Abstract
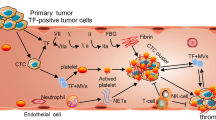
Metastasis is a complex process that ultimately results in secondary tumor formation, posing a threat to patient survival. However, the mechanisms by which circulating tumor cells adhere to the endothelium and escape from the vasculature are not fully understood. To bind to the endothelium, tumor cells must resist the shear forces induced by flow, largely through receptor-mediated cell–cell interactions. Tumor cells are able to manipulate the metastatic site microenvironment via thrombin and soluble fibrin (sFn) regulation, impacting both coagulation and cell adhesion processes. Thus, thrombosis may be recognized as a prognostic indicator of highly metastatic tumors. Herein, we describe some correlations between the metastatic potential of tumor cells and coagulation. This perspectives review focuses on the role of sFn in melanoma-endothelial adhesions under shear conditions. Specifically, sFn serves as a divalent ligand for αvβ3, CD11b/CD18 (αmβ2, Mac-1), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) transmembrane receptors. The cross-linking role of sFn is examined in relation to host leukocytes, in particular, the polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN)-mediated adhesions of melanoma cells to the endothelium. These results have shed light on the significant interplay between melanoma cells, PMNs, and the endothelium under shear conditions, which is key in the struggle to better diagnose and treat melanoma metastases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso, S. R., et al. A high-throughput study in melanoma identifies epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a major determinant of metastasis. Cancer Res. 67:3450–3460, 2007.
Alves, C. S., M. M. Burdick, S. N. Thomas, P. Pawar, and K. Konstantopoulos. The dual role of CD44 as a functional P-selectin ligand and fibrin receptor in colon carcinoma cell adhesion. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 294:C907–C916, 2008.
Biggerstaff, J. P., N. B. Seth, T. V. Meyer, A. Amirkhosravi, and J. L. Francis. Fibrin monomer increases platelet adherence to tumor cells in a flowing system: a possible role in metastasis? Thromb Res 92:S53–S58, 1998.
Biggerstaff, J. P., et al. Soluble fibrin augments platelet/tumor cell adherence in vitro and in vivo, and enhances experimental metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 17:723–730, 1999.
Bluff, J. E., N. J. Brown, M. W. R. Reed, and C. A. Staton. Tissue factor, angiogenesis and tumour progression. Breast Cancer Res. 10:1–10, 2008.
Bolliger, D., F. Szlam, R. J. Molinaro, N. Rahe-Meyer, J. H. Levy, and K. A. Tanaka. Finding the optimal concentration range for fibrinogen replacement after severe haemodilution: an in vitro model. Br. J. Anaesth. 102:793–799, 2009.
Brooks, D. E. The biorheology of tumor-cells. Biorheology 21:85–91, 1984.
Chatterjee, K., J. L. Thornton, J. W. Bauer, and E. A. Vogler. Moderation of Prekallikrein-factor XII interactions in surface activation of coagulation by protein-adsorption competition. Biomaterials 30:4915–4920, 2010.
Coughlin, S. R. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 407:258–264, 2000.
Dong, C., M. J. Slattery, S. Liang, and H.-H. Peng. Melanoma cell extravasation under flow conditions is modulated by leukocytes and endogenously produced interleukin 8. Mol. Cell. Biomech. 2:145–159, 2005.
Evani, S. J., R. G. Prabhu, V. Gnanaruban, E. A. Finol, and A. K. Ramasubramanian. Monocytes mediate metastatic breast tumor cell adhesion to endothelium under flow. FASEB J. 27:3017–3029, 2013.
Evans, M. S., S. V. Madhunapantula, G. P. Robertson, and J. J. Drabick. Current and future trials of targeted therapies in cutaneous melanoma. In: Impact of Genetic Targets on Cancer Therapy, edited by W. S. El-Deiry. New York: Springer, 2013, pp. 223–255.
Felding-Habermann, B., R. Habermann, E. Saldivar, and Z. M. Ruggeri. Role of B3 integrins in melanoma cell adhesion to activated platelets under flow. J. Biol. Chem. 271:5892–5900, 1996.
