Abstract
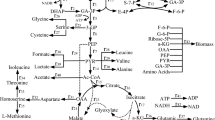
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is a key parameter for the production of L-tryptophan, and maintenance of appropriate DO levels can be used to increase the formation of L-tryptophan and reduce the accumulation of acetate and glutamate. In addition, controlling the level of DO by adjusting the feeding rate of glucose solution affects the concentration of glucose in the fermentation process. In this study, the effects of DO levels on L-tryptophan production were investigated, and four strategies of DO stage control were developed for use in L-tryptophan fermentation. The results indicate that the application of DO stage control I (20 % oxygen at 0–20 h, 30 % at 20–38 h) during L-tryptophan fermentation resulted in the highest dry cell weight (51.2 g/L) and production of L-tryptophan (46.8 g/L), which were 1.10 and 1.28 times as high, respectively, as those obtained during DO stage control III (50 % oxygen at 0–20 h and 20 % at 20–38 h). Additionally, the total glucose conversion percentage with DO stage control I was 17.2 %, which was 13.16 % higher than that of DO stage control III. Furthermore, the metabolic flux distribution with DO stage control I and III revealed greater carbon flux into the pentose phosphate pathway, while the flux of byproducts (acetate, glutamate, and lactate) was lower during DO stage control I. Finally, the flux of tryptophan with DO stage control I was 19.3 %, which was 1.79 times as high as that obtained with DO stage control III.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkesson M, Hagander P, Axelsson JP (2001) Avoiding acetate accumulation in Escherichia coli cultures using feedback control of glucose feeding. Biotechnol Bioeng 73(3):223–230
Baez A, Shiloach J (2013) Escherichia coli avoids high dissolved oxygen stress by activation of SoxRS and manganese superoxide dismutase. Microb Cell Factories 12:23. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-12-23
Báez-Viveros JL, Osuna J, Hernández-Chávez G, Soberón X, Bolívar F, Gosset G (2004) Metabolic engineering and protein directed evolution increase the yield of L-phenylalanine synthesized from glucose in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 87:516–524
Báez-Viveros JL, Flores N, Juárez K, Castillo-España P, Bolivar F, Gosset G (2007) Metabolic transcription analysis of engineered Escherichia coli trains that overproduce L-phenylalanine. Microb Cell Factories 6:30. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-6-30
Castaño-Cerezo S, Pastor JM, Renilla S, Bernal V, Iborra JL, Cánovas M (2009) An insight into the role of phosphotransacetylase (pta) and the acetate/acetyl-CoA node in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Factories 8:54. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-8-54
Chandran SS, Yi J, Draths KM, Daeniken R, Weber W, Frost JW (2003) Phosphoenolpyruvate availability and the biosynthesis of shikimic acid. Biotechnol Prog 19:808–814
Cheng LK, Wang J, Xu QY, Xie XX, Zhang YJ, Zhao CG, Chen N (2012) Effect of feeding strategy on L-tryptophan production by recombinant Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 62:1625–1634
Cheng LK, Wang J, Xu QY, Zhao CG, Shen ZQ, Xie XX, Chen N (2013) Strategy for pH control and pH feedback-controlled substrate feeding for high-level production of L-tryptophan by Escherichia coli. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:883–890
De Mey M, Lequeux GJ, Beauprez JJ, Maertens J, Horen EV, Soetaert MK, Vanrolleghem PA, Vandamme EJ (2007) Comparison of different strategies to reduce acetate formation in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 23:1053–1063
Dodge TC, Gerstner JM (2002) Optimization of the glucose feed rate profile for the production of tryptophan from recombinant E. coli. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77:1238–1245
Eiteman MA, Altman E (2006) Overcoming acetate in Escherichia coli recombinant protein fermentations. Trends Biotechnol 24(11):530–536
Gosset G (2005) Improvement of Escherichia coli production strains by modification of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Microb Cell Factories 4:14. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-4-14
Huang J, Xu QY, Wen TY, Chen N (2008) Metabolic flux analysis of L-threonine biosynthesis strain under diverse dissolved oxygen conditions. Acta Microbiol Sin 48(8):1056–1600
Huang J, Shi JM, Liu Q, Xu QY, Xie XX, Wen TY, Chen N (2011) Effects of gene pta disruption on L-tryptophan fermentation. Acta Microbiol Sin 51(4):480–487
Ikeda M (2006) Towards bacterial strains overproducing L-tryptophan and other aromatics by metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69(6):615–626
