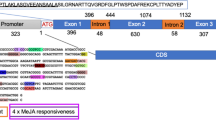
Abstract
Plant growth and productivity are greatly affected by environmental stresses such as dehydration, high salinity, low temperature and pathogen infection. Plant adaptation to these environmental stresses is controlled by cascades of molecular networks. The dehydration-responsive element-binding (DREB) transcription factors play an important role in the response of plants to environmental stresses by controlling the expression of many stress-related genes. They specifically interact with C-repeat/DRE (A/GCCGAC) sequences present in the promoter regions of target genes. One of the DREB1 cDNA was previously cloned and overexpressed in transgenic potato plants. These transgenic plants displayed an improved tolerance to high salinity and drought stresses. The StDREB1 factor belongs to A-4 group that seem to be involved in biotic stress response. This report investigates the effect of Fusarium solani infection on the StDREB1 transgenic lines. Since a number of pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins are considered as DREB1 target genes, the expression of PR2, PR9 and PR3 genes were tested under biotic stress conditions. The β-1,3-glucanase (PR2) was specifically induced upon infection, whereas the chitinase and the peroxydase were expressed constitutively. The data also show that high levels of DREB1 transcripts accumulated rapidly when wild-type and transgenic plants were infected by F. solani. DREB1 transgenic potato plants accumulated higher levels of pathogenesis-related gene transcripts, such as PR2. These results showed that StDREB1 plays an important role in response to fungal attack in potato.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CBF/DREB:
-
c-Repeat binding factor/Dehydration-responsive element-binding
- DRE:
-
Dehydration-responsive element
- PR:
-
Pathogenesis related
- ERF:
-
Ethylene-responsive factor
- LEA:
-
Late embryogenesis abundant
- AP2:
-
Apetala2
- bZIP:
-
Basic region leucine zipper
- RAV:
-
Related to ABI3/VP1
References
Agarwal P, Agarwal PK, Joshi AJ, Sopory SK, Reddy MK (2010) Overexpression of PgDREB2A transcription factor enhances abiotic stress tolerance and activates downstream stress-responsive genes. Mol Biol Report 37:1125–1135
Bouaziz D, Pirrello J, Ben Amor H, Hammami A, Charfeddine M, Dhieb A, Bouzayen M, Gargouri-Bouzid R (2012) Ectopic expression of dehydration-responsive element-binding proteins (StDREB2) confers higher tolerance to salt stress in potato. Plant Physiol Biochem 60:98–108
Bouaziz D, Pirrello J, Charfeddine M, Hammami A, Jbir R, Dhieb A, Bouzayen M, Gargouri-Bouzid R (2013) Overexpression of StDREB1 transcription factor increases tolerance to salt in transgenic potato plants. Mol Biotechnol 54:803–817
Bray EA (1997) Plant responses to water deficit. Trends Plant Sci 2:48–54
Carlos M (1987) la bactériose vasculaire de la pomme de terre “pseudomonas Solanaceanum”. Bulletin d’Information Technique 1 à 19. Centre de la pomme de terre (CIP) 83–88
Choi DW, Rodriguez EM, Close TJ (2002) Barley Cbf3 gene identification expression pattern and map location. Plant Physiol 129:1781–1787
Collinge M, Boller T (2001) Differential induction of two potato genes Stprx2 and StNAC in response to infection by Phytophthora infestans and to wounding. Plant Mol Biol 46:521–529
Cong L, Chai TY, Zhang YX (2008) Characterization of the novel gene BjDREB1B encoding a DRE-binding transcription factor from Brassica juncea L. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371:702–706. doi:10.1016/jbbrc.2008.04.126
D’Ippólito S, Martín ML, Salcedo MF, Atencio HM, Casalongué CA, Godoy AV, Fiol DF (2010) Transcriptome profiling of Fusarium solani f sp Eumartii-infected potato tubers provides evidence of an inducible defense response. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 75:3–12
Dubouzet JG, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet EG, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) OsDREB genes in rice Oryza sativa L encode transcription activators that function in drought high salt and cold responsive gene expression. Plant J 33:751–763
Ebel J, Cosio EG (1994) Elicitors of plant defense responses. Int Rev Cytol 148:1–36
