Abstract
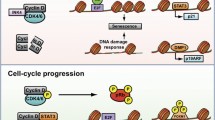
Deregulation of the G1/G0 phase of the cell cycle can lead to cancer. During G1, most cells commit alternatively to DNA replication and division, or to cell-cycle exit and differentiation. The anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) activated by Cdh1 coordinately eliminates positive cell-cycle regulators as well as inhibitors of differentiation, thereby coupling cell-cycle exit and differentiation. Misregulation of Cdh1 thus has the potential to promote both cell-cycle re-entry and either perturbed differentiation or dedifferentiation. In addition, APC/CCdh1 is required to maintain genomic stability. As a result, loss of Cdh1 can contribute to tumorigenesis in the form of proliferation of poorly differentiated and genetically unstable cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J . (2004). The proteasome: a suitable antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 349–360.
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR . (2003). AURORA-A amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell 3: 51–62.
Araki M, Wharton RP, Tang Z, Yu H, Asano M . (2003). Degradation of origin recognition complex large subunit by the anaphase-promoting complex in Drosophila. EMBO J 22: 6115–6126.
Archambault V, Glover DM . (2009). Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 265–275.
Barr AR, Gergely F . (2007). Aurora-A: the maker and breaker of spindle poles. J Cell Sci 120: 2987–2996.
Bashir T, Dorrello NV, Amador V, Guardavaccaro D, Pagano M . (2004). Control of the SCF(Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase by the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase. Nature 428: 190–193.
Bassermann F, Frescas D, Guardavaccaro D, Busino L, Peschiaroli A, Pagano M . (2008). The Cdc14B-Cdh1-Plk1 axis controls the G2 DNA-damage-response checkpoint. Cell 134: 256–267.
Benmaamar R, Pagano M . (2005). Involvement of the SCF complex in the control of Cdh1 degradation in S-phase. Cell Cycle 4: 1230–1232.
Binne UK, Classon MK, Dick FA, Wei W, Rape M, Kaelin Jr WG et al. (2007). Retinoblastoma protein and anaphase-promoting complex physically interact and functionally cooperate during cell-cycle exit. Nat Cell Biol 9: 225–232.
Bloom J, Cross FR . (2007). Multiple levels of cyclin specificity in cell-cycle control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 149–160.
Carroll CW, Morgan DO . (2002). The Doc1 subunit is a processivity factor for the anaphase-promoting complex. Nat Cell Biol 4: 880–887.
Carter SL, Eklund AC, Kohane IS, Harris LN, Szallasi Z . (2006). A signature of chromosomal instability inferred from gene expression profiles predicts clinical outcome in multiple human cancers. Nat Genet 38: 1043–1048.
Castro A, Vigneron S, Bernis C, Labbe JC, Lorca T . (2003). Xkid is degraded in a D-box, KEN-box, and A-box-independent pathway. Mol Cell Biol 23: 4126–4138.
Castro A, Vigneron S, Bernis C, Labbe JC, Prigent C, Lorca T . (2002). The D-Box-activating domain (DAD) is a new proteolysis signal that stimulates the silent D-Box sequence of Aurora-A. EMBO Rep 3: 1209–1214.
Chaudhary J, Sadler-Riggleman I, Ague JM, Skinner MK . (2005). The helix-loop-helix inhibitor of differentiation (ID) proteins induce post-mitotic terminally differentiated Sertoli cells to re-enter the cell cycle and proliferate. Biol Reprod 72: 1205–1217.
Crasta K, Huang P, Morgan G, Winey M, Surana U . (2006). Cdk1 regulates centrosome separation by restraining proteolysis of microtubule-associated proteins. EMBO J 25: 2551–2563.
Crasta K, Lim HH, Giddings Jr TH, Winey M, Surana U . (2008). Inactivation of Cdh1 by synergistic action of Cdk1 and polo kinase is necessary for proper assembly of the mitotic spindle. Nat Cell Biol 10: 665–675.
Cross FR . (2003). Two redundant oscillatory mechanisms in the yeast cell cycle. Dev Cell 4: 741–752.
Cuende J, Moreno S, Bolanos JP, Almeida A . (2008). Retinoic acid downregulates Rae1 leading to APC (Cdh1) activation and neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y differentiation. Oncogene 27: 3339–3344.
