Abstract
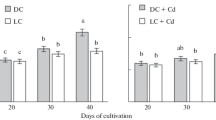
The effects of cadmium (6.3 × 10−5 M or 10.6 × 10−5 M) on the growth of tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) callus cultures derived from leaves, stems, and roots and on the formation, in these cultures, of phenolic compounds, including flavans and lignin, which are characteristic of the tea plant, were investigated. In the calli derived from leaves and stems, cadmium treatment decreased the biomass increment, while in the calli derived from roots, growth characteristics remained at the control level. Under the effect of cadmium, the content of phenolic compounds, including flavans, in the leaf calli decreased, while in the stem and root calli, it either increased (at the cadmium concentration of 6.3 × 10−5 M), or was close to a control one (at the cadmium concentration of 10.6 × 10−5 M). The lignin content in the root and stem calli increased, but it did not change in the leaf calli. All this data demonstrate that the cadmium-induced changes in phenolic metabolism of the tea plant callus culture depended both on the cadmium concentration in the medium and on the origin of calli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanita di Toppi, L. and Gabbrielli, R., Response to Cadmium in Higher Plants, Environ. Exp. Bot., 1999, vol. 41, pp. 105–130.
Seregin, I.V. and Ivanov, V.B., Physiological Aspects of Cadmium and Lead Toxic Effects on Higher Plants, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2001, vol. 48, pp. 523–544.
Gadallah, M.A.A., Effect of Cd and Kinetin on Chlorophyll Content, Saccharides and Dry Matter Accumulation in Sunflower Plants, Biol. Plant., 1995, vol. 37, pp. 233–240.
Sandalio, L.M., Dalurzo, N.C., and Gomez, M., Cadmium-Induced Changes in the Growth and Oxidative Metabolism of Pea Plants, J. Exp. Bot., 2001, vol. 52, pp. 2115–2126.
Baryla, A., Carrier, P., and Franck, F., Leaf Chlorosis in Oilseed Rape Plants (Brassica napus) Grown on Cadmium-Polluted Soil: Causes and Consequences for Photosynthesis and Growth, Planta, 2001, vol. 212, pp. 696–709.
Zhang, Y. and Xiao, H., Antagonistic Effect of Cadmium-Induced Chromosomal Aberration and Micronuclei in Root Cells of Hordeum vulgare, Mutat. Res., 1998, vol. 420, pp. 1–6.
Kuthanova, A., Gemperlova, L., Zelenkova, S., Eder, J., Machackova, I., Opatrny, Z., and Cvikrova, M., Cytological Changes and Alterations in Polyamine Contents Induced by Cadmium in Tobacco BY-2 Cells, Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2004, vol. 42, pp. 149–156.
Dixit, V., Pandey, V., and Shyam, R., Differential Antioxidative Responses to Cadmium in Roots and Leaves of Pea (Pisum sativum L., cv. Azad.), J. Exp. Bot., 2001, vol. 52, pp. 1101–1109.
Ferreira, R., Fornazier, R., and Vitoria, A., Changes in Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Soybean under Cadmium Stress, J. Plant Nutr., 2002, vol. 25, pp. 327–342.
Maier, T., Yu, C., Kullertz, G., and Clemens, S., Localization and Functional Characterization on Metal-Binding Sites in Phytochelatin Synthases, Planta, 2003, vol. 218, pp. 300–308.
Vassilev, A., Lidon, F., Scotti, P., Graca, M., and Yordanov, I., Cadmium-Induced Changes in Chloroplast and Photosystem Activities in Barley Plants, Biol. Plant., 2004, vol. 48, pp. 153–156.
Lee, S., Moon, J.S., Ko, T.-S., Petros, D., Goldsbrough, P.B., and Korban, S.S., Overexpression of Arabidopsis Phytochelatin Synthase Paradoxically Leads to Hypersensitivity to Cadmium Stress, Plant Physiol., 2003, vol. 131, pp. 656–663.