Fry WE, Goodwin SB (1997) Re-emergence of potato and tomato late blight in the United States. Plant Dis 81:349–357
Gao MJ, Allard G, Byass L, Flanagan AM, Singh J (2002) Regulation and characterization of four CBF transcription factors from Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol 49:459–471
Gutha LR, Reddy AR (2008) Rice DREB1B promoter shows distinct stress-specific responses and the overexpression of cDNA in tobacco confers improved abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 68:533–555
Ito Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, Taji T, Kobayashi M, Seki M et al (2006) Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47:141–153. doi:10.1093/pcp/pci230
Li YC, Bi Y, Ge YH, Sun XJ, Wang Y (2009) Antifungal activity of sodium silicate on Fusarium sulphureum and its effect on dry rot of potato tubers. J Food Sci 74:213–218
Li J, Sima W, Ouyang B, Wang T, Ziaf K, Luo Z, Liu L, Li H, Chen M, Huang Y, Feng Y, Hao Y, Ye Z (2012) Tomato SlDREB gene restricts leaf expansion and internode elongation by down regulating key genes for gibberellins biosynthesis. J Exp Bot 63:6407–6420
Liu Y, Zhao TJ, Liu JM, Liu WQ, Liu Q, Yan YB (2006) The conserved Ala37 in the ERF/AP2 domain is essential for binding with the DRE element and the GCC box. FEBS Lett 580:1303–1308
Mauch F, Mauch-Mani B, Boller T (1988) Antifungal hydrolases in pea tissuesII Inhibition of fungal growth by combinations of chitinase and b-13-glucanase. Plant Physiol 88:936–942
Mizoi J, Ohori T, Moriwaki T, Kidokoro S, Todaka D, Maruyama K, Kusakabe K, Osakabe Y, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2013) GmDREB2A;2 a Canonical dehydration-responsive element-binding protein2 Type Transcription Factor in Soybean is Post translationally Regulated and Mediates Dehydration-Responsive Element-Dependent Gene Expression. Plant Physiol 161:346–361
Morel G, Wetmore RH (1951) Fern callus tissue culture. Am J Bot 38:141–143
Murachige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140:411–432
Nasreen S, Amudha J, Pandey SS (2013) Isolation and characterization of Soybean DREB 3 transcriptional activator. J Applied Biol Biotechnol 1:9–12
Ohme-Takagi M, Shinshi H (1995) Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 7:173–182
Onate-Sanchez L, Singh KB (2002) Identification of Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors with distinct induction kinetics after pathogen infection. Plant Physiol 128:1313–1322
Ortiz R, Watanabe KN (2004) Genetic contribution to breeding polyploid crops. Recent Res Develop in Genet Breed 1:269–286
Pirrello J, Prasad N, Zhang W, Chen K, Mila I, Zouine M, Latché A, Pech JC, Ohme-Takagi M, Regad F, Bouzayen M (2012) Functional analysis and binding affinity of tomato ethylene response factors provide insight on the molecular bases of plant differential responses to ethylene. BMC Plant Biol 12–90
Qin F, Sakuma Y, Li J, Liu Q, Li YQ, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Cloning and functional analysis of a novel DREB1/CBF transcription factor involved in cold-responsive gene expression in Zea mays L. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1042–1052
Sabater-Jara AB, Almagro L, Belchí-Navarro S, Ferrer MA, Ros-Barceló A, Pedreno MA (2010) Induction of sesquiterpenes phytoesterols and extracellular pathogenesis related proteins in elicited cell cultures of Capsicum annuum. J Plant Physiol 167:1273–1281
Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2002) DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 290:998–999
Sambrook J, Fritish EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning A Molecular Manuel second edition Cold Spring Harbor
Shen YG, Zhang WK, He SJ, Zhang JS, Liu Q, Chen SY (2003) An EREBP/AP2-type protein in Triticum aestivum was a DRE binding transcription factor induced by cold dehydration and ABA stress. Theor Appl Genet 106:923–930
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (1997) Gene expression and signal transduction in water-stress response. Plant Physiol 115:327–334
Simmons CR, Litts C, Huang N, Rodriguez RL (1992) Structure of a rice β-glucanase gene regulated by ethylene cytokinin wounding salicylic acid and fungal elicitors. Plant Mol Biol 18:33–45