Diffley JF . (2004). Regulation of early events in chromosome replication. Curr Biol 14: R778–R786.
Ekholm-Reed S, Mendez J, Tedesco D, Zetterberg A, Stillman B, Reed SI . (2004). Deregulation of cyclin E in human cells interferes with prereplication complex assembly. J Cell Biol 165: 789–800.
Engelbert D, Schnerch D, Baumgarten A, Wäsch R . (2008). The ubiquitin ligase APC(Cdh1) is required to maintain genome integrity in primary human cells. Oncogene 27: 907–917.
Enquist-Newman M, Sullivan M, Morgan DO . (2008). Modulation of the mitotic regulatory network by APC-dependent destruction of the Cdh1 inhibitor Acm1. Mol Cell 30: 437–446.
Ferrell Jr JE . (2002). Self-perpetuating states in signal transduction: positive feedback, double-negative feedback and bistability. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14: 140–148.
Floyd S, Pines J, Lindon C . (2008). APC/C Cdh1 targets aurora kinase to control reorganization of the mitotic spindle at anaphase. Curr Biol 18: 1649–1658.
Fujita T, Liu W, Doihara H, Date H, Wan Y . (2008a). Dissection of the APCCdh1-Skp2 cascade in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14: 1966–1975.
Fujita T, Liu W, Doihara H, Wan Y . (2008b). Regulation of Skp2-p27 axis by the Cdh1/anaphase-promoting complex pathway in colorectal tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol 173: 217–228.
Garcia-Higuera I, Manchado E, Dubus P, Canamero M, Mendez J, Moreno S et al. (2008). Genomic stability and tumour suppression by the APC/C cofactor Cdh1. Nat Cell Biol 10: 802–811.
Gieffers C, Peters BH, Kramer ER, Dotti CG, Peters JM . (1999). Expression of the CDH1-associated form of the anaphase-promoting complex in postmitotic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 11317–11322.
Glotzer M, Murray AW, Kirschner MW . (1991). Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature 349: 132–138.
Hayes MJ, Kimata Y, Wattam SL, Lindon C, Mao G, Yamano H et al. (2006). Early mitotic degradation of Nek2A depends on Cdc20-independent interaction with the APC/C. Nat Cell Biol 8: 607–614.
Hildebrandt ER, Hoyt MA . (2001). Cell cycle-dependent degradation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle motor Cin8p requires APC(Cdh1) and a bipartite destruction sequence. Mol Biol Cell 12: 3402–3416.
Hsu JY, Reimann JD, Sorensen CS, Lukas J, Jackson PK . (2002). E2F-dependent accumulation of hEmi1 regulates S phase entry by inhibiting APC(Cdh1). Nat Cell Biol 4: 358–366.
Jacobs H, Richter D, Venkatesh T, Lehner C . (2002). Completion of mitosis requires neither fzr/rap nor fzr2, a male germline-specific Drosophila Cdh1 homolog. Curr Biol 12: 1435–1441.
Jaquenoud M, van Drogen F, Peter M . (2002). Cell cycle-dependent nuclear export of Cdh1p may contribute to the inactivation of APC/C(Cdh1). EMBO J 21: 6515–6526.
Ji M, Li H, Suh HC, Klarmann KD, Yokota Y, Keller JR . (2008). Id2 intrinsically regulates lymphoid and erythroid development via interaction with different target proteins. Blood 112: 1068–1077.
Juang YL, Huang J, Peters JM, McLaughlin ME, Tai CY, Pellman D . (1997). APC-mediated proteolysis of Ase1 and the morphogenesis of the mitotic spindle. Science 275: 1311–1314.
Keppler A, Gendreizig S, Gronemeyer T, Pick H, Vogel H, Johnsson K . (2003). A general method for the covalent labeling of fusion proteins with small molecules in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 21: 86–89.
Konishi Y, Stegmuller J, Matsuda T, Bonni S, Bonni A . (2004). Cdh1-APC controls axonal growth and patterning in the mammalian brain. Science 303: 1026–1030.
Kramer E, Scheuringer N, Podtelejnikov AV, Mann M, Peters J . (2000). Mitotic regulation of the APC activator proteins CDC20 and CDH1. Mol Biol Cell 11: 1555–1569.
