Abstract
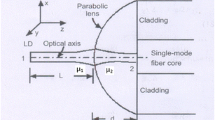
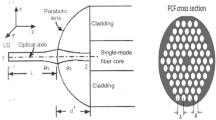
We report what to our knowledge is the first theoretical prediction of the coupling efficiency of a laser diode emitting two wavelengths either 1.3 or 1.5 μm, to three elliptic core step index fibers with different aspect ratios via quadric interface microlens of three different focal lengths on the fiber tip. Here, quadric interface microlens contains elliptical (hemispherical included), hyperbolic and parabolic microlenses. Instead of considering special ABCD matrix for individual microlens, a simple, accurate, and popular unified transfer ABCD matrix for refraction of quadric microlens under paraxial approximation is utilized to analyze the theoretical coupling efficiency, based on Gaussian beam approximation. The coupling efficiency can reach as high as 98.63 % with optimizing structure parameters of specific lensed fiber. The analysis can give some guidance for fabricating quadric interface lensed elliptic core fiber which are mainly useful in polarisation-maintaining fiber optic sensors and coherent fiber optic communication systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.-M. Yang, S.-Y. Huang, C.-W. Lee, T.-S. Lay, W.-H. Cheng, High-coupling tapered hyperbolic fiber microlens and taper asymmetry effect. J. Lightwave Technol. 22, 1395–1401 (2004)
H.L. An, Theoretical investigation on the effective coupling from laser diode to tapered lensed single-mode optical fiber. Opt. Commun. 181, 89–95 (2000)
S.K. Mondal, S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Analysis of an upside-down taper lens end from a single-mode step index fiber. Appl. Opt. 37, 1006–1009 (1998)
L. Yuan, A. Qui, Analysis of a single-mode fiber with taper lens end. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 9, 950–952 (1992)
Z. Tang, R. Zhang, S.K. Mondal, F.G. Shi, Optimization of fiber-optic coupling and alignment tolerance for coupling between a laser diode and a wedged single-mode fiber. Opt. Commun. 199, 95–101 (2001)
H.M. Presby, C.A. Edwards, Near 100 % efficient fibre microlenses. Electron. Lett. 28, 582–584 (1992)
H.M. Presby, C.A. Edwards, Efficient coupling of polarization maintaining fiber to laser diodes. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 4, 897–899 (1992)
C.A. Edwards, H.M. Presby, C. Dragone, Ideal microlenses for laser to fiber coupling. J. Lightwave Technol. 11, 252–257 (1993)
J. John, T.S.M. Maclean, H. Ghafouri-Shiraz, J. Niblett, Matching of single- mode fibre to laser diode by microlenses at 1.5μm wavelength. IEE Proc.: Optoelectron. 141, 178–184 (1994)
S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Laser diode to single-mode fibre excitation via hyperbolic lens on the fibre tip: formulation of ABCD matrix and efficiency computation. Opt. Commun. 132, 55–60 (1996)
S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, ABCD matrix for reflection and refraction of Gaussian light beams at surfaces of hyperboloid of revolution and efficiency computation for laser diode to single-mode fiber coupling by way of a hyperbolic lens on the fiber tip. Appl. Opt. 36, 8582–8586 (1997)
S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Misalignment considerations in laser diode to single-mode fibre excitation via hyperbolic lens on the fibre tip. Opt. Commun. 146, 104–108 (1998)
S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Laser diode to single-mode fiber excitation via hemispherical lens on the fiber tip: efficiency computation by ABCD matrix with consideration for allowable aperture. J. Opt. Commun. 19, 42–44 (1998)
F. Favre, L. Jeunhomme, I. Joindot, M. Monerie, J.C. Simon, Progress towards heterodyne-type single mode communication systems. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-17, 897–906 (1981)
D.N. Payne, A.J. Barlow, J.J.R. Hansen, Development of low and high birefringence optical fibers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-18, 477–487 (1982)