Imlay JA (2008) Cellular defenses against superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Annu Rev Biochem 77:755–776
Konstantinov K, Kishimoto M, Seki T, Yoshida T (1990) A balanced DO-stat and its application to the control of acetic acid excretion by recombinant E. coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 36(7):750–758
Kulis-Horn RK, Persicke M, Kalinowski J (2014) Histidine biosynthesis, its regulation and biotechnological application in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Biotechnol 7(1):5–25
Lin H, Castro NM, Bennett GN, San KY (2006) Acetyl-CoA synthetase overexpression in Escherichia coli demonstrates more efficient acetate assimilation and lower acetate accumulation: a potential tool in metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:870–874
Liu Q, Cheng YS, Xie XX, Xu QY, Chen N (2012) Modification of tryptophan transport system and its impact on production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 114:549–554
Marx A, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H, de Graaf AA, Eggeling L (1999) Response of the central metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum to the use of an NADH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. Metab Eng 1:35–48
Mostovenko E, Deelder AM, Palmblad M (2011) Protein expression dynamics during Escherichia Coli glucose-lactose diauxie. BMC Microbiol 11:126
Phue JN, Shiloach J (2005) Impact of dissolved oxygen concentration on acetate accumulation and physiology of E. coli BL21, evaluating transcription levels of key genes at different dissolved oxygen conditions. Metab Eng 7:353–363
Pomposiello PJ, Demple B (2001) Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of the Escherichia coli responses to superoxide stress and sodium salicylate. J Bacteriol 183:3890–3902
Rittmann D, Schaffer S, Wendisch VF, Sahm H (2003) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Corynebacterium glutamicum: expression and deletion of the fbp gene and biochemical characterization of the enzyme. Arch Microbiol 180:285–292
Rui B, Shen T, Zhou H, Liu JP, Chen JS, Pan XS, Liu HY, Wu JH, Zheng HR, Shi YY (2010) A systematic investigation of Escherichia coli central carbon metabolism in response to superoxide stress. BMC Syst Biol 4:122
San KY, Bennett GN, Berrios-Rivera SJ, Vadali RV, Yang YT, Horton E, Rudolph FB, Sariyar B, Blackwood K (2002) Metabolic engineering through cofactor manipulation and its effects on metabolic flux redistribution in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 4:182–192
Schmid JW, Mauch K, Reuss M, Gilles ED, Kremling A (2004) Metabolic design based on a coupled gene expression—metabolic network model of tryptophan production in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 6:364–377
Shen T, Liu Q, Xie XX, Xu QY, Chen N (2012) Improved production of tryptophan in genetically engineered Escherichia coli with TktA and PpsA overexpression. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2012/605219
Thomas AD, Doelle HW, Westwood AW, Gordon GL (1972) Effect of oxygen on several enzymes involved in the aerobic and anaerobic utilization of glucose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 112(3):1099–1105
Wang J, Huang J, Shi JM, Xu QY, Xie XX, Chen N (2013a) Fermentation characterization of an L-tryptophan producing Escherichia coli strain with inactivated phosphotransacetylase. Ann Microbiol 63:1219–1224
Wang J, Cheng LK, Wang J, Liu Q, Shen T, Chen N (2013b) Genetic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance production of L-tryptophan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7587–7596
Zhao CG, Cheng LK, Wang J, Shen ZQ, Chen N (2015) Impact of deletion of the genes encoding acetate kinase on production of L-tryptophan by Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s13213-015-1103-4
Zhao ZJ, Zou C, Zhu YX, Dai J, Chen S, Wu D, Wu J, Chen J (2011) Development of L-tryptophan production strains by defined genetic modification in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1921–1929
Zhu HF, Shimizu K (2005) Effect of a single-gene knockout on the metabolic regulation in Escherichia coli for D-lactate production under microaerobic condition. Metab Eng 7:104–115
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program: 2012AA02A703), and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team at the University of the Ministry of Education of China (IRT 1166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Cheng, L., Xu, Q. et al. Improvement of the production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia coli by application of a dissolved oxygen stage control strategy. Ann Microbiol 66, 843–854 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1172-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1172-4