Abstract
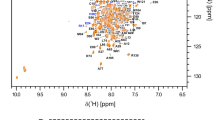
Most of microbes hijack the cellular machinery to their advantage by interacting with specific target of the host cell. Glycoprotein of rabies virus is a key factor controlling the homeostasis of infected neuronal cells and proteins belonging to the human microtubule associated serine threonine kinase family have been identified as potential cellular partners. As a first step towards its structural study, we have assigned the backbone and side chain nuclei resonances of the PDZ domain (PSD-95, Discs Large, ZO-1) of MAST205 in complex with the C-terminal residues of the glycoprotein of rabies virus. The BMRB accession code is 155972.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jackson D, Hossain MJ, Hickman D, Perez DR, Lamb RA (2008) A new influenza virus virulence determinant: the NS1 protein four C-terminal residues modulate pathogenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(11):4381–4386. doi:10.1073/pnas.0800482105
Lee SS, Glaunsinger B, Mantovani F, Banks L, Javier RT (2000) Multi-PDZ domain protein MUPP1 is a cellular target for both adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus type 18 E6 oncoproteins. J Virol 74(20):9680–9693. doi:10.1128/JVI.74.20.9680-9693.2000
Lumeng C, Phelps S, Crawford GE, Walden PD, Barald K et al (1999) Interactions between beta 2-syntrophin and a family of microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinases. Nat Neurosci 2(7):611–617. doi:10.1038/10165
Nourry C, Grant SG, Borg JP (2003) PDZ domain proteins: plug and play! Sci STKE 2003(179):RE7
Prehaud C, Lay S, Dietzschold B, Lafon M (2003) Glycoprotein of nonpathogenic rabies viruses is a key determinant of human cell apoptosis. J Virol 77(19):10537–10547. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.19.10537-10547.2003
Rousset R, Fabre S, Desbois C, Bantignies F, Jalinot P (1998) The C-terminus of the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein mediates interaction with the PDZ domain of cellular proteins. Oncogene 16(5):643–654. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201567
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) Chemical shifts as a tool for structure determination. Methods Enzymol 239:363–392. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(94)39014-2
Acknowledgements
We thanks J. D’Alayer from Institut Pasteur Facility “Analyse et Microséquençage des Protéines” for mass spectrometry and microsequencing and V. Bondet, E. Frachon and J. Bellalou from Institut Pasteur Facility “Production de Protéines recombinantes et d’Anticorps” for protein expression and purification. This work was supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-MIME Patho-PDZ). E. Terrien is recipient of a MRT fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terrien, E., Simenel, C., Prehaud, C. et al. 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the PDZ of microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase 205 (MAST205) in complex with the C-terminal motif from the rabies virus glycoprotein. Biomol NMR Assign 3, 45–48 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-008-9138-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-008-9138-0