S.N. Sarkar, K. Thyagarajan, A. Kumar, Gaussian approximation of the fundamental mode in single mode elliptic core fibers. Opt. Commun. 49, 178–183 (1984)
S.N. Sarkar, B.P. Pal, K. Thyagarajan, Lens coupling of laser diodes to monomode elliptic core fibers. J. Opt. Commun. 7, 92–96 (1986)
M.C. Kundu, S. Gangopadhyay, Laser diode to monomode elliptic core fiber excitation via hemispherical lens on the fiber tip: efficiency computation by ABCD matrix with consideration for allowable aperture. Optik 117, 586–590 (2006)
S. Mukhopadhyay, S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Coupling of a laser diode to a monomode elliptic-core fiber via a hyperbolic microlens on the fiber tip: efficiency computation with the ABCD matrix. Opt. Eng. 46(2), 025008(1–5) (2007)
S. Mukhopadhyay, S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Misalignment considerations in a laser diode to monomode elliptic core fiber coupling via a hyperbolic microlens on the fiber tip : efficiency computation by the ABCD matrix. Opt. Eng. 46(9), 095008 (1–5) (2007)
S. Mukhopadhyay, S. Gangopadhyay, S.N. Sarkar, Coupling of a laser diode to monomode elliptic core fiber via upside down tapered microlens on the fiber tip : estimation of coupling efficiency with consideration for possible misalignments by ABCD matrix formalism. Optik 121, 142–150 (2010)
H. Liu, L. Liu, R. Xu, Z. Luan, ABCD matrix for reflection and refraction of Gaussian beams at the surface of a parabola of revolution. Appl. Opt. 44, 4809–4813 (2005)
H. Liu, The approximate ABCD matrix for a parabolic lens of revolution and its application in calculating the coupling efficiency. Optik 119, 666–670 (2008)
J. Huang, H.J. Yang, ABCD matrix model of quadric interface-lensed fiber and its application in coupling efficiency calculation. Optik 121, 531–534 (2010)
A. Keshavarz, M. Kazempour, Numerical calculation of coupling efficiency for an elegant Hermite-Cosh-Gaussian beams. Int. J. Opt. Photon. 6(2), 75–82 (2012)
G.A. Massey, A.E. Siegman, Reflection and refraction of Gaussian light beams at tilted ellipsoidal surfaces. Appl. Opt. 8, 975–978 (1969)
G.A. Deschamps, Ray techniques in electromagnetics. Proc. IEEE 60, 1022–1035 (1972)
P. Das, Lasers and Optical Engineering (Springer, New York, 1991), pp. 11–13
A. Yariv, Optical Electronics, (Saunders College Publishing, 1991)
M. Bass, V.N. Mahajan, Handbook of Optics in Geometrical and Physical Optics, Polarised Light, Components and Instruments. Vol. 1, 3rd edn. (McGraw-Hill, NewYork, 2010) Chapters 22 and 29
A. Yariv, P. Yeh, Optical Waves in Crystals (Wiley, New York, 1984)
Acknowledgment
The author is grateful to University Grants Commission (UGC) for providing financial assistance in a UGC- Minor Research Project (No. PSW-076/14-15 (ERO)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The relation between input and output parameters (q 1,q 2) of the light beam is given by
where
with symbols having their usual meanings as already described.
The ray matrix M for the QML on the tip of the fiber is given by [24]
where
where P is the structure parameter of the quadric interface lensed fiber, and L is the working distance which is also the distance of the LD from the microlens.
Again, the refractive index of the material of the microlens with respect to the incident medium is represented by \( \mu \left(=\raisebox{1ex}{${\mu}_2$}\!\left/ \!\raisebox{-1ex}{${\mu}_1$}\right.\right). \) The transformed beam spot sizes and radii of curvature in the X and Y directions are found by using Eqs. (A4a-A4d) in Eqs. (A1) and (A2) and can be expressed as
where
In plane wavefront model, the radius of curvature R 1 of the wavefront from the laser facet → ∞. This leads to A 1 = A and C 1 = C.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, S. Coupling of a laser diode to a quadric interface lensed monomode elliptic-core step index fiber: efficiency computation with the ABCD matrix. J Opt 45, 167–174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-015-0291-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-015-0291-4