Ferrigno, D., G. Buccheri, and I. Ricca. Prognostic significance of blood coagulation tests in lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 17:667–673, 2001.
Goldsmith, H. L., T. A. Quinn, G. Drury, C. Spanos, F. A. Mcintosh, and S. I. Simon. Dynamics of neutrophil aggregation in Couette flow revealed by videomicroscopy: effect of shear rate on two-body collision efficiency and doublet lifetime. Biophys. J. 81:2020–2034, 2001.
Gopalan, P. K., C. W. Smith, H. Lu, E. L. Berg, L. V. McIntire, and S. I. Simon. Neutrophil CD18-dependent arrest on intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) in shear flow can be activated through L-selectin. J. Immunol. 158:367–375, 1997.
Gorelik, E., R. H. Wiltrout, K. Okumura, S. Habu, and R. B. Herberman. Role of NK cells in the control of metastatic spread and growth of tumor cells in mice. Int. J. Cancer 30:107–112, 1982.
Hanley, W., O. McCarty, S. Jadhav, Y. Tseng, D. Wirtz, and K. Konstantopoulos. Single molecule characterization of P-selectin/ligand binding. J. Biol. Chem. 278:10556–10561, 2003.
Harouaka, R., Z. Kang, S.-Y. Zheng, and L. Cao. Circulating tumor cells: advances in isolation and analysis, and challenges for clinical applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 141:209–221, 2014.
Hu, L., M. Lee, W. Campbell, R. Perez-soler, and S. Karpatkin. Role of endogenous thrombin in tumor implantation, seeding, and spontaneous metastasis. Hemostasis, Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 104:2746–2751, 2004.
Huh, S. J., S. Liang, A. Sharma, C. Dong, and G. P. Robertson. Transiently entrapped circulating tumor cells interact with neutrophils to facilitate lung metastasis development. Cancer Res. 70:6071–6082, 2010.
Jadhav, S., B. S. Bochner, and K. Konstantopoulos. Hydrodynamic shear regulates the kinetics and receptor specificity of polymorphonuclear leukocyte-colon carcinoma cell adhesive interactions. J. Immunol. 167:5986–5993, 2001.
Kadash, K. E., M. B. Lawrence, and S. L. Diamond. Neutrophil string formation: hydrodynamic thresholding and cellular deformation during cell collisions. Biophys. J. Elsevier 86:4030–4039, 2004.
Kojima, N., M. Shiota, Y. Sadahira, K. Handa, and S. Hakomori. Cell adhesion in a dynamic flow system as compared to static system. J. Biol. Chem. 267:17264–17270, 1992.
Konstantopoulos, K., and S. N. Thomas. Cancer cells in transit: the vascular interactions of tumor cells. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 11:177–202, 2009.
Kuijper, P. H., et al. Neutrophil adhesion to fibrinogen and fibrin under flow conditions is diminished by activation and L-selectin shedding. Blood 89:2131–2138, 1997.
Liang, S., M. J. Slattery, and C. Dong. Shear stress and shear rate differentially affect the multi-step process of leukocyte-facilitated melanoma adhesion. Exp. Cell Res. 310:282–292, 2005.
Liang, S., M. J. Slattery, D. Wagner, S. I. Simon, and C. Dong. Hydrodynamic shear rate regulates melanoma-leukocyte aggregation, melanoma adhesion to the endothelium, and subsequent extravasation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 36:661–671, 2008.
Liang, S., et al. Two-dimensional kinetics of beta 2-integrin and ICAM-1 bindings between neutrophils and melanoma cells in a shear flow. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Chysiol 294:C743–C753, 2008.
Marchetti, M., E. Diani, H. ten Cate, and A. Falanga. Characterization of the thrombin generation potential of leukemic and solid tumor cells by calibrated automated thrombography. Haematologica 97:1173–1180, 2012.
Middleton, J., A. M. Patterson, L. Gardner, C. Schmutz, and B. A. Ashton. Leukocyte extravasation: chemokine transport and presentation by the endothelium. Blood 100:3853–3860, 2002.
