Abstract
Purpose
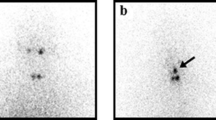
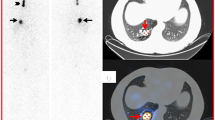
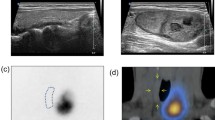
124I-PET/CT can be used for pre-therapeutic assessment of radioactive iodine uptake in benign thyroid disorders, however systematic comparisons with intra-therapeutic uptake are still lacking for these disorders. The goals of this study were to compare 124I RAIU and conventional 131I RAIU tests with each other; to compare both tests with intra-therapeutic uptake (reference); and to verify the time course of radioactive iodine uptake at three time points (30, 102, and 336 h [14 days] post administration; p.a.).
Methods
Thirteen patients with benign thyroid diseases underwent 131I RAIU test and 124I RAIU test one after another before the intra-therapeutic 131I uptake (reference) was measured via short-range and long-range measurements. After correction for decay, relative uptake differences were calculated and subjected to the Bland-Altman method for the evaluation of levels of agreement.
Results
Radioactive iodine uptake tests with 124I-PET/CT and 131I probe did not show systematic deviations at any time point. Likewise, at 30 and 102 h p.a. there was no systematic discrepancy between pre-therapeutic and intra-therapeutic uptake levels. At 14 days p.a., however, both pre-therapeutic tests tended to overestimate the uptake compared to reference. Findings showed, for the first time with 124I, that radioiodine therapy has some early radiobiological effects possibly limiting the accuracy of pre-therapeutic dosimetry.
Conclusions
124I RAIU tests represent a feasible alternative to standard 131I RAIU tests. The additional benefits of 124I-PET/CT (e.g., functional topography, inclusion of retrosternal areas, possibility to enable fusion imaging) may thus increase the scope of this technology in benign thyroid disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.S. Bahn, H.B. Burch, D.S. Cooper, J.R. Garber, M.C. Greenlee, I. Klein, P. Laurberg, I.R. McDougall, V.M. Montori, S.A. Rivkees, D.S. Ross, J.A. Sosa, M.N. Stan, American Thyroid, A., American Association of Clinical, E., Hyperthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis: management guidelines of the American Thyroid Association and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Endocr. Pract. 17(3), 456–520 (2011)
S.J. Bonnema, L. Hegedus, Radioiodine therapy in benign thyroid diseases: effects, side effects, and factors affecting therapeutic outcome. Endocr. Rev. 33(6), 920–980 (2012)
E.T. Wong, A.L. Schultz, Changing values for the normal thyroid radioactive iodine uptake test. JAMA 238(16), 1741–1743 (1977)
C. Kobe, W. Eschner, M. Wild, I. Rahlff, F. Sudbrock, M. Schmidt, M. Dietlein, H. Schicha, Radioiodine therapy of benign thyroid disorders: what are the effective thyroidal half-life and uptake of 131I? Nucl. Med. Commun. 31(3), 201–205 (2010)
P. Reinartz, M. Zimny, W. Schaefer, B. Mueller, U. Buell, O. Sabri, Radioiodine therapy in patients with hyperthyroid disorder: standard versus dosimetric activity application. Nucl. Med. Commun. 24(12), 1247–1253 (2003)
A.M. Darr, T. Opfermann, T. Niksch, D. Driesch, R.J. Marlowe, M. Freesmeyer, Low-activity 124I-PET/low-dose CT versus 99mTc-pertechnetate planar scintigraphy or 99mTc-pertechnetate single-photon emission computed tomography of the thyroid: a pilot comparison. Clin. Nucl. Med. 38(10), 770–777 (2013)
A.S. Gabler, C. Kuhnel, T. Winkens, M. Freesmeyer, Assessment of minimum activity of 124Iodine in pre-therapeutic uptake measurement prior to radioiodine therapy of benign thyroid diseases. J. Nucl. Med. 57(8), 1201–1206 (2016)
J.G. Westphal, T. Winkens, C. Kuhnel, M. Freesmeyer, Low-activity (124)I-PET/low-dose CT versus (131)I probe measurements in pretherapy assessment of radioiodine uptake in benign thyroid diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99(6), 2138–2145 (2014)
