Abstract
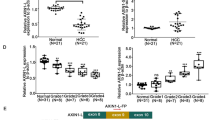
The role of RNA-binding proteins in cancer biology is recognized increasingly. The nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and AU-rich RNA-binding protein HuR stabilizes several cancer-related target mRNAs. The proto-oncogene c-fms, whose 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) is not AU-rich, is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Using a large breast-cancer tissue array (N=670), we found nuclear HuR expression to be associated with nodal metastasis and independently with poor survival (P=0.03, RR 1.45), as well as to be co-expressed with c-fms in the breast tumors (P=0.0007). We described c-fms mRNA as a direct target of HuR in vivo, and that HuR bound specifically to a 69-nt region containing ‘CUU’ motifs in 3′UTR c-fms RNA. Overexpressing or silencing HuR significantly up- or down-regulated c-fms RNA expression, respectively. We also found that known glucocorticoid stimulation of c-fms RNA and protein is largely dependent on the presence of HuR. HuR, by binding to the 69-nt wild type, but not mutant, c-fms sequence can regulate reporter gene expression post-transcriptionally. We are the first to describe that HuR can regulate gene expression by binding non-AU-rich sequences in 3′UTR c-fms RNA. Collectively, our findings suggest that HuR plays a supportive role for c-fms in breast cancer progression by binding a 69-nt element in its 3′UTR, thus regulating its expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
AU-rich elements
- 3′UTR:
-
3′untranslated region; dex, dexamethasone
- IP:
-
immunoprecipitation
- qRT–PCR:
-
reverse transcription and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR)
References
Abdelmohsen K, Pullmann Jr R, Lal A, Kim HH, Galban S, Yang X et al. (2007). Phosphorylation of HuR by Chk2 regulates SIRT1 expression. Mol Cell 25: 543–557.
Allegra JC, Lippman ME, Thompson EB, Simon R, Barlock A, Green L et al. (1979). Distribution, frequency, and quantitative analysis of estrogen, progesterone, androgen, and glucocorticoid receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 39: 1447–1454.
Apponi LH, Kelly SM, Harreman MT, Lehner AN, Corbett AH, Valentini SR . (2007). An interaction between two RNA binding proteins, Nab2 and Pub1, links mRNA processing/export and mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol 27: 6569–6579.
Brennan CM, Steitz JA . (2001). HuR and mRNA stability. Cell Mol Life Sci 58: 266–277.
Camp RL, Charette LA, Rimm DL . (2000). Validation of tissue microarray technology in breast carcinoma. Lab Invest 80: 1943–1949.
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, King BL, Rimm DL . (2003). Quantitative analysis of breast cancer tissue microarrays shows that both high and normal levels of HER2 expression are associated with poor outcome. Cancer Res 63: 1445–1448.
Chambers SK, Gilmore-Hebert M, Wang Y, Rodov S, Benz Jr EJ, Kacinski BM . (1993). Posttranscriptional regulation of colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and CSF-1 receptor gene expression during inhibition of phorbol-ester-induced monocytic differentiation by dexamethasone and cyclosporin A: potential involvement of a destabilizing protein. Exp Hematol 21: 1328–1334.
Chambers SK, Ivins CM, Kacinski BM, Hochberg RB . (2004). An unexpected effect of glucocorticoids on stimulation of c-fms proto-oncogene expression in choriocarcinoma cells that express little glucocorticoid receptor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 190: 974–985.
Chambers SK, Kacinski BM, Ivins CM, Carcangiu ML . (1997). Overexpression of epithelial macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) and CSF-1 receptor: a poor prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer, contrasted with a protective effect of stromal CSF-1. Clin Cancer Res 3: 999–1007.
Chambers SK, Wang Y, Gilmore-Hebert M, Kacinski BM . (1994). Post-transcriptional regulation of c-fms proto-oncogene expression by dexamethasone and of CSF-1 in human breast carcinomas in vitro. Steroids 59: 514–522.
Chen CY, Xu N, Shyu AB . (2002). Highly selective actions of HuR in antagonizing AU-rich element-mediated mRNA destabilization. Mol Cell Biol 22: 7268–7278.
