Abstract
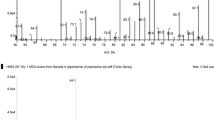
A simple, robust and reliable method for the determination of residual robenidine in chicken muscle using high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet (UV) detection was developed and validated according to the Codex Alimentarius Commission guidelines. Chicken muscle was extracted by acetonitrile/formic acid (98:2, v/v) and defatted with hexane. Analytes were isocratically separated on a Luna C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm) using 70 % methanol in water containing 0.1 % trifluoroacetic acid at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min at 30 °C. UV detection was performed at 312 nm. The method was validated by assessing performance parameters including selectivity, linearity, limit of quantification (LOQ), precision, accuracy, recovery, stability and robustness. A calibration curve that was constructed over 0.05–0.5 μg/g showed correlation coefficients of more than 0.999. The intra- and inter-day precisions (as coefficient of variation) were 1.45–3.32 and 2.63–4.99 %, respectively. The intra- and inter-day accuracies were 99.4–105.3 and 98.3–101.6 %, respectively. The recoveries were in the range of 76.6–81.8 % and the LOQ was 0.05 μg/g. The developed method showed suitable performance for the determination of robenidine residues in chicken muscle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, P., and S. Pace. 2001. The coordination chemistry of guanidines and guanidinates. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 214: 91–141.
Cai, B., and J. Li. 1999. Evaluation of trifluoroacetic acid as an ion-pair reagent in the separation of small ionizable molecules by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta 399: 249–258.
CODEX ALIMENTARIUS COMMISSION. 2008. Procedural manual 18th edition, Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 101/2009 of 3 February 2009 amending Regulation (EC) No 1800/2004 as regards the terms of the authorisation of the feed additive Cycostat 66G. Official Journal of the European Union 52(L34): 5–7.
Delahaut, P., G. Pierret, N. Ralet, M. Dubois, and N. Gillard. 2010. Multi-residue method for detecting coccidiostats at carry-over level in feed by HPLC-MS/MS. Food Additives & Contaminants 27: 801–809.
Dowling, G., M. O’keeffe, and M.R. Smyth. 2005. Determination of robenidine in eggs by liquid chromatography with UV spectrophotometric detection. Analytica Chimica Acta 539: 31–34.
Dubois, M., G. Pierret, and P. Delahaut. 2004. Efficient and sensitive detection of residues of nine coccidiostats in egg and muscle by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B 813: 181–189.
Dubreil-Cheneau, E., M. Bessiral, B. Roudaut, E. Verdon, and P. Sanders. 2009. Validation of a multi-residue liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry confirmatory method for 10 anticoccidials in eggs according to Commission Decision 2002/657/EC. Journal of Chromatography A 1216: 8149–8157.
EFSA-Q-2003-043. 2004. Opinion of the scientific panel on additives and products or substances in animal feed on a request from the commission on the re-evaluation of coccidiostat Cycostat 66G in accordance with article 9G of Council Directive 70/524/EEC. The EFSA Journal 69: 1–40.
EFSA-Q-2007-180. 2008. Scientific opinion of the panel on additives and products or substances used in animal feed (FEEDAP) on a request from the European Commission on a proposal for MRLs and withdrawal period for Cycostat®66G for chickens and turkeys for fattening. The EFSA Journal 798: 1–15.
Ellis, R.L. 2008. Development of veterinary drug residue controls by the Codex Alimentarius Commission: a review. Food Additives & Contaminants 25: 1432–1438.
FDA. 2008. Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, 556.580 Robenidine hydrochloride. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=556.580. Accessed 2 May 2012.
Gobbi, A., and G. Frenking. 1993. Y-conjugated compounds: the equilibrium geometries and electronic structures of guanidine, guanidinium cation, urea, and 1,1-diaminoethylene. Journal of the American Chemical Society 115: 2362–2372.
Hansen, M., K.A. Krogh, A. Brandt, J.H. Christensen, and B. Halling-Sorensen. 2009. Fate and antibacterial potency of anticoccidial drugs and their main abiotic degradation products. Environmental Pollution 157: 474–480.
Kinsella, B., J. O’mahony, E. Malone, M. Moloney, H. Cantwell, A. Furey, and M. Danaher. 2009. Current trends in sample preparation for growth promoter and veterinary drug residue analysis. Journal of Chromatography A 1216: 7977–8015.
Liu, Y., Y. Wu, and Y. Jiang. 2010. Determination of robenidine residue in chicken tissues and eggs by high performance liquid chromatography. Se Pu 28: 905–907.
Mortier, L., E. Daeseleire, and P. Delahaut. 2003. Simultaneous detection of five coccidiostats in eggs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta 483: 27–37.
Olejnik, M., T. Szprengier-Juszkiewicz, and P. Jedziniak. 2009. Multi-residue confirmatory method for the determination of twelve coccidiostats in chicken liver using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A 1216: 8141–8148.
Ridgway, K., S.P. Lalljie, and R.M. Smith. 2007. Sample preparation techniques for the determination of trace residues and contaminants in foods. Journal of Chromatography A 1153: 36–53.
Shirley, M.W., A.L. Smith, and D.P. Blake. 2007. Challenges in the successful control of the avian coccidia. Vaccine 25: 5540–5547.
Wilga, J., A.K. Wasik, and J. Namiesnik. 2007. Comparison of extraction techniques of robenidine from poultry feed samples. Talanta 73: 812–819.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant (09062KFDA011) from the Korea Food and Drug Administration in 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hyesun Yeom and Dong-Hyug Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeom, H., Yang, DH., Suh, J.H. et al. Determination of robenidine residues in chicken muscle by high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 359–365 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0065-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0065-y