Abstract
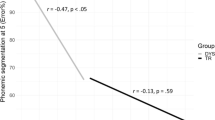
A phonological deficit constitutes a primary cause of developmental dyslexia, which persists into adulthood and can explain some aspects of their reading impairment. Nevertheless, some dyslexic adults successfully manage to study at university level, although very little is currently known about how they achieve this. The present study investigated at both the individual and group levels, whether the development of another oral language skill, namely, morphological knowledge, can be preserved and dissociated from the development of phonological knowledge. Reading, phonological, and morphological abilities were measured in 20 dyslexic and 20 non-dyslexic university students. The results confirmed the persistence of deficits in phonological but not morphological abilities, thereby revealing a dissociation in the development of these two skills. Moreover, the magnitude of the dissociation correlated with reading level. The outcome supports the claim that university students with dyslexia may compensate for phonological weaknesses by drawing on morphological knowledge in reading.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Society (2013) ‘Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).’ <http://www.dsm5.org/Pages/Default.aspx> (accessed 10 July 2014).
Anglin, J. (1993). Vocabulary development: a morphological analysis. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 58(10, Serial No. 238).
Arnbak, E., & Elbro, C. (2000). The effects of morphological awareness training on the reading and spelling skills of young dyslexics. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 44, 229–251.
Boets, B., Op de Beeck, H. P., Vandermosten, M., Scott, S. K., Gillebert, C. R., Mantini, D., Bulthé, J., Sunaert, S., Wouters, J., & Ghesquière, P. (2013). Intact but less accessible phonetic representations in adults with dyslexia. Science, 342(6163), 1251–1254.
Bogacz, R., Wagenmakers, E. J., Forstmann, B. U., & Nieuwenhuis, S. (2010). The neural basis of the speed-accuracy tradeoff. Trends Neuroscience, 33, 10–16.
Bruck, M. (1990). Word-recognition skills of adults with childhood diagnoses of dyslexia. Developmental Psychology, 26, 439–454.
Bruck, M. (1992). Persistence of dyslexics’ phonological awareness deficits. Developmental Psychology, 28, 874–886.
Burani, C., Marcolini, S., De Luca, M., & Zoccolotti, P. (2008). Morpheme-based reading aloud: evidence from dyslexic and skilled Italian readers. Cognition, 108, 243–262.
Callens, M., Tops, W., & Brysbaert, M. (2012). Cognitive profile of students who enter higher education with an indication of dyslexia. PloS One, 7, e38081.
Callens, M., Tops, W., Stevens, M., & Brysbaert, M. (2014). An exploratory factor analysis of the cognitive functioning of first-year bachelor students with dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 64, 91–119.
Carlisle, J. F. (1987). The use of morphological knowledge in spelling derived forms by learning-disabled and normal students. Annals of dyslexia., 37, 90–108.
Carlisle, J. F. (1995). Morphological awareness and early reading achievement. In L. B. Feldman (Ed.), Morphological aspects of language processing (pp. 189–209). Hillsdale: NJ: Erlbaum.
Casalis, S., Mathiot, E., Bécavin, A. S., & Colé, P. (2003). Conscience morphologique chez des lecteurs tout venant et en difficultés. Silexicales, 3, 57–66.
Casalis, S., Colé, P., & Sopo, D. (2004). Morphological awareness in developmental dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 54, 114–138.
Cavalli, E., Casalis, S., El-Ahmadi, A., Zira, M., Poracchia-George, F., & Colé, P. (2016). Vocabulary skills are well developed in university students with dyslexia: evidence from multiple case studies. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 51-52, 89–102.
Colé, P., Casalis, S., Dufayard, C. (2012). Logiciel Morphorem. Isbergues, Ortho-Editions.
Corkett, J. K., & Parrila, R. (2008). Use of context in the word recognition process by adults with a significant history of reading difficulties. Annals of Dyslexia, 58, 139–161.
Crawford, J. R., & Garthwaite, P. H. (2005a). Evaluation of criteria for classical dissociations in single-case studies by Monte Carlo simulation. Neuropsychology, 19, 664–678.
Crawford, J. R., & Garthwaite, P. H. (2005b). Testing for suspected impairments and dissociations in single-case studies in neuropsychology: evaluation of alternatives using Monte Carlo simulations and revised tests for dissociations. Neuropsychology, 19, 318–331.