Coussens L, Van Beveren C, Smith D, Chen E, Mitchell RL, Isacke CM et al. (1986). Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature 320: 277–280.
de Boer P, Vos HR, Faber AW, Vos JC, Raue HA . (2006). Rrp5p, a trans-acting factor in yeast ribosome biogenesis, is an RNA-binding protein with a pronounced preference for U-rich sequences. RNA 12: 263–271.
Denkert C, Weichert W, Winzer KJ, Muller BM, Noske A, Niesporek S et al. (2004). Expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR is associated with higher tumor grade and increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10: 5580–5586.
Erkinheimo TL, Lassus H, Sivula A, Sengupta S, Furneaux H, Hla T et al. (2003). Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with poor outcome and with cyclooxygenase 2 expression in serous ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res 63: 7591–7594.
Fan XC, Steitz JA . (1998). Overexpression of HuR, a nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling protein, increases the in vivo stability of ARE-containing mRNAs. EMBO J 17: 3448–3460.
Gallouzi IE, Steitz JA . (2001). Delineation of mRNA export pathways by the use of cell-permeable peptides. Science 294: 1895–1901.
Gott JM, Willis MC, Koch TH, Uhlenbeck OC . (1991). A specific, UV-induced RNA-protein cross-link using 5-bromouridine-substituted RNA. Biochemistry 30: 6290–6295.
Heinonen M, Bono P, Narko K, Chang SH, Lundin J, Joensuu H et al. (2005). Cytoplasmic HuR expression is a prognostic factor in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 65: 2157–2161.
Ide H, Seligson DB, Memarzadeh S, Xin L, Horvath S, Dubey P et al. (2002). Expression of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor during prostate development and prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 14404–14409.
Kacinski BM, Flick MB, Sapi E . (2001). RU-486 can abolish glucocorticoid-induced increases in CSF-1 receptor expression in primary human breast carcinoma specimens. J Soc Gynecol Investig 8: 114–116.
Kacinski BM, Scata KA, Carter D, Yee LD, Sapi E, King BL et al. (1991). FMS (CSF-1 receptor) and CSF-1 transcripts and protein are expressed by human breast carcinomas in vivo and in vitro. Oncogene 6: 941–952.
Kluger HM, Dolled-Filhart M, Rodov S, Kacinski BM, Camp RL, Rimm DL . (2004). Macrophage colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor expression is associated with poor outcome in breast cancer by large cohort tissue microarray analysis. Clin Cancer Res 10: 173–177.
Lal A, Mazan-Mamczarz K, Kawai T, Yang X, Martindale JL, Gorospe M . (2004). Concurrent versus individual binding of HuR and AUF1 to common labile target mRNAs. EMBO J 23: 3092–3102.
Lin EY, Nguyen AV, Russell RG, Pollard JW . (2001). Colony-stimulating factor 1 promotes progression of mammary tumors to malignancy. J Exp Med 193: 727–740.
Lopez de Silanes I, Fan J, Yang X, Zonderman AB, Potapova O, Pizer ES et al. (2003). Role of the RNA-binding protein HuR in colon carcinogenesis. Oncogene 22: 7146–7154.
Lopez de Silanes I, Zhan M, Lal A, Yang X, Gorospe M . (2004). Identification of a target RNA motif for RNA-binding protein HuR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 2987–2992.
Maher MG, Sapi E, Turner B, Gumbs A, Perrotta PL, Carter D et al. (1998). Prognostic significance of colony-stimulating factor receptor expression in ipsilateral breast cancer recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 4: 1851–1856.
Meisner NC, Hackermuller J, Uhl V, Aszodi A, Jaritz M, Auer M . (2004). mRNA openers and closers: modulating AU-rich element-controlled mRNA stability by a molecular switch in mRNA secondary structure. Chembiochem 5: 1432–1447.
Moore MJ . (2002). Nuclear RNA turnover. Cell 108: 431–434.
