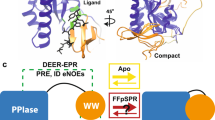
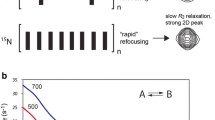
Abstract
Allostery is commonly described as a functional connection between two distant sites in a protein, where a binding event at one site alters affinity at the other. Here, we review the conformational dynamics that encode an allosteric switch in the PDZ domain of Par-6, which is a scaffold protein that organizes other proteins into a complex required to initiate and maintain cell polarity. NMR measurements revealed that the PDZ domain samples an evolutionarily conserved unfolding intermediate allowing rearrangement of two adjacent loop residues that control ligand binding affinity. Cdc42 binding to Par-6 creates a novel interface between the PDZ domain and the adjoining CRIB motif that stabilizes the high-affinity PDZ conformation. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies suggest that partial PDZ unfolding is an integral part of the Par-6 switching mechanism. The Par-6 CRIB-PDZ module illustrates two important structural aspects of protein evolution: the interface between adjacent domains in the same protein can give rise to allosteric regulation, and thermodynamic stability may be sacrificed to increase the sampling frequency of an unfolding intermediate required for conformational switching.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Manan N, Aghazadeh B, Liu GA, Majumdar A, Ouerfelli O, Siminovitch KA, Rosen MK (1999) Structure of Cdc42 in complex with the GTPase-binding domain of the ‘Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome’ protein. Nature 399:379–383
Bai Y, Sosnick TR, Mayne L, Englander SW (1995) Protein folding intermediates: native-state hydrogen exchange. Science 269:192–197
Bai Y, Feng H, Zhou Z (2007) Population and structure determination of hidden folding intermediates by native-state hydrogen exchange-directed protein engineering and nuclear magnetic resonance. Methods Mol Biol 350:69–81
Bilder D (2003) PDZ domain polarity complexes. Curr Biol 13:R661–R662
Chi CN, Gianni S, Calosci N, Travaglini-Allocatelli C, Engstrom K, Jemth P (2007) A conserved folding mechanism for PDZ domains. FEBS Lett 581:1109–1113
Chi CN, Bach A, Engstrom A, Wang H, Stromgaard K, Gianni S, Jemth P (2009) A sequential binding mechanism in a PDZ domain. Biochemistry 48:7089–7097
Feng H, Zhou Z, Bai Y (2005a) A protein folding pathway with multiple folding intermediates at atomic resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:5026–5031
Feng H, Vu ND, Bai Y (2005b) Detection of a hidden folding intermediate of the third domain of PDZ. J Mol Biol 346:345–353
Fuentes EJ, Der CJ, Lee AL (2004) Ligand-dependent dynamics and intramolecular signaling in a PDZ domain. J Mol Biol 335:1105–1115
Garrard SM, Capaldo CT, Gao L, Rosen MK, Macara IG, Tomchick DR (2003) Structure of Cdc42 in a complex with the GTPase-binding domain of the cell polarity protein, Par6. EMBO J 22:1125–1133
Gianni S, Geierhaas CD, Calosci N, Jemth P, Vuister GW, Travaglini-Allocatelli C, Vendruscolo M, Brunori M (2007) A PDZ domain recapitulates a unifying mechanism for protein folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:128–133
Gillespie JR, Shortle D (1997) Characterization of long-range structure in the denatured state of staphylococcal nuclease. II. Distance restraints from paramagnetic relaxation and calculation of an ensemble of structures. J Mol Biol 268:170–184
Hansen DF, Vallurupalli P, Lundstrom P, Neudecker P, Kay LE (2008) Probing chemical shifts of invisible states of proteins with relaxation dispersion NMR spectroscopy: how well can we do? J Am Chem Soc 130:2667–2675
Hung TJ, Kemphues KJ (1999) PAR-6 is a conserved PDZ domain-containing protein that colocalizes with PAR-3 in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Development 126:127–135
Ivarsson Y, Travaglini-Allocatelli C, Jemth P, Malatesta F, Brunori M, Gianni S (2007) An on-pathway intermediate in the folding of a PDZ domain. J Biol Chem 282:8568–8572
Jemth P, Gianni S (2007) PDZ domains: folding and binding. Biochemistry 46:8701–8708
Johnston CA, Whitney DS, Volkman BF, Doe CQ, Prehoda KE (2011) Conversion of the enzyme guanylate kinase into a mitotic-spindle orienting protein by a single mutation that inhibits GMP-induced closing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:E973–E978
Kim AS, Kakalis LT, Abdul-Manan N, Liu GA, Rosen MK (2000) Autoinhibition and activation mechanisms of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein. Nature 404:151–158
Kovrigin EL, Kempf JG, Grey MJ, Loria JP (2006) Faithful estimation of dynamics parameters from CPMG relaxation dispersion measurements. J Magn Reson 180:93–104
Lee HJ, Zheng JJ (2010) PDZ domains and their binding partners: structure, specificity, and modification. Cell Commun Signal 8:8
Lee J, Natarajan M, Nashine VC, Socolich M, Vo T, Russ WP, Benkovic SJ, Ranganathan R (2008) Surface sites for engineering allosteric control in proteins. Science 322:438–442