Crawford, J. R., & Garthwaite, P. H. (2007). Comparison of a single case to a control or normative sample in neuropsychology: development of a Bayesian approach. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 24, 343–372.
Crawford, J. R., Garthwaite, P. H., & Porter, S. (2010). Point and interval estimates of effect sizes for the case-controls design in neuropsychology: rationale, methods, implementations, and proposed reporting standards. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 27, 245–260.
Deacon, S. H., & Kirby, J. R. (2004). Morphological awareness: just “more phonological”? The roles of morphological and phonological awareness in reading development. Applied PsychoLinguistics, 25, 223–238.
Deacon, S. H., Parrila, R., & Kirby, J. R. (2006). Processing of derived forms in high-functioning dyslexics. Annals of Dyslexia, 56, 103–128.
Deacon, S. H., Tong, X., & Mimeau, C. (in press). Morphological and semantic processing in developmental dyslexia across languages: a theoretical and empirical review. In C. Perfetti & L. Verhoeven (Eds.), Dyslexia across languages and writing systems: a handbook. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Di Betta, A. M., & Romani, C. (2006). Lexical learning and dysgraphia in a group of adults with developmental dyslexia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 23, 376–400.
Duncan, L. G., Casalis, S., & Colé, P. (2009). Early metalinguistic awareness of derivational morphology: observations from a comparison of English and French. Applied PsychoLinguistics, 30, 405–440.
Dunn, L. M., & Dunn, L. M. (1981). Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-Revised.Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Dunn, L. M., Theriault-Whalen, C. M., & Dunn, L. M. (1993). Echelle de vocabulaire en images Peabody, adaptation française. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Psycan.
Elbro, C. (1989). Morphological awareness in dyslexia. In C. Von Euler, I. Lundberg, & G. Lennerstrand (Eds.), Brain and reading: structural and functional anomalies in developmental dyslexia with special reference to interactions, memory functions, linguistic processes and visual analysis in reading (pp. 189–209). London: MacMillan.
Elbro, C., & Arnbak, E. (1996). The role of morpheme recognition and morphological awareness in dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 46, 209–240.
Elbro, C. (1986). Morphemes in the reading process. In K. Trondhjem (Ed.), Aspects in reading processes—with special regards to the education of hearing-impaired students. Twelvth Danavox Symposium (pp. 167–185). Copenhagen: Danavox.
Elbro, C., Nielsen, I., & Petersen, D. K. (1994). Dyslexia in adults: evidence for deficits in non-word reading and in the phonological representation of lexical items. Annals of Dyslexia, 44, 205–226.
Elbro, C., King, M., Rown, D., & Oakhill, J. (2016). How morphological knowledge can affect the process of word decoding. Porto, Portugal: Paper presented at the Twenty-Third Annual Meeting of the Society for the Scientific Study of Reading.
Fowler, A. E., & Liberman, I. Y. (1995). The role of phonology and orthography in morphological awareness. In L. B. Feldman (Ed.), Morphological aspects of language processing. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Gombert, J. E. (1990). Le développement métalinguistique. Paris: PUF.
Goodwin, A. P., & Ahn, S. (2010). A meta-analysis of morphological interventions: effects on literacy achievement of children with literacy difficulties. Annals of Dyslexia, 60, 183–208.
Goswami, U., & Bryant, P. (1989). The interpretation of studies using the reading level design. Journal of Reading Behavior, 21, 413–424.
Guo, Y., Roehrig, A. D., & Williams, R. S. (2011). The relation of morphological awareness and syntactic awareness to adults’ reading comprehension: is vocabulary knowledge a mediating variable? Journal of Literacy Research: A Publication of the Literacy Research Association, 43, 159–183.
Haft, S. L., Myers, C. A., & Hoeft, F. (2016). Socio-emotional and cognitive resilience in children with reading disabilities. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 10, 133–141.
Helenius, P., Salmelin, R., Service, E., & Connolly, J. F. (1999). Semantic cortical activation in dyslexic readers. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 11, 535–550.
Kunert, R., & Scheepers, C. (2014). Speed and accuracy of dyslexic versus typical word recognition: an eye-movement investigation. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 1129.
Law, J. M., Wouters, J., & Ghesquière, P. (2015). Morphological awareness and its role in compensation in adults with dyslexia. Dyslexia, 21, 254–272.
Lefavrais, P. (2005). Alouette-R. Paris: ECPA.
Leikin, M., & Zur Hagit, E. (2006). Morphological processing in adult dyslexia. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 35, 471–490.
