Abstract
Human antigen R (HuR) is a ubiquitous protein that recognizes adenylate and uridylate-rich elements in mRNA, thereby interfering with the fate of protein translation. This protein plays a central role in the outcome of the inflammatory response as it may stabilize or silence mRNAs of key components of the immune system. HuR is able to interact with other RNA-binding proteins, reflecting a complex network that dictates mRNAs post-transcriptional control. HuR is composed of three functional domains, known as RNA-recognition motifs (RRM1, RRM2 and RRM3). It is known that RRM1 is the most important domain for mRNA-binding affinity. In this study, we completed the NMR chemical shift assignment of the RRM1 domain of HuR, as a first step to further establishing the structure, dynamics and function relationship for this protein.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson P (2008) Post-transcriptional control of cytokine production. Nat Immunol 9:353–359
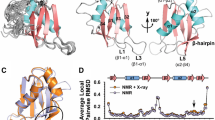
Benoit RM, Meisner NC, Kallen J, Graff P, Hemmig R, Cebe R (2010) The X-ray crystal structure of the first RNA recognition motif and site-directed mutagenesis suggest a possible HuR redox sensing mechanism. J Mol Biol 397:1231–1244
Denkert C, Weichert W, Pest S, Koch I, Licht D, Kobel M (2004) Overexpression of the embryonic-lethal abnormal vision-like protein HuR in ovarian carcinoma is a prognostic factor and is associated with increased cyclooxygenase 2 expression. Cancer Res 64:189–195
Eberhardt W, Doller A, Akool E, Pfeilschifter J (2007) Modulation of mRNA stability as a novel therapeutic approach. Pharmacol Ther 114:56–73
Kang MJ, Ryu BK, Lee MG, Han J, Lee JH, Ha TK, Byun DS, Chae KS, Lee BH, Chun HS, Lee KY, Kim HJ, Chi SG (2008) NF-κB activates transcription of the RNA-binding factor HuR, via PI3K-AKT signaling, to promote gastric tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 135:2030–2042
Kazan H, Ray D, Chan ET, Hughes TR, Morris Q (2010) RNA context: a new method for learning the sequence and structure binding preferences of RNA-binding proteins. PLoS Comput Biol 6:e1000832
Meisner NM, Filipowicz W (2010) Properties of the regulatory RNA-binding protein HuR and its role in controlling miRNA repression. Adv Exp Med Biol 10:106–124
Meisner NC, Hintersteiner M, Seifert JM, Bauer R, Benoit RM, Widmer A, Schindler T, Uhl V, Lang M, Gstach H, Auer M (2009) Terminal adenosyl transferase activity of posttranscriptional regulator HuR revealed by confocal on-bead screening. J Mol Biol 386:435–450
Roretz VC, Beauchamp P, Marco SD, Gallouzi I (2011) HuR and myogenesis: being in the right place at the right time. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:1663–1667
Shen Y, Bax A (2013) Protein backbone and side chain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J Biomol NMR 56:227–241
Wang H, Zeng F, Liu Q, Liu H, Liu Z, Niu L, Teng M, Li X (2012) The structure of the ARE-binding domains of Hu antigen R (HuR) undergoes conformational changes during RNA binding. Acta Crystallogr D: Biol Crystallogr 69:373–380
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ) and by a Brazil Initiative Collaboration grant from Brown University to A. S. P. A. M. and C. L. are recipients of a Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) graduate fellowship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mujo, A., Lixa, C., Carneiro, L.A.M. et al. 1H, 15N and 13C resonance assignments of the RRM1 domain of the key post-transcriptional regulator HuR. Biomol NMR Assign 9, 281–284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-014-9592-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-014-9592-9