Mueller, B. M., R. A. Reisfeld, T. S. Edgington, and W. Ruf. Expression of tissue factor by melanoma cells promotes efficient hematogenous metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:11832–11836, 1992.
Mueller, B. M., and W. Ruf. Requirement for binding of catalytically active factor VIIa in tissue factor-dependent experimental metastasis. J. Clin. Invest. 101:1372–1378, 1998.
Nieswandt, B., M. Hafner, B. Echtenacher, and D. N. Mannel. Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 59:1295–1300, 1999.
Ozdemir, T., P. Zhang, C. Fu, and C. Dong. Fibrin serves as a divalent ligand that regulates neutrophil-mediated melanoma cells adhesion to endothelium under shear conditions. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 302:C1189–C1201, 2012.
Pillay, J., et al. Acute-phase concentrations of soluble fibrinogen inhibit neutrophil adhesion under flow conditions in vitro through interactions with ICAM-1 and MAC-1 (CD11b/CD18). J. Thromb. Haemost. 11:1172–1182, 2013.
Raman, P. S., C. S. Alves, D. Wirtz, and K. Konstantopoulos. Single-molecule binding of CD44 to fibrin versus P-selectin predicts their distinct shear-dependent interactions in cancer. J. Cell Sci. 124:1903–1910, 2011.
Rickles, F. R., S. Patierno, and P. M. Fernandez. Tissue factor, thrombin, and cancer. Chest 124:58s–68s, 2003.
Sutherland, D. E., I. C. Weitz, and H. A. Liebman. Thromboembolic complications of cancer: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 72:43–52, 2003.
Ueda, C., et al. Pancreatic cancer complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with production of tissue factor. J. Gastroenterol. 36:848–850, 2001.
Uppal, A., S. C. Wightman, S. Ganai, R. R. Weichselbaum, and G. An. Investigation of the essential role of platelet-tumor cell interactions in metastasis progression using an agent-based model. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 11:17, 2014.
Versteeg, H. H., et al. Inhibition of tissue factor signaling suppresses tumor growth. Blood 111:190–199, 2008.
Villanueva, J., and M. Herlyn. Melanoma and the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 10:439–446, 2008.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., L. R. Zacharski, T. E. Moritz, K. Hur, R. L. Edwards, and F. R. Rickles. Prognostic significance of blood coagulation tests in carcinoma of the lung and colon. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 3:429–437, 1992.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., et al. Thrombin increases the metastatic potential of tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 54:793–806, 1993.
Wysoczynski, M., R. Liu, M. Kucia, J. Drukala, and M. Z. Ratajczak. Thrombin regulates the metastatic potential of human rhabdomyosarcoma cells: distinct role of PAR1 and PAR3 signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 8:677–690, 2010.
Zhang, P., T. Ozdemir, C.-Y. Chung, G. P. Robertson, and C. Dong. Sequential binding of avb3 and ICAM-1 determines fibrin-mediated melanoma capture and stable adhesion to CD11b/CD18 on neutrophils. J. Immunol. 186:242–254, 2011.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Erwin Vogler for use of his facilities in performing coagulation experiments. Additionally, we thank Dr. Scott I. Simon (UC Davis) for kindly providing EI cells; Dr. Meenhard Herlyn (The Wistar Institute Melanoma Research Center) for providing WM35 melanoma cells; Dr. Gavin Robertson (Penn State Hershey Medical Center) for Lu1205 melanoma cells. We also thank Virginia Aragon-Sanabria and David Gaddes for critically reading the manuscript. This study was partially funded by NIH (CA-125707), NSF (CBET-0729091), NSF (CBET-1330663), and NSF (CBET- 1340173).
Conflict of interest
T Ozdemir, E. Gaddes, Y. Wang, and C. Dong declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Standards
No human or animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Edward Sander oversaw the review of this article.
Tugba Ozdemir and Erin Gaddes are equal first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdemir, T., Gaddes, E., Wang, Y. et al. Perspectives: Interplay Between Melanoma Regulated Fibrin and Receptor Mediated Adhesion Under Shear Flow. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 8, 86–95 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-014-0369-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-014-0369-0