Nabors LB, Gillespie GY, Harkins L, King PH . (2001). HuR, a RNA stability factor, is expressed in malignant brain tumors and binds to adenine- and uridine-rich elements within the 3′ untranslated regions of cytokine and angiogenic factor mRNAs. Cancer Res 61: 2154–2161.
Peng SS, Chen CY, Xu N, Shyu AB . (1998). RNA stabilization by the AU-rich element binding protein, HuR, an ELAV protein. EMBO J 17: 3461–3470.
Peritz T, Zeng F, Kannanayakal TJ, Kilk K, Eiriksdottir E, Langel U et al. (2006). Immunoprecipitation of mRNA-protein complexes. Nat Protoc 1: 577–580.
Sapi E, Flick MB, Gilmore-Hebert M, Rodov S, Kacinski BM . (1995). Transcriptional regulation of the c-fms (CSF-1R) proto-oncogene in human breast carcinoma cells by glucocorticoids. Oncogene 10: 529–542.
Sapi E, Flick MB, Rodov S, Gilmore-Hebert M, Kelley M, Rockwell S et al. (1996). Independent regulation of invasion and anchorage-independent growth by different autophosphorylation sites of the macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor. Cancer Res 56: 5704–5712.
Stolow DT, Berget SM . (1990). UV cross-linking of polypeptides associated with 3′-terminal exons. Mol Cell Biol 10: 5937–5944.
Sureban SM, Murmu N, Rodriguez P, May R, Maheshwari R, Dieckgraefe BK et al. (2007). Functional antagonism between RNA binding proteins HuR and CUGBP2 determines the fate of COX-2 mRNA translation. Gastroenterology 132: 1055–1065.
Toy EP, Bonafe N, Savlu A, Zeiss C, Zheng W, Flick M et al. (2005). Correlation of tumor phenotype with c-fms proto-oncogene expression in an in vivo intraperitoneal model for experimental human breast cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 22: 1–9.
Urlaub H, Hartmuth K, Kostka S, Grelle G, Luhrmann R . (2000). A general approach for identification of RNA-protein cross-linking sites within native human spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). Analysis of RNA-protein contacts in native U1 and U4/U6.U5 snRNPs. J Biol Chem 275: 41458–41468.
Weber B, Horiguchi J, Luebbers R, Sherman M, Kufe D . (1989). Posttranscriptional stabilization of c-fms mRNA by a labile protein during human monocytic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 9: 769–775.
Wein G, Rossler M, Klug R, Herget T . (2003). The 3′-UTR of the mRNA coding for the major protein kinase C substrate MARCKS contains a novel CU-rich element interacting with the mRNA stabilizing factors HuD and HuR. Eur J Biochem 270: 350–365.
Yeap BB, Voon DC, Vivian JP, McCulloch RK, Thomson AM, Giles KM et al. (2002). Novel binding of HuR and poly(C)-binding protein to a conserved UC-rich motif within the 3′-untranslated region of the androgen receptor messenger RNA. J Biol Chem 277: 27183–27192.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Department of Defense Grant DAMD 17-02-1-0633 (to SKC), and in part by the Susan G Komen Breast Cancer Foundation and by the Breast Cancer Alliance (to HMK). We thank Joan A Steitz for providing the GST plasmids, and Ite A Laird-Offringa for providing purified HuR protein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, HH., Zhou, Y., Yi, X. et al. Regulation of non-AU-rich element containing c-fms proto-oncogene expression by HuR in breast cancer. Oncogene 28, 1176–1186 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.469
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.469
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Musashi RNA-binding protein 2 regulates estrogen receptor 1 function in breast cancer
Oncogene (2017)
-
Human antigen R-regulated CCL20 contributes to osteolytic breast cancer bone metastasis
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
AngiotensinII induces HuR shuttling by post-transcriptional regulated CyclinD1 in human mesangial cells
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Inhibition of the c-fms proto-oncogene autocrine loop and tumor phenotype in glucocorticoid stimulated human breast carcinoma cells
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2011)
-
Production and Characterization of Polyclonal and Monoclonal Abs Against the RNA-Binding Protein QKI
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2011)