S.M. Eschmann, G. Reischl, K. Bilger, J. Kupferschlager, M.H. Thelen, B.M. Dohmen, H. Besenfelder, R. Bares, Evaluation of dosimetry of radioiodine therapy in benign and malignant thyroid disorders by means of iodine-124 and PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 29(6), 760–767 (2002)
D. Becker, N.D. Charkes, H. Dworkin, J. Hurley, I.R. McDougall, D. Price, H. Royal, S. Sarkar, Procedure guideline for thyroid uptake measurement: 1.0. Society of Nuclear Medicine. J. Nucl. Med. 37(7), 1266–1268 (1996)
H. Hanscheid, C. Canzi, W. Eschner, G. Flux, M. Luster, L. Strigari, M. Lassmann, EANM dosimetry committee series on standard operational procedures for pre-therapeutic dosimetry II. Dosimetry prior to radioiodine therapy of benign thyroid diseases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 40(7), 1126–1134 (2013)
J.M. Bland, D.G. Altman, Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476), 307–310 (1986)
A. de Rooij, J.P. Vandenbroucke, J.W. Smit, M.P. Stokkel, O.M. Dekkers, Clinical outcomes after estimated versus calculated activity of radioiodine for the treatment of hyperthyroidism: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 161(5), 771–777 (2009)
M. Salvatori, M. Luster, Radioiodine therapy dosimetry in benign thyroid disease and differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 37(4), 821–828 (2010)
A.C. Traino, B. Xhafa, Accuracy of two simple methods for estimation of thyroidal 131I kinetics for dosimetry-based treatment of Graves’ disease. Med. Phys. 36(4), 1212–1218 (2009)
M. Schiavo, M.C. Bagnara, L. Camerieri, E. Pomposelli, M. Giusti, G. Pesce, C. Reitano, M. Caputo, M. Bagnasco, Clinical efficacy of radioiodine therapy in multinodular toxic goiter, applying an implemented dose calculation algorithm. Endocrine 48(3), 902–908 (2015)
J.C. Sisson, A.M. Avram, D. Rubello, M.D. Gross, Radioiodine treatment of hyperthyroidism: fixed or calculated doses; intelligent design or science? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 34(7), 1129–1130 (2007)
M. Dietlein, J. Dressler, W. Eschner, M. Lassmann, B. Leisner, C. Reiners, H. Schicha, N. Deutsche Gesellschaft fur, P. Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Medizinische, [Procedure guideline for radioiodine test (Version 3)]. Nuklearmedizin 46(5), 198–202 (2007)
B.K. Menon, R.D. Rao, A. Abhyankar, M.G. Rajan, S. Basu, Comparative evaluation of 24-hour thyroid 131I uptake between gamma camera-based method using medium-energy collimator and standard uptake probe-based method. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 42(3), 194–197 (2014)
L.S. Freudenberg, W. Jentzen, A. Stahl, A. Bockisch, S.J. Rosenbaum-Krumme, Clinical applications of 124I-PET/CT in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 38(Suppl 1), S48–S56 (2011)
D. Van Nostrand, S. Moreau, V.V. Bandaru, F. Atkins, S. Chennupati, M. Mete, K. Burman, L. Wartofsky, (124)I positron emission tomography versus (131)I planar imaging in the identification of residual thyroid tissue and/or metastasis in patients who have well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 20(8), 879–883 (2010)
A. Bockisch, T. Jamitzky, R. Derwanz, H.J. Biersack, Optimized dose planning of radioiodine therapy of benign thyroidal diseases. J. Nucl. Med. 34(10), 1632–1638 (1993)
H. Hanscheid, M. Lassmann, C. Reiners, Dosimetry prior to I-131-therapy of benign thyroid disease. Z. Med. Phys. 21(4), 250–257 (2011)
T. Rink, F.J. Bormuth, S. Braun, M. Zimny, H.J. Schroth, [Concept and validation of a simple model of the intrathyroidal iodine kinetics]. Nuklearmedizin 43(1), 21–25 (2004)
J.W. Van Isselt, J.M. de Klerk, H.P. Koppeschaar, P.P. Van Rijk, Iodine-131 uptake and turnover rate vary over short intervals in Graves’ disease. Nucl. Med. Commun. 21(7), 609–616 (2000)
