Abstract
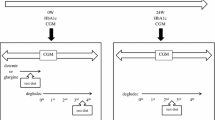
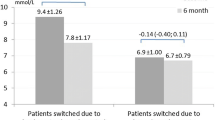
For elderly hemodialysis patients with diabetes, the treatment options are restricted, and insulin therapy plays an important role. However, sometimes it might be difficult for them to inject insulin by themselves because of technical and/or social problems. The recently introduced basal insulin analog degludec has a longer half life than the previous basal insulin analogs such as glargine or detemir. Here we report an elderly hemodialysis patient with type 2 diabetes who was successfully treated with insulin degludec injection by the medical staff at every hemodialysis clinic visit. Throughout this treatment, he did not experience any side effects due to degludec, including hypoglycemia. There are few reports of using degludec for HD patients. In addition, this is the first report showing the validity of a three-times-a-week degludec regimen as a basal supported oral therapy for a hemodialysis patient with diabetes who could not inject insulin by himself. The inferiority of the three-times-a-week degludec regimen compared with the once-a-day glargine regimen in non-hemodialysis patients has already been reported. Based on this, this three-times-a-week degludec regimen should also not be considered as a standard regimen in hemodialysis patients. However, this three-times-a-week degludec regimen may be useful as an alternative for hemodialysis patients who cannot inject insulin once a day by themselves to achieve good and safe glycemic control, improving the prognosis and avoiding problems with hyperglycemia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirkman MS, Briscoe VJ, Clark N, Florez H, Haas LB, Halter JB, et al. Diabetes in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:2650–64.
Strachan MW, Reynolds RM, Marioni RE, Price JF. Cognitive function, dementia and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7:108–14.
Yokono K. Total management of diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Diabetol Int. 2014;5:155–7.
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2009;301:1565–72.
Cheng G, Huang C, Deng H, Wang H. Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern Med J. 2012;42:484–91.
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012;35:1364–79.
Williams ME. Diabetic CKD/ESRD 2010: a progress report? Semin Dial. 2010;23:129–33.
Kishimoto M, Noda M. Glucose management in diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Diabetol Int. 2014;5:84–91.
Harvey JN. Trends in the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003;12:317–22.
Inaba M, Maekawa K, Okuno S, Imanishi Y, Hayashino Y, Emoto M, et al. Impact of atherosclerosis on the relationship of glycemic control and mortality in diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Clin Nephrol. 2012;78:273–80.
Abe M, Okada K, Soma M. Antidiabetic agents in patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease on dialysis: metabolism and clinical practice. Curr Drug Metab. 2011;12:57–69.
Heise T, Nosek L, Bottcher SG, Hastrup H, Haahr H. Ultra-long-acting insulin degludec has a flat and stable glucose-lowering effect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:944–50.
Heise T, Hermanski L, Nosek L, Feldman A, Rasmussen S, Haahr H. Insulin degludec: four times lower pharmacodynamic variability than insulin glargine under steady-state conditions in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:859–64.
Kiss I, Arold G, Roepstorff C, Bottcher SG, Klim S, Haahr H. Insulin degludec: pharmacokinetics in patients with renal impairment. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53:175–83.
Zinman B, DeVries JH, Bode B, Russell-Jones D, Leiter LA, Moses A, et al. Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec three times a week versus insulin glargine once a day in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: results of two phase 3, 26 week, randomised, open-label, treat-to-target, non-inferiority trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013;1:123–31.
Scheen AJ. Pharmacokinetic considerations for the treatment of diabetes in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013;9:529–50.
Shoji T, Emoto M, Mori K, Morioka T, Fukumoto S, Takahashi T, et al. Thrice-weekly insulin injection with nurse’s support for diabetic hemodialysis patients having difficulty with self injection. Osaka City Med J. 2012;58:35–8.
Bouchi R, Babazono T, Onuki T, Mitamura K, Ishikawa Y, Uchigata Y, et al. Administration of insulin glargine thrice weekly by medical staff at a dialysis unit: a new insulin regimen for diabetic management in physically impaired patients undergoing hemodialysis. Diabetol Int. 2011;2:197–201.
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86.
Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2643–53.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study. UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33. Lancet. 1998;352:837–53.
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1577–89.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank members of Iiri Laboratory and Masaomi Nangaku for assistance and helpful suggestions. We also would like to thank Dr. Masanori Abe, Dr. Tatsuhide Azuma and Dr. Kouta Ozawa for performing CGM and the staff in our clinic for helping with this treatment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Oishi, A., Makita, N., Manaka, K. et al. Successful glycemic control with three times a week degludec injection by medical staff for an elderly hemodialysis patient with type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Int 7, 95–99 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0220-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0220-4