Lapenna S, Giordano A . (2009). Cell cycle kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8: 547–566.
Lasorella A, Stegmuller J, Guardavaccaro D, Liu G, Carro MS, Rothschild G et al. (2006). Degradation of Id2 by the anaphase-promoting complex couples cell cycle exit and axonal growth. Nature 442: 471–474.
Lassar AB, Thayer MJ, Overell RW, Weintraub H . (1989). Transformation by activated ras or fos prevents myogenesis by inhibiting expression of MyoD1. Cell 58: 659–667.
Lehman NL, Tibshirani R, Hsu JY, Natkunam Y, Harris BT, West RB et al. (2007). Oncogenic regulators and substrates of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome are frequently overexpressed in malignant tumors. Am J Pathol 170: 1793–1805.
Lengronne A, Schwob E . (2002). The yeast CDK inhibitor Sic1 prevents genomic instability by promoting replication origin licensing in late G1. Mol Cell 9: 1067–1078.
Li M, Shin YH, Hou L, Huang X, Wei Z, Klann E et al. (2008). The adaptor protein of the anaphase promoting complex Cdh1 is essential in maintaining replicative lifespan and in learning and memory. Nat Cell Biol 10: 1083–1089.
Li M, Zhang P . (2009). The function of APC/CCdh1 in cell cycle and beyond. Cell Div 4: 2.
Li W, Wu G, Wan Y . (2007). The dual effects of Cdh1/APC in myogenesis. FASEB J 21: 3606–3617.
Lindon C, Pines J . (2004). Ordered proteolysis in anaphase inactivates Plk1 to contribute to proper mitotic exit in human cells. J Cell Biol 164: 233–241.
Listovsky T, Oren YS, Yudkovsky Y, Mahbubani HM, Weiss AM, Lebendiker M et al. (2004). Mammalian Cdh1/Fzr mediates its own degradation. EMBO J 23: 1619–1626.
Littlepage LE, Ruderman JV . (2002). Identification of a new APC/C recognition domain, the A box, which is required for the Cdh1-dependent destruction of the kinase Aurora-A during mitotic exit. Genes Dev 16: 2274–2285.
Liu W, Wu G, Li W, Lobur D, Wan Y . (2007). Cdh1-anaphase-promoting complex targets Skp2 for destruction in transforming growth factor beta-induced growth inhibition. Mol Cell Biol 27: 2967–2979.
Lorca T, Castro A, Martinez AM, Vigneron S, Morin N, Sigrist S et al. (1998). Fizzy is required for activation of the APC/Cyclosome in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J 17: 3565–3575.
Lukas C, Sorensen CS, Kramer E, Santoni-Rugiu E, Lindeneg C, Peters JM et al. (1999). Accumulation of cyclin B1 requires E2F and cyclin-A-dependent rearrangement of the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature 401: 815–818.
Lwin T, Hazlehurst LA, Dessureault S, Lai R, Bai W, Sotomayor E et al. (2007). Cell adhesion induces p27Kip1-associated cell-cycle arrest through down-regulation of the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase pathway in mantle-cell and other non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas. Blood 110: 1631–1638.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M . (2009). Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9: 153–166.
McGarry TJ, Kirschner MW . (1998). Geminin, an inhibitor of DNA replication, is degraded during mitosis. Cell 93: 1043–1053.
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA . (2002). Aurora-A overexpression reveals tetraploidization as a major route to centrosome amplification in p53−/− cells. EMBO J 21: 483–492.
Passmore LA, McCormack EA, Au SW, Paul A, Willison KR, Harper JW et al. (2003). Doc1 mediates the activity of the anaphase-promoting complex by contributing to substrate recognition. EMBO J 22: 786–796.
Perk J, Iavarone A, Benezra R . (2005). Id family of helix-loop-helix proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 603–614.
Pesin JA, Orr-Weaver TL . (2008). Regulation of APC/C activators in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24: 475–499.
Peters JM . (2006). The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed to destroy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 644–656.
Pfleger CM, Kirschner MW . (2000). The KEN box: an APC recognition signal distinct from the D box targeted by Cdh1. Genes Dev 14: 655–665.
