Abstract
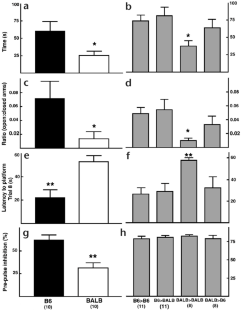
Inbred mouse strains are classically used to search for the genes associated with behavioral traits, including emotionality. To distinguish genetic and environmental contributions to the expression of adult behavior in mice, we investigated the effects of prenatal (embryo transfer) and postnatal (cross-fostering) environments in two strains of inbred mice with profound and reliable differences in behavior1. Here we report that strain-related behavioral differences may result from environmental factors during development rather than genetic differences between the offspring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bucan, M. & Abel, T. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3, 114–123 (2002).
Crabbe, J.C., Wahlsten, D. & Dudek, B.C. Science 284, 1670–1672 (1999).
Dulawa, S.C. & Geyer, M.A. Neuropharmacology 39, 2170–2179 (2000).
Paylor, R. & Crawley, J.N. Psychopharmacology 132, 169–180 (1997).
DeFries, J.C., Thomas, E.A., Hegmann, J.P. & Weir, M.W. Psychon. Sci. 8, 207–208 (1967).
Carlier, M., Roubertoux, P. & Cohen-Salmon, C. Physiol. Behav. 30, 837–844 (1983).
Rhees, B.K., Ernst, C.A., Miao, C.H. & Atchley, W.R. Genetics 153, 905–917 (1999).
Le Roy, I., Carlier, M. & Roubertoux, P.L. Behav. Brain Res. 125, 57–64 (2001).
Brown, R.E., Mathieson, W.B., Stapleton, J. & Neumann, P.E. Physiol. Behav. 67, 599–605 (1999).
Zaharia, M.D., Kulczycki, J., Shanks, N., Meaney, M.J. & Anisman, H. Psychopharmacology 128, 227–239 (1996).
Liu, D. et al. Science 277, 1659–1662 (1997).
Liu, D., Diorio, J., Day, J.C., Francis, D.D. & Meaney, M.J. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 799–806 (2000).
Francis, D., Diorio, J., Liu, D. & Meaney, M.J. Science 286, 1155–1158 (1999).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank T. Etzel for assistance with animal care, and Cure Autism Now and the National Science Foundation IBN 9876754 for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, D., Szegda, K., Campbell, G. et al. Epigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice. Nat Neurosci 6, 445–446 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1038
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1038
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Prenatal programming of environmental sensitivity
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
Prospective longitudinal assessment of sensorimotor gating as a risk/resiliency factor for posttraumatic stress disorder
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Causal-role myopia and the functional investigation of junk DNA
Biology & Philosophy (2022)
-
Baseline prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex predicts the sensitivity to the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine in male and female mice
Psychopharmacology (2018)
-
Quantitative inheritance of volatile pheromones and darcin and their interaction in olfactory preferences of female mice
Scientific Reports (2017)