Sun S, Yu JP, Chen F, Zhao TJ, Fang XH, Li YQ, Sui SF (2008) TINY a dehydration-responsive element (DRE)-binding protein-like transcription factor connecting the DRE and ethylene-responsive element-mediated signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 283:6261–6271
Tournier B, Sanchez-Ballesta MT, Jones B, Pesquet E, Regad F, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2003) New members of the tomato ERF family show specific expression pattern and diverse DNAbinding capacity to the GCC box element. FEBS Lett 550:149–154
Tsutsui T, Kato W, Asada Y, Sako K, Sato T, Sonoda Y, Kidokoro S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Tamaoki M, Arakawa K, Ichikawa T, Nakazawa M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Matsui M, Ikeda A, Yamaguchi J (2009) DEAR1 a transcriptional repressor of DREB protein that mediates plant defense and freezing stress responses in Arabidopsis. J Plant Res 122:633–643
Van Loon LC, Van Strien EA (1999) The families of pathogenesis-related proteins their activities and comparative analysis of PR-1 proteins. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 55:85–97
Van Loon LC, Pierpoint WS, Boller T, Conejero V (1994) Recommendations for naming plant pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12:245–264
Van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CM (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Ann Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
Verwoerd TC, Dekker BM, Hoekema A (1989) A small scale procedure for the rapid isolation of plant RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:23–62
Welinder KG (1992) Structure and evolution of peroxidases. In: Welider KG Rasmussen SK Penel C Greppin H (eds) Plant Peroxidases: Biochemistry and Physiology University of Geneva Switzerland, pp 35–42
Wu K, Tian L, Hollingworth J, Brown DC, Miki B (2002) Functional analysis of tomato Pti4 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 128:30–37
Xu ZS, Chen M, Li LC, Ma YZ (2011) Functions and Application of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Crop Improvement. J Integr Plant Biol 53:570–585
Zhou ML, Ma JT, Pang JF, Zhang ZL, Tang YX, Wu YM (2010) Regulation of plant stress response by dehydration responsive element binding (DREB) transcription factors. Af J Biotechnol 9:255–279
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research. Authors are grateful to Dr. Anne-Lise Haenni from Institute Jacques Monod (France) for her kind help with the English language and to Mofida Bouaziz-Kannoun from the “Institut Supérieur d’Administration des Affaires de Sfax” (Tunisia) for her kind help with the English language.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Charfeddine and D. Bouaziz have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig S1: RT-PCR analyses of StDREB1 mRNA expression using 25 cycles in potato plants inoculated with F. solani at different treatment periods (a) StDREB1 gene transcription 7 dpi with F. solani (b) log2 (StDREB1 expression level in inoculated plants/control plants) (c) log2 (StDREB1 expression level in transgenic plants/NT ones) (d).
Fig S2: Evaluation of Log2 (stem elongation of transgenic plants/stem elongation of NT) under control conditions and 7dpi with F. solani
Fig S3: RT-PCR analyses of the expression of: a PR2 b PR3 c PR9 d ef1α in Nicola cultivar after 7 dpi with F. solani. The 25 cycles PCR amplification products are presented for Controls: non-infected plants in addition to F. solani infected ones.
Fig S4: RT-PCR analyses using 25 cycles of the expression of the stress-induced PR2 gene (a) and ef1α (b) in transgenic lines (BF1 BF2 BF3 BF4 and BF5) and in NT (BF) plants under standard conditions and 7 dpi with F. solani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charfeddine, M., Bouaziz, D., Charfeddine, S. et al. Overexpression of dehydration-responsive element-binding 1 protein (DREB1) in transgenic Solanum tuberosum enhances tolerance to biotic stress. Plant Biotechnol Rep 9, 79–88 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0345-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0345-8