Rape M, Kirschner M . (2004). Autonomous regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex couples mitosis to S-phase entry. Nature 432: 588–595.
Rape M, Reddy SK, Kirschner MW . (2006). The processivity of multiubiquitination by the APC determines the order of substrate degradation. Cell 124: 89–103.
Reis A, Levasseur M, Chang HY, Elliott DJ, Jones KT . (2006). The CRY box: a second APCcdh1-dependent degron in mammalian cdc20. EMBO Rep 7: 1040–1045.
Ross KE, Cohen-Fix O . (2003). The role of Cdh1p in maintaining genomic stability in budding yeast. Genetics 165: 489–503.
Rudner A, Murray A . (2000). Phosphorylation by Cdc28 activates the Cdc20-dependent activity of the anaphase-promoting complex. J Cell Biol 149: 1377–1390.
Schwab M, Lutum AS, Seufert W . (1997). Yeast Hct1 is a regulator of Clb2 cyclin proteolysis. Cell 90: 683–693.
Shirayama M, Toth A, Galova M, Nasmyth K . (1999). APCCdc20 promotes exit from mitosis by destroying the anaphase inhibitor Pds1 and cyclin Clb5. Nature 402: 203–207.
Sigrist SJ, Lehner CF . (1997). Drosophila fizzy-related down-regulates mitotic cyclins and is required for cell proliferation arrest and entry into endocycles. Cell 90: 671–681.
Skotheim JM, Di Talia S, Siggia ED, Cross FR . (2008). Positive feedback of G1 cyclins ensures coherent cell cycle entry. Nature 454: 291–296.
Sorensen CS, Lukas C, Kramer ER, Peters JM, Bartek J, Lukas J . (2001). A conserved cyclin-binding domain determines functional interplay between anaphase-promoting complex-Cdh1 and cyclin A-Cdk2 during cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 21: 3692–3703.
Spellman PT, Sherlock G, Zhang MQ, Iyer VR, Anders K, Eisen MB et al. (1998). Comprehensive identification of cell cycle-regulated genes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by microarray hybridization. Mol Biol Cell 9: 3273–3297.
Stegmüller J, Huynh MA, Yuan Z, Konishi Y, Bonni A . (2008). TGFbeta-Smad2 signaling regulates the Cdh1-APC/SnoN pathway of axonal morphogenesis. J Neurosci 28: 1961–1969.
Stegmüller J, Konishi Y, Huynh MA, Yuan Z, Dibacco S, Bonni A . (2006). Cell-intrinsic regulation of axonal morphogenesis by the Cdh1-APC target SnoN. Neuron 50: 389–400.
Steigemann P, Wurzenberger C, Schmitz MH, Held M, Guizetti J, Maar S et al. (2009). Aurora B-mediated abscission checkpoint protects against tetraploidization. Cell 136: 473–484.
Stewart S, Fang G . (2005). Anaphase-promoting compley/cyclosome controls the stability of TPX2 during mitotic exit. Mol Cell Biol 25: 10516–10527.
Strebhardt K, Ullrich A . (2006). Targeting polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 321–330.
Stroschein SL, Bonni S, Wrana JL, Luo K . (2001). Smad3 recruits the anaphase-promoting complex for ubiquitination and degradation of SnoN. Genes Dev 15: 2822–2836.
Sudo T, Ota Y, Kotani S, Nakao M, Takami Y, Takeda S et al. (2001). Activation of Cdh1-dependent APC is required for G1 cell cycle arrest and DNA damage-induced G2 checkpoint in vertebrate cells. EMBO J 20: 6499–6508.
Suh HC, Leeanansaksiri W, Ji M, Klarmann KD, Renn K, Gooya J et al. (2008). Id1 immortalizes hematopoietic progenitors in vitro and promotes a myeloproliferative disease in vivo. Oncogene 27: 5612–5623.
Sullivan M, Morgan DO . (2007). A novel destruction sequence targets the meiotic regulator Spo13 for anaphase-promoting complex-dependent degradation in anaphase I. J Biol Chem 282: 19710–19715.
Takahashi C, Ewen ME . (2006). Genetic interaction between Rb and N-ras: differentiation control and metastasis. Cancer Res 66: 9345–9348.
