Abstract
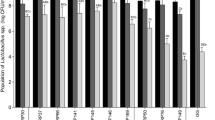
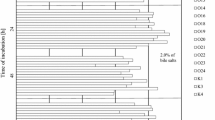
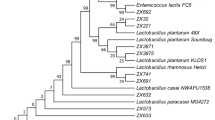
Before use in practice, it is necessary to precisely identify and characterize a new probiotic candidate. Eight animal lactobacilli and collection strain Lactobacillus reuteri CCM 3625 were studied from the point of saccharide fermentation profiles, bile salt resistance, antibiogram profiles, and influence of bile on sensitivity to antibiotics. Studied lactobacilli differed in their sugar fermentation ability determined by API 50CHL and their identification based on these profiles did not correspond with molecular-biological one in most cases. Survival of strains Lactobacillus murinus C and L. reuteri KO4b was not affected by presence of bile. The resistance of genus Lactobacillus to vancomycin and quinolones (ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin) was confirmed in all strains tested. This study provides the new information about oxgall (0.5 and 1 %) effect on the lactobacilli antibiotic susceptibility. Antibiotic profiles were not noticeably affected, and both bile concentrations tested had comparable impact on the lactobacilli antibiotic sensitivity. Interesting change was noticed in L. murinus C, where the resistance to cephalosporins was reverted to susceptibility. Similarly, susceptibility of L. reuteri E to ceftazidime arose after incubation in both concentration of bile. After influence of 1 % bile, Lactobacillus mucosae D lost its resistance to gentamicin. On the base of gained outcomes, the best probiotic properties manifested L. reuteri KO4b, Lactobacillus plantarum KG4, and L. reuteri E due to their survival in the presence of bile.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammor MS, Flórez AB, Mayo B (2007) Antibiotic resistance in non-enterococcal lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Food Microbiol 24:559–570
Begley M, Hill C, Gahan CGM (2005a) Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1729–1738
Begley M, Gahan CGM, Hill C (2005b) The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol Res 29:625–651
Belicová A, Mikulášová M, Dušinský R (2013) Probiotic potential and safety properties of Lactobacillus plantarum from Slovak bryndza cheese. Biomed Res Int 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/760298
Bernardeau M, Vernoux JP, Henri-Dubernet S, Guéguen M (2008) Safety assessment of dairy microorganisms: the Lactobacillus genus. Int J Food Microbiol 126:278–285
Bilková A, Kiňová Sepová H, Bilka F, Bukovský M, Balažová A, Bezáková L (2008) Identification of newly isolated lactobacilli from the stomach mucus of lamb. Acta Facult Pharm Univ Comenianae 55:64–72
Charteris WP, Kelly PM, Morelli L, Collins JK (1998) Antibiotic susceptibility of potentially probiotic Lactobacillus species. J Food Prot 61:1636–1643
Claesson MJ, van Sinderen D, O’Toole PW (2007) The genus Lactobacillus – a genomic basis for understanding its diversity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 269:22–28
Clementi F, Aquilanti L (2011) Recent investigations and updated criteria for the assessment of antibiotic resistance in food lactic acid bacteria. Anaerobe 17:394–398
Collins MD, Rodrigues U, Ash C, Aguirre M, Farrow JAE, Martine-Murcia A, Phillips BA, Williams AM, Wallbanks S (1991) Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Lactobacillus and related lactic acid bacteria as determined by reverse transcriptase sequencing of 16S rRNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 77:5–12
Coyle MB, Ed (2005) Manual of antimicrobial susceptibility testing. American Society for Microbiology
Danielsen M, Wind A (2003) Susceptibility of Lactobacillus spp. to antimicrobial agents. Int J Food Microbiol 82:1–11
De Boever P, Verstraete W (1999) Bile salts deconjugation by Lactobacillus plantarum 80 and its implication for bacterial toxicity. J Appl Microbiol 87:345–352
Dušková M, Karpíšková R (2013) Antimicrobial resistance of lactobacilli isolated from food. Czech J Food Sci 31:27–32