B. Meller, K. von Hof, E. Genina, W. Deisting, J. Meller, E. Richter, M. Baehre, Diagnostic 123I and 131I activities and radioiodine therapy. Effects on urinary iodine excretion in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Nuklearmedizin 44(6), 243–248 (2005)
B. Meller, A. Haase, M. Seyfarth, B.E. Wenzel, E. Richter, M. Baehre, [Reduced radioiodine uptake at increased iodine intake and 131I-induced release of “cold” iodine stored in the thyroid]. Nuklearmedizin 44(4), 137–142 (2005)
M. Berman, E. Hoff, M. Barandes, D.B. Becker, M. Sonenberg, R. Benua, D.A. Koutras, Iodine kinetics in man–a model. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 28(1), 1–14 (1968)
L.F. Morris, A.D. Waxman, G.D. Braunstein, Thyroid stunning. Thyroid 13(4), 333–340 (2003)
I.R. McDougall, A. Iagaru, Thyroid stunning: fact or fiction? Semin. Nucl. Med. 41(2), 105–112 (2011)
R.W. Rawson, J.E. Rall, W. Peacock, Limitations and indications in the treatment of cancer of the thyroid with radioactive iodine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 11(10), 1128–1142 (1951)
S. Walrand, M. Hesse, F. Jamar, Statistical and radiobiological analysis of the so-called thyroid stunning. EJNMMI Res. 5(1), 67 (2015)
C. Lundh, U. Lindencrona, P. Postgard, T. Carlsson, M. Nilsson, E. Forssell-Aronsson, Radiation-induced thyroid stunning: differential effects of (123)I, (131)I, (99m)Tc, and (211)At on iodide transport and NIS mRNA expression in cultured thyroid cells. J. Nucl. Med. 50(7), 1161–1167 (2009)
M. Lassmann, M. Luster, H. Hanscheid, C. Reiners, Impact of 131I diagnostic activities on the biokinetics of thyroid remnants. J. Nucl. Med. 45(4), 619–625 (2004)
O. Sabri, M. Zimny, M. Schreckenberger, A. Meyer-Oelmann, P. Reinartz, U. Buell, Does thyroid stunning exist? A model with benign thyroid disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 27(11), 1591–1597 (2000)
C. Lundh, M.M. Norden, M. Nilsson, E. Forssell-Aronsson, Reduced iodide transport (stunning) and DNA synthesis in thyrocytes exposed to low absorbed doses from 131I in vitro. J. Nucl. Med. 48(3), 481–486 (2007)
J.C. Sisson, A.M. Avram, S.A. Lawson, P.G. Gauger, G.M. Doherty, The so-called stunning of thyroid tissue. J. Nucl. Med. 47(9), 1406–1412 (2006)
T.E. Hilditch, M.F. Dempsey, A.A. Bolster, R.M. McMenemin, N.S. Reed, Self-stunning in thyroid ablation: evidence from comparative studies of diagnostic 131I and 123I. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 29(6), 783–788 (2002)
F. Guiraud-Vitaux, G. Feldmann, N. Vadrot, S. Charles-Gupta, A.M. Durand-Schneider, N. Colas-Linhart, A. Petiet, Early ultrastructural injuries in the thyroid of the normal rat radioinduced by diagnostic and/or therapeutic amounts of iodine-131. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand). 47(3), 495–502 (2001)
K.H. Lee, M.E. Siegel, O.A. Fernandez, Discrepancies in thyroid uptake values. Use of commercial thyroid probe systems versus scintillation cameras. Clin. Nucl. Med. 20(3), 199–202 (1995)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Ernesta Palombo-Kinne for help in reviewing and translating the manuscript and Dominik Driesch for analyzing the data. This study was funded exclusively by intramural grants of the University Hospital Jena.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the local ethics committee and the German Federal Office of Radiation Protection. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. The non-anonymized person in Fig. 2 (solely symbolizing a patient), gave additional full permission for publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gühne, F., Kühnel, C. & Freesmeyer, M. Comparing pre-therapeutic 124I and 131I uptake tests with intra-therapeutic 131I uptake in benign thyroid disorders. Endocrine 56, 43–53 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1267-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1267-8