Taylor S, Peters JM . (2008). Polo and Aurora kinases: lessons derived from chemical biology. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20: 77–84.
Vaziri C, Saxena S, Jeon Y, Lee C, Murata K, Machida Y et al. (2003). A p53-dependent checkpoint pathway prevents rereplication. Mol Cell 11: 997–1008.
Visintin R, Prinz S, Amon A . (1997). CDC20 and CDH1: a family of substrate-specific activators of APC-dependent proteolysis. Science 278: 460–463.
Wan Y, Liu X, Kirschner MW . (2001). The anaphase-promoting complex mediates TGF-beta signaling by targeting SnoN for destruction. Mol Cell 8: 1027–1039.
Wang CX, Fisk BC, Wadehra M, Su H, Braun J . (2000). Overexpression of murine fizzy-related (fzr) increases natural killer cell-mediated cell death and suppresses tumor growth. Blood 96: 259–263.
Wäsch R, Cross FR . (2002). APC-dependent proteolysis of the mitotic cyclin Clb2 is essential for mitotic exit. Nature 418: 556–562.
Wäsch R, Engelbert D . (2005). Anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteolysis of cell cycle regulators and genomic instability of cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 1–10.
Wei W, Ayad NG, Wan Y, Zhang GJ, Kirschner MW, Kaelin Jr WG . (2004). Degradation of the SCF component Skp2 in cell-cycle phase G1 by the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature 428: 194–198.
Wirth KG, Ricci R, Gimenez-Abian JF, Taghybeeglu S, Kudo NR, Jochum W et al. (2004). Loss of the anaphase-promoting complex in quiescent cells causes unscheduled hepatocyte proliferation. Genes Dev 18: 88–98.
Wu G, Glickstein S, Liu W, Fujita T, Li W, Yang Q et al. (2007). The anaphase-promoting complex coordinates initiation of lens differentiation. Mol Biol Cell 18: 1018–1029.
Yamano H, Gannon J, Mahbubani H, Hunt T . (2004). Cell cycle-regulated recognition of the destruction box of cyclin B by the APC/C in Xenopus egg extracts. Mol Cell 13: 137–147.
Yeong FM, Lim HH, Padmashree CG, Surana U . (2000). Exit from mitosis in budding yeast: biphasic inactivation of the Cdc28-Clb2 mitotic kinase and the role of Cdc20. Mol Cell 5: 501–511.
Zachariae W, Schwab M, Nasmyth K, Seufert W . (1998). Control of cyclin ubiquitination by CDK-regulated binding of Hct1 to the anaphase promoting complex. Science 282: 1721–1724.
Zhao WM, Fang G . (2005). Anillin is a substrate of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) that controls spatial contractility of myosin during late cytokinesis. J Biol Chem 280: 33516–33524.
Zhou Y, Ching YP, Chun AC, Jin DY . (2003). Nuclear localization of the cell cycle regulator CDH1 and its regulation by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 278: 12530–12536.
Zielke N, Querings S, Rottig C, Lehner C, Sprenger F . (2008). The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is required for rereplication control in endoreplication cycles. Genes Dev 22: 1690–1703.
Acknowledgements
We thank Andrea Schmidts for helping us with Figure 2 and Monika Engelhardt for critical reading of the paper. RW thanks Roland Mertelsmann for continuous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wäsch, R., Robbins, J. & Cross, F. The emerging role of APC/CCdh1 in controlling differentiation, genomic stability and tumor suppression. Oncogene 29, 1–10 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.325
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.325
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulated interaction of ID2 with the anaphase-promoting complex links progression through mitosis with reactivation of cell-type-specific transcription
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Efficient terminal erythroid differentiation requires the APC/C cofactor Cdh1 to limit replicative stress in erythroblasts
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Phosphorylation of the Anaphase Promoting Complex activator FZR1/CDH1 is required for Meiosis II entry in mouse male germ cell
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Chk1-mediated phosphorylation of Cdh1 promotes the SCFβTRCP-dependent degradation of Cdh1 during S-phase and efficient cell-cycle progression
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Oral Soft Tissue Regeneration Using Nano Controlled System Inducing Sequential Release of Trichloroacetic Acid and Epidermal Growth Factor
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2020)