Kupper, H., Mijovilovich, A., Meyer-Klaucke, W., and Kroneck, P.M.H., Tissue-and Age-Dependent Differences in the Complexation of Cadmium and Zinc in the Cadmium/Zinc Hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges Ecotype) Revealed by X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy, Plant Physiol., 2004, vol. 134, pp. 748–757.
Dunbar, K.R., McLaughlin, M.J., and Reid, R.J., The Uptake and Partitioning of Cadmium in Two Cultivars of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), J. Exp. Bot., 2003, vol. 54, pp. 349–354.
Zaprometov, M.N., Fenol’nye soedineniya (Phenolic Compounds), Moscow: Nauka, 1993.
Rice-Evans, C.A., Miller, N.J., and Paganga, G., Antioxidant Properties of Phenolic Compounds, Trends Plant Sci., 1997, vol. 2, pp. 152–159.
Dixon, R.A. and Paiva, N.L., Stress-Induced Phenylpropanoid Metabolism, Plant Cell, 1995, vol. 7, pp. 1085–1097.
Butenko, R.G., Biologiya kletok vysshikh rastenii In Vitro i biotekhnologii na ikh osnove (Biology of Cultured Higher Plant Cells and Their Use in Biotechnology), Moscow: FBK, 1999.
Stafford, A., Natural Products and Metabolites from Plants and Plant Tissue Cultures, Plant Cell and Tissue Culture, Stafford, A. and Warren, G., Eds., Milton Keynes: Open Univ.., 1991, pp. 124–162.
Zaprometov, M.N., The Formation of Phenolic Compounds in Plant Cell and Tissue Cultures and the Possibility of Its Regulation, Adv. Cell Cult., 1989, vol. 7, pp. 201–260.
Zagoskina, N.V., Dubravina, G.A., Alyavina, A.K., and Goncharuk, E.A., Effect of Ultraviolet (UV-B) Radiation on the Formation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in Tea Plant Callus Cultures, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2003, vol. 50, pp. 270–275.
Zaprometov, M.N., Zagoskina, N.V., Strekova, V.Yu., and Morozova, G.A., Phenolic Compound Formation and Differentiation in Tea Plant Callus Cultures, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1979, vol. 26, pp. 485–491.
Koretskaya, T.F. and Zaprometov, M.N., Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) Callus Cultures as the Model for Investigation of Conditions for Phenolic Compound Formation, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1975, vol. 22, pp. 282–288.
Zaprometov, M.N., Phenolic Compounds and the Methods for Their Investigation, Biokhimicheskie metody v fiziologii rastenii (Biochemical Methods in Plant Physiology), Pavlinova, O.A., Ed., Moscow: Nauka, 1971, pp. 185–197.
Carceller, M., Davey, M.R., Fowler, M.V., and Street, H.E., The Influence of Sucrose, 2,4-D and Kinetin on the Growth, Fine Structure and Lignin Content of Cultured Sycamore Cells, Protoplasma, 1971, vol. 73, pp. 337–345.
Zaprometov, M.N., Biokhimiya katekhinov (Biochemistry of Catechines), Moscow: Nauka, 1964.
Dubravina, G.A., Zaitseva, S.M., and Zagoskina, N.V., Changes in Formation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in the Tissues of European and Canadian Yew during Dedifferentiation In Vitro, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 672–678.
Zhao, H.J. and Zou, Q., Protective Effects of Exogenous Antioxidants and Phenolic Compounds on Photosynthesis of Wheat Leaves under High Irradiance and Oxidative Stress, Photosynthetica, 2002, vol. 40, pp. 523–527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.V. Zagoskina, E.A. Goncharuk, A.K. Alyavina, 2007, published in Fiziologiya Rastenii, 2007, Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. 267–274.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zagoskina, N.V., Goncharuk, E.A. & Alyavina, A.K. Effect of cadmium on the phenolic compounds formation in the callus cultures derived from various organs of the tea plant. Russ J Plant Physiol 54, 237–243 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443707020124
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443707020124