Ebringer L, Ferenčík M, Krajčovič J (2008) Beneficial effects of milk and fermented dairy products – review. Folia Microbiol 53:378–394
Elkins CA, Mullis LB (2004) Bile-mediated aminogycosyte sensitivity in Lactobacillus species likely results from increased membrane permeability attributable to cholic acid. App Environ Microbiol 70:7200–7209
Euzéby JP 2014 List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. http://www.bacterio.net/lactobacillus.html Accessed 28 March 2014
FAO/WHO (2001) Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.pdf Accessed 7 April 2014
Fontana L, Bermudez-Brito M, Plaza-Diaz J, Munoz-Quezada S, Gil A (2013) Sources, isolation, characterization and evaluation of probiotics. Brit J Nutr 109:35–50
Fukao M, Yajima N (2012) Antibiotic resistant bacteria – a continuous challenge in the new millennium. In: Pana M (ed) Assessment of antibiotic resistance in probiotic lactobacilli, 1st edn. InTech, Rijeka, pp 503–512
Horošová K, Bujňáková D, Kmeť V (2006) Effect of lactobacilli on E. coli adhesion to Caco-2 cells in vitro. Folia Microbiol 51:281–282
Hummel AS, Hertel C, Holtzapfel WA, Franz CMAP (2007) Antibiotic resistances of starter and probiotic strains of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:730–739
Kandler O, Stetter KO, Kohl R (1980) Lactobacillus reuteri sp. nov., a new species of heterofermentative lactobacilli. Zbl Bakt Hyg I Abt Orig C 1:264–269
Kiňová Sepová H, Bilková A (2013) Isolation and identification of new lactobacilli from goatling stomach and investigation of reuterin production in Lactobacillus reuteri strains. Folia Microbiol 58:33–38
Klare I, Konstabel C, Müller-Bertling S, Reissbrodt R, Huys G, Vanncaneyt M, Swings J, Goossens H, Witte W (2005) Evaluation of new broth media for microdilution antibiotic susceptibility testing of lactobacilli, pediococci, lactococci and bifidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8982–8986
Lebeer S, Vanderleyden J, De Keersmaecker SCJ (2008) Genes and molecules of Lactobacilli supporting probiotic action. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72:728–764
Liong MT, Shah NP (2005) Bile salt deconjugation ability, bile salt hydrolase activity and cholesterol co-precipitation ability of lactobacilli strains. Int Dairy J 15:391–398
Lorca GL, de Valdez GF (2009) Lactobacillus molecular biology. From genomics to probiotics. In: Ljung Å, Wadström T (eds) Lactobacillus stress responses, 1st edn. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, pp 115–138
Patel AK, Singhania RR, Pandey A, Chincholkar SB (2010) Probiotic bile salt hydrolase: current developments and perspectives. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:166–180
Ruiz L, Margolles A, Sánchez B (2013) Bile resistance mechanisms in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Front Microbiol. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2013.00396
Sepp E, Štšepetova J, Smidt I, Rätsep M, Kõljalg S, Lõivukene K, Mändar R, Jaanimäe L, Löhr HI, Natås OB, Naaber P (2011) Intestinal lactoflora in Estonian and Norwegian patients with antibiotic associated diarrhea. Anaerobe 17:407–409
Siciliano RA, Mazzeo MF (2012) Molecular mechanisms of probiotic action: a proteomic perspective. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:1–7
Turková K, Mavrič A, Narat M, Rittich B, Španová A, Rogelj I, Matjašić BB (2013) Evaluation of Lactobacillus strains for selected probiotic properties. Folia Microbiol 58:261–267
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Professor Dušan Mlynarčík, DrSc., for critical reading of manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyacinta, M., Hana, K.S., Andrea, B. et al. Bile tolerance and its effect on antibiotic susceptibility of probiotic Lactobacillus candidates. Folia Microbiol 60, 253–257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-014-0365-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-014-0365-8