD. BMC Med Genet 18, 127 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-017-0492-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-017-0492-6