Lei M, Lu W, Meng W, Parrini MC, Eck MJ, Mayer BJ, Harrison SC (2000) Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch. Cell 102:387–397
Li X, Zhang J, Cao Z, Wu J, Shi Y (2006) Solution structure of GOPC PDZ domain and its interaction with the C-terminal motif of neuroligin. Protein Sci Publ Protein Soc 15:2149–2158
Li J, Kim H, Aceto DG, Hung J, Aono S, Kemphues KJ (2010) Binding to PKC-3, but not to PAR-3 or to a conventional PDZ domain ligand, is required for PAR-6 function in C. elegans. Dev Biol 340:88–98
Lin D, Edwards AS, Fawcett JP, Mbamalu G, Scott JD, Pawson T (2000) A mammalian PAR-3-PAR-6 complex implicated in Cdc42/Rac1 and aPKC signalling and cell polarity. Nat Cell Biol 2:540–547
Lockless SW, Ranganathan R (1999) Evolutionarily conserved pathways of energetic connectivity in protein families. Science 286:295–299
Mott HR, Owen D, Nietlispach D, Lowe PN, Manser E, Lim L, Laue ED (1999) Structure of the small G protein Cdc42 bound to the GTPase-binding domain of ACK. Nature 399:384–388
Nishimura T, Yamaguchi T, Kato K, Yoshizawa M, Nabeshima Y, Ohno S, Hoshino M, Kaibuchi K (2005) PAR-6-PAR-3 mediates Cdc42-induced Rac activation through the Rac GEFs STEF/Tiam1. Nat Cell Biol 7:270–277
O’Connor C, Kovrigin EL (2008) Global conformational dynamics in ras. Biochemistry 47:10244–10246
Palmer AG 3rd (2001) Nmr probes of molecular dynamics: overview and comparison with other techniques. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 30:129–155
Palmer AG 3rd, Massi F (2006) Characterization of the dynamics of biomacromolecules using rotating-frame spin relaxation NMR spectroscopy. Chem Rev 106:1700–1719
Penkert RR, DiVittorio HM, Prehoda KE (2004) Internal recognition through PDZ domain plasticity in the Par-6-Pals1 complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:1122–1127
Peterson FC, Penkert RR, Volkman BF, Prehoda KE (2004) Cdc42 regulates the Par-6 PDZ domain through an allosteric CRIB-PDZ transition. Mol Cell 13:665–676
Petit CM, Zhang J, Sapienza PJ, Fuentes EJ, Lee AL (2009) Hidden dynamic allostery in a PDZ domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:18249–18254
Prehoda KE, Scott JA, Mullins RD, Lim WA (2000) Integration of multiple signals through cooperative regulation of the N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex. Science 290:801–806
Terrien E, Simenel C, Prehaud C, Buc H, Delepierre M, Lafon M, Wolff N (2009) 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the PDZ of microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase 205 (MAST205) in complex with the C-terminal motif from the rabies virus glycoprotein. Biomol NMR Assignments 3:45–48
Tochio H, Mok YK, Zhang Q, Kan HM, Bredt DS, Zhang M (2000) Formation of nNOS/PSD-95 PDZ dimer requires a preformed beta-finger structure from the nNOS PDZ domain. J Mol Biol 303:359–370
Tokuriki N, Tawfik DS (2009) Stability effects of mutations and protein evolvability. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:596–604
Volkman BF, Nohaile MJ, Amy NK, Kustu S, Wemmer DE (1995) Three-dimensional solution structure of the N-terminal receiver domain of NTRC. Biochemistry 34:1413–1424
Walma T, Spronk CA, Tessari M, Aelen J, Schepens J, Hendriks W, Vuister GW (2002) Structure, dynamics and binding characteristics of the second PDZ domain of PTP-BL. J Mol Biol 316:1101–1110
Wang Q, Margolis B (2007) Apical junctional complexes and cell polarity. Kidney Int 72:1448–1458
Watts JL, Etemad-Moghadam B, Guo S, Boyd L, Draper BW, Mello CC, Priess JR, Kemphues KJ (1996) par-6, a gene involved in the establishment of asymmetry in early C. elegans embryos, mediates the asymmetric localization of PAR-3. Development 122:3133–3140
Welchman DP, Mathies LD, Ahringer J (2007) Similar requirements for CDC-42 and the PAR-3/PAR-6/PKC-3 complex in diverse cell types. Dev Biol 305:347–357
Whitney DS, Peterson FC, Volkman BF (2011) A conformational switch in the CRIB-PDZ module of Par-6. Structure 19:1711–1722
Whitney DS, Peterson FC, Kovrigin EL, Volkman BF (2013) Allosteric activation of the Par-6 PDZ via a partial unfolding transition. J Am Chem Soc 135:9377–9383
Zhang J, Sapienza PJ, Ke H, Chang A, Hengel SR, Wang H, Phillips GN, Lee AL (2010) Crystallographic and nuclear magnetic resonance evaluation of the impact of peptide binding to the second PDZ domain of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1E. Biochemistry 49:9280–9291
Compliance with ethical standards
Funding
This work was supported by NIH research grants R01 AI058072, R56 AI013225, and S10 RR024665.
Conflict of interest
Dustin Whitney declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Brian Volkman declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of a Special Issue on ‘The Role of Protein Dynamics in Allosteric Effects’ edited by Gordon Roberts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitney, D.S., Volkman, B.F. Some (dis)assembly required: partial unfolding in the Par-6 allosteric switch. Biophys Rev 7, 183–190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-015-0164-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-015-0164-8