Leong, C. K. (1989). Productive knowledge of derivational rules in poor readers. Annals of Dyslexia, 39, 94–115.
Leong, C. K. (1999). Phonological and morphological processing in adult students with learn- ing/reading disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 32, 224–238.
Litt, R. A., & Nation, K. (2014). The nature and specificity of paired associate learning deficits in children with dyslexia. Journal of Memory and Language, 71, 71–88.
Lyon, G. R., Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2003). A definition of dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 53, 1–14.
Martin, J., Colé, P., Leuwers, C., Casalis, S., Zorman, M., & Sprenger-Charolles, L. (2010). Reading in French-speaking adults with dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 60, 238–264.
Martin, J., Frauenfelder, U. H., & Colé, P. (2013). Morphological awareness in dyslexic university students. Applied Psycholinguistics, 1–21.
Nagy, W., Berninger, V. W., & Abott, R. D. (2006). Contribution of morphology beyond phonology to literacy outcomes of upper elementary and middle-school students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 134–147.
New, B., Pallier, C., Ferrand, L., & Matos, R. (2001). Une base de données lexicales du français contemporain sur internet : LEXIQUE. L’année psychologique, 101, 447–462.
Quémart, P., & Casalis, S. (2013). Visual processing of derivational morphology in children with developmental dyslexia: Insights from masked priming. Applied Psycholinguistics (pp. 1–32).
Ramus, F., Rosen, S., Dakin, S. C., Day, B. L., Castellote, J. M., White, S., & Frith, U. (2003). Theories of developmental dyslexia: insights from a multiple case study of dyslexic adults. Brain, 126, 841–865.
Raven, J. C., Court, J. H., & Raven, J. (1995). Raven manual: Coloured progressive matrices. Oxford, UK: Oxford Psychologists Press.
Re, A. M., Tressoldi, P. E., Cornoldi, C., & Lucangeli, D. (2011). Which tasks best discriminate between dyslexic university students and controls in a transparent language? Dyslexia, 17, 227–241.
Reid, A. A., Szczerbinski, M., Iskierka-Kasperek, E., & Hansen, P. C. (2006). Cognitive profiles of adult developmental dyslexics: theoretical implications. Dyslexia, 13, 1–24.
Rey-Debove, J. (1984). Le domaine de la morphologie lexicale [The domain of lexical morphology. Cahiers de Lexicologie, 45, 3–19.
Richlan, F., Kronbichler, M., & Wimmer, H. (2011). Meta-analyzing brain dysfunctions in dyslexic children and adults. NeuroImage, 56, 1735–1742.
Romani, C., Di Betta, A. M., Tsouknida, E., & Olson, A. (2008). Lexical and nonlexical processing in developmental dyslexia: a case for different resources and different impairments. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 25, 798–830.
Rüsseler, J., Becker, P., Johannes, S., & Münte, T. F. (2007). Semantic, syntactic, and phonological processing of written words in adult developmental dyslexic readers: an event-related brain potential study. BMC Neuroscience, 8, 52.
Schiff, R., & Raveh, M. (2007). Deficient morphological processing in adults with developmental dyslexia: another barrier to efficient word recognition? Dyslexia, 13, 110–129.
Schiff, R., & Ravid, D. (2007). Morphological analogies in Hebrew-speaking university students with dyslexia compared with typically developing gradeschoolers. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 36, 237–253.
Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2005). Dyslexia (specific reading disability. Biological Psychiatry, 57, 1301–1309.
Shaywitz, B. A., Shaywitz, S. E., Pugh, K. R., Fulbright, R. K., Mencl, W. E., Constable, R. T., Skudlarsi, P., Fletcher, J. M., Lyon, G. R., & Gore, J. C. (2001). The neurobiology of dyslexia. Clinical Neuroscience Research, 1, 291–299.
Shaywitz, S. E., Mody, M., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2006). Neural mechanisms in dyslexia. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 15, 278–281.
Sprenger-Charolles, L., & Colé, P. (2003). Lecture et dyslexie. Paris, Dunod.
Sprenger-Charolles, L., Colé, P., Béchennec, D., & Kipffer-Piquard, A. (2005). French normative data on reading and related skills from EVALEC, a new computerized battery of tests (end grade 1, grade 2, grade 3, and grade 4). Revue Européenne de Psychologie Appliquée/European Review of Applied Psychology, 55, 157–186.
Suárez-Coalla, P., & Cuetos, F. (2015). Reading difficulties in Spanish adults with dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 65, 33–51.
Swanson, H. L. (2012). Adults with reading disabilities: converting a meta-analysis to practice. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 45, 17–30.
Swanson, H. L., & Hsieh, C.-J. (2009). Reading disabilities in adults: a selective meta-analysis of the literature. Review of Educational Research, 79, 1362–1390.
Tops, W., Callens, M., Bijn, E., & Brysbaert, M. (2012). Spelling in adolescents with dyslexia: errors and modes of assessment. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 47, 295–306.
Tractenberg, R. E. (2002). Exploring hypotheses about phonological awareness, memory, and reading achievement. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35, 407–424.
Tsesmeli, S., & Seymour, P. (2006). Derivational morphology and spelling in dyslexia. Reading and Writing, 19, 587–625.
Vellutino, F. R., Scanlon, D. M., & Spearing, D. (1995). Semantic and phonological coding in poor and normal readers. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 59, 76–123.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Jennifer Martin for having allowed us to use her materials and Mélody Zira for her help in testing participants. In addition, we would like to thank all the participants in this study. Special thanks are due to Professor John R. Crawford for giving us permission to use and disseminate his single-case study method. Finally, we would also like to thank Florence Poracchia-George (CERTA, Salvator Hospital Marseille, France) for helping with the recruitment of dyslexic participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Appendix
Appendix
Items for the suffixation decision task
Suffixed word | Pseudosuffixed word | ||
|---|---|---|---|
French item | English translation | French item | English translation |
Chorale | Choral | Mistral | Mistral |
Lamelle | Strip | Pirouette | Pirouette |
Noisette | Hazelnut | Mirabelle | Mirabelle plum |
Provençal | Provencal | Salopette | Dungarees |
Citronnelle | Citronella | Sidéral | Sidereal |
Vinaigrette | Vinaigrette | Coccinelle | Ladybird |
Rural | Rural | Guillerette | Cheerful |
Nasale | Nasal | Oral | Oral |
Sauterelle | Grasshopper | Bretelle | Strap |
Courgette | Courgette | Charnière | Hinge |
Nominal | Nominal | Cardinal | Cardinal |
Citadelle | Citadel | Hirondelle | Swallow |
Rondelette | Plump | Montgolfière | Hot air balloon |
Frontal | Frontal | Renard | Fox |
Ombrelle | Parasol | Mercure | Mercury |
Chatière | Cat flap | Stature | Stature |
Terminal | Terminal | Épinard | Spinach |
Violoncelle | Cello | Galipette | Somersault |
Gazinière | Gas cooker | Envergure | Wingspan |
Aigrette | Egret | Étendard | Standard |
Petard | Firecracker | Quenelle | Quenelle |
Jeunette | Young girl | Gazette | Gazette |
Pendulette | Little clock | Feudal | Feudal |
Moisissure | Mold | Flanelle | Flannel |
Items for the suffixed word detection task (morphologically complex words are in bold)
French items | English translation |
|---|---|
Chaussette–lunette–omelette | Sock–telescope–omelet |
Truelle–rondelle–gazelle | Trowel–slice–gazelle |
Aquarelle–mortadelle–varicelle | Watercolor–mortadella–chickenpox |
Guépard–hussard–têtard | Cheetah–hussar–tadpole |
Lanière–glacière–tanière | Strap–cooler–den |
Crevette–maquette–boulette | Prawn–model–little ball |
Escampette–ciboulette–maisonnette | “Go away”–chive–little house |
Clochette–squelette–baguette | Small bell–skeleton–baguette |
Aisselle–gamelle–tourelle | Armpit–metal dish–turret |
Tourterelle–balancelle–ribambelle | Turtledove–swing seat–bunch |
Musical–carnaval–arsenal | Musical–carnival–arsenal |
Glissière–chaumière–paupière | Slide–thatched cottage–eyelid |
Items for the phonemic awareness task
Phoneme deletion |
|---|
fla |
spo |
klo |
pra |
sri |
tsé |
blo |
sti |
pso |
flin |
sla |
vri |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavalli, E., Duncan, L.G., Elbro, C. et al. Phonemic—Morphemic dissociation in university students with dyslexia: an index of reading compensation?. Ann. of Dyslexia 67, 63–84 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-